螺旋换热盘管内的流体传热研究毕业论文
2020-05-28 06:57:22
摘 要
随着中国经济的发展和人民生活水平的提高,公共建筑和住宅的卫生热水、空调已成为普遍需求。螺旋盘管热交换器传热因其结构紧凑、易于制造、维护和较高的热效率,广泛应用于一些,如蒸汽发生器、冰箱、核反应堆,化工厂和家用热水系统。在螺旋板式热交换器的基础上,对于螺旋盘管式热交换器进行了大量的模拟及实验研究之后,新开发的一种利用钢管替换钢板的全新构造。
目前我们所遇到的问题可以通过实验分析以及数值模拟这两种方法来进行研究,通过实验来分析研究问题时,我们会根据实验的原理,并且通过模拟实验的方法去对问题进行分析,这被广泛应用在各种领域,但是实际上,需要消耗大量的时间以及人力物力。
本文即尝试利用有限元模拟技术对螺旋盘管换热过程进行模拟和分析,考察管内流体流动的速度、温度和压强的变化。主要研究内容及结论如下:
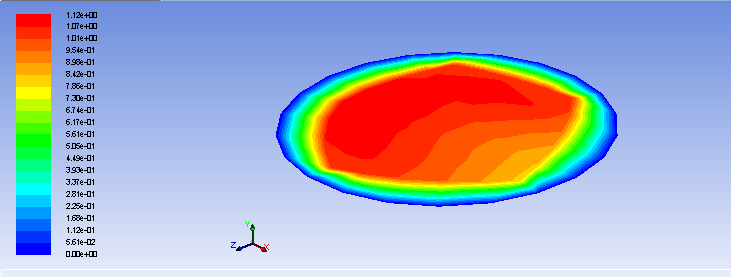
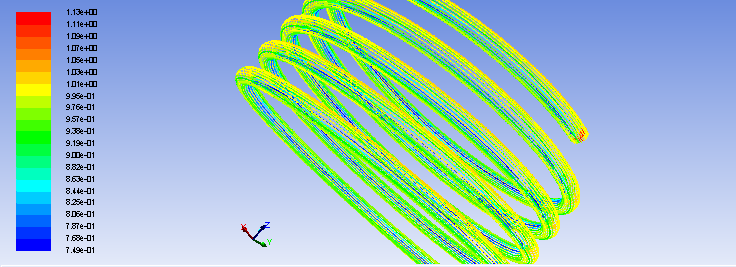
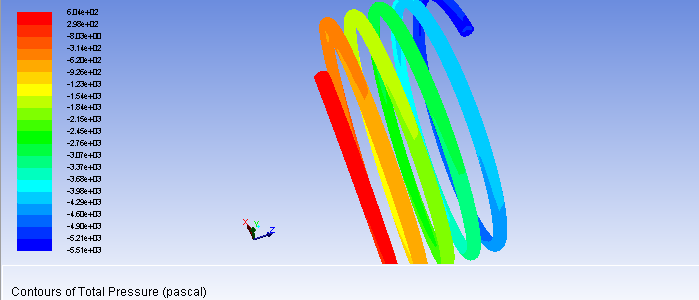
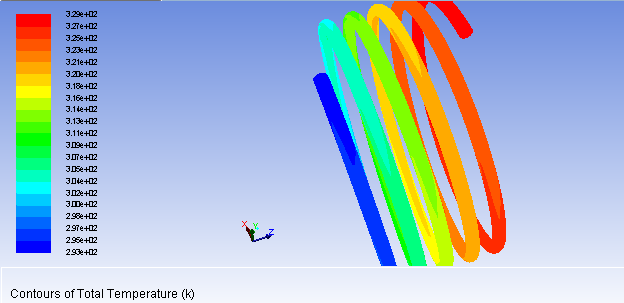
(1)基于同一规格的螺旋盘管模型,对管内流体传热过程进行研究,数值模拟分析管内流体压强、温度、速度的分布情况。结果表明:管内流体温度、压强分布均匀,从管口到封闭端,压强逐渐下降,而温度逐渐上升;速度矢量分布较为整齐统一;而在螺旋盘管横截面上,速度大小由圆心到管壁逐渐降低,管壁速度大小为0。
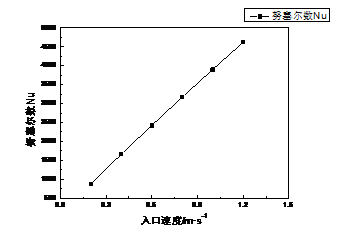
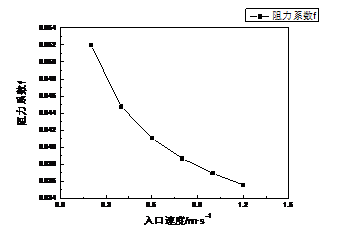
(2)对液态水在螺旋盘管内各指标变化进行研究,讨论了入口速度对管壁的努塞尔数、阻力系数、传热系数和进出口的压降、温差的影响。结果表明:入口速度对各指标均有很大的影响,入口速度越大,管壁的努塞尔数和换热系数呈正比增长,压降呈线性增长且增长速度逐渐增加,而管壁的阻力系数和温差呈线性减小且减小速度逐渐降低。
(3)基于不同工况的螺旋盘管模型,模拟并讨论了不同管径和螺旋直径对管内流体传热各指标的影响。结果表明:随着螺旋盘管管径的增大,管壁的努塞尔数和传热系数也随之增大,趋势呈线性增长且增长速度逐渐减小;管壁的阻力系数和进出口的压降随之减小,趋势呈线性下降且下降速度逐渐减小;进出口的温差随之减小,趋势呈线性减小且减小速度基本不变。随着螺旋盘管螺旋直径的增大,管壁的三个指标努塞尔数、阻力系数和传热系数均随之减小,趋势也同样呈线性下降且下降速度逐渐减少;进出口压降随之增大,趋势呈线性增大且增长速度基本不变;进出口温差随之增大,趋势呈线性增大且增长速度逐渐下降。这为管子规格尺寸的选择提供了帮助,从而实现选材的合理性与优化性。
关键词:螺旋盘管;传热系数;压降;温差;有限元模拟
ABSTRACT
Coil heat exchanger as a special kind of shell and tube heat exchanger, with its compact, easy to manufacture, heat transfer coefficient is large, widely used in many areas of petrochemical, cryogenic engineering, electrical machinery and so on. Helical coiled tube heat exchanger, is based on the spiral plate heat exchanger, a series of experimental studies, the new development of a new structure use steel instead of steel. That it has the advantage of spiral plate heat exchanger, and overcomes many of the deficiencies spiral plate heat exchanger, higher heat transfer efficiency, it can withstand high working pressure and differential pressure, and light weight advantages.
At present the research question is based on the problem of experimental analysis and numerical simulation of two types of experimental analysis research method is based on similar principles to guide, through the practical problems of experimental simulation approach to identify, with a wide range of applications in engineering research, there is far, time-consuming, relatively high cost.
This paper attempts to use finite element simulation of spiral coil heat exchanger process simulation and analysis, changes in the study of fluid flow tube velocity, temperature and pressure. The main contents and conclusions are as follows:
(1) Based on the same specifications of the spiral coil model of heat transfer process fluid tube studies, numerical simulation analysis of the distribution of the fluid pipe pressure, temperature, speed. The results show that: the inner tube fluid temperature, pressure distribution, from the mouth to the closed end of the tube, the pressure is gradually decreased, while the temperature gradually rises; velocity vector relatively tidy unity; and in cross-section helical coiled tube, size is determined by the speed of the center to the wall decreased, the size of the wall velocity is zero.
(2) Changes in the index for liquid water within the helical coil study discusses the inlet velocity drop on wall Nusselt number, drag coefficient, heat transfer coefficient and the import and export, the temperature impact of the decline. The results show that: the inlet velocity of each index has a great influence, the greater the inlet velocity, wall heat transfer coefficient and Nusselt number is proportional to the growth, the pressure drop increases linearly and the growth rate is gradually increased, and the wall resistance and the temperature drops linearly decreases and the rate of decline decreased.
(3) Based on different operating conditions of the spiral coil model, simulate and discuss the effects of different diameter and the diameter of the spiral tube heat transfer fluid each index. The results show that: with the increase of the spiral coil diameter, wall heat transfer coefficient and Nusselt number also increased, the trend is linear growth and the growth rate is gradually reduced; drag coefficient wall and Importers pressure drop decreases, the trend rate of decline decreased linearly and gradually reduced; import and export temperature drops fall, the trend is linear and the rate of decline decreased substantially unchanged. With the spiral coil helix diameter increases, the three indicators Nusselt number, drag coefficient and wall heat transfer coefficient were decreases, the trend is also linearly decreases and the rate of decline decreased; import and export drop increases, the trend is linearly increased and the growth rate will remain basically unchanged; import and export temperature drop increases, the trend is linearly increased and the growth rate is gradually reduced. This has helped the tube sizes of selection, enabling selection and optimization of rationa
Keywords: Helical coil heat exchanger;Heat transfer coefficient;Pressure Drop;Temperature difference;Finite element simulation
目 录
摘 要 2
ABSTRACT 4
目 录 6
第一章 绪论 8
1.1 螺旋盘管换热器简介 8
1.1.1 课题背景 8
1.1.2螺旋盘管换热器的研究进展 8
1.1.3 螺旋盘管式热交换器的构造和使用 8
1.2螺旋盘管换热器传热过程分析 9
1.3螺旋盘管传热研究的意义 10
1.4本文所做工作 11
第二章 部分数值的计算方法 12
2.1 计算流体力学(CFD)简介 12
2.2 管内流动与传热的计算 12
2.2.1雷诺数与努赛尔数的计算 12
2.2.2管内侧界膜导热系数的计算 13
2.2.3螺旋盘管内侧的压力损失 14
第三章 物理模型建立 16
3.1 简化假设 16
3.2螺旋盘管模型的数据 16
3.3 圆形截面管建模过程 16
3.4 网格划分 17
3.5 定义边界条件 18
第四章 固定尺寸下管内的数值模拟分析 19
4.1 使用Fluent 14.0软件对螺旋盘管模型进行求解 19
4.2 螺旋盘管换热器的数值模拟分析 21
4.2.1 速度分布 21
4.2.2 压力分布 22
4.2.3 温度分布 22
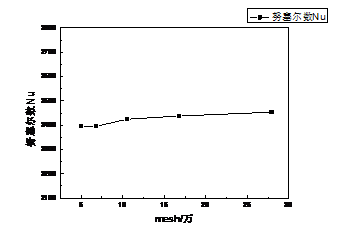
4.2.3 网格无关性验证 23
4.2.4 不同入口速度对各指标的影响 24
4.3 小结 27
第五章 不同工况下换热过程的分析 28
5.1 不同管径的影响 28
5.1.1不同管径对管壁的努塞尔数的影响 28
5.1.2不同管径对管壁的阻力系数的影响 28
5.1.3不同管径对管壁的传热系数的影响 29
5.1.4不同管径对进出口压降的影响 30
5.1.5不同管径对进出口温差的影响 30
5.2 不同螺旋直径的影响 31
5.2.1不同螺旋直径对努塞尔数的影响 31
5.2.2不同螺旋直径对阻力系数的影响 32
5.2.3不同螺旋直径对传热系数的影响 33
5.2.4不同螺旋直径对进出口压降的影响 33
5.2.5不同螺旋直径对进出口温差的影响 34
5.3 小结 35
第六章 结论与展望 36
6.1 结论 36
6.2 展望 37
参考文献 38
致 谢 42
第一章 绪论
1.1 螺旋盘管换热器简介
1.1.1 课题背景
伴随着科技与经济的飞速发展,在日常的生活里人们的需求也随之越来越高,其中对生活环境的舒适性显得尤为关心。例如已经成为生活必需品的热水系统以及空调等。而此次我们所要研究的螺旋盘管热交换器就是其中的重要组成部分。螺旋盘管热交换器作为一个集合了多种优点的热交换器常常被我们使用在热水系统、石化产业、蒸汽装置等方面。相比于上一代的螺旋板式热交换器,在这基础上研发出来的螺旋盘管热交换器不仅继承了上一代的优点,同时也去除了原有的缺陷,具有热交换效率高,不易损坏,制造流程简便等大量优点。这些成果完全是建立在大量的模拟以及实际试验上所得到的。
1.1.2螺旋盘管换热器的研究进展
19 世纪20 年代,Dean首次建立了螺旋盘管中层流流动的理论。K.N.Murty 研究了螺旋盘管的最佳传热性能。国内对该领域的研究不多,西安交通大学白博峰等研究了卧式螺旋管内流动传热问题。上海机械学院夏雅君对螺旋盘管中强制对流换热进行了研究,综述了国外在该领域的研究情况及螺旋盘管中作湍流流动时的换热关联式。周云龙等从实际工程设计出发, 对多头螺旋管式换热器的设计进行了研究, 提出了多头螺旋管束受热面结构的设计方法。张琳等进行了换热器自转螺旋扭带自动阻垢技术的应用研究。流体在螺旋盘管内流动,由于受到离心力的作用,产生了二次环流。二次环流不仅影响了管内侧的边界层,还影响到管内流动速度特性,流线在空间上发生了弯曲,近似于直管流动和环状流动的叠加。
1.1.3 螺旋盘管式热交换器的构造和使用
螺旋盘管式热交换器由绕管芯体和壳体两部分组成。绕管芯体由中心筒、换热管、垫条及管卡等组成。换热管紧密地绕在中心筒上,用平垫条及异形垫条分隔,保证管子之间的横向和纵向间距,垫条与管子之间用管卡固定连接,中心筒在制造中起支撑作用。壳体由筒体和封头等组成。
相关图片展示: