P2O5对铝硅酸盐微晶玻璃制备工艺的影响毕业论文
2020-02-19 15:33:26
摘 要
手机屏幕玻璃的硬度和韧性更加难以兼得,往往在提升防破碎性能的同时,抗划伤性能又成为短板。铝硅酸盐微晶玻璃具有高硬度、突出的抗折强度和耐冲击强度,而且膨胀系数较低等特点,通过控制晶化工艺,可以实现透明、半透明、不透明产品的制备。其在手机屏幕方面有很大前景。
论文主要研究P2O5含量对微晶玻璃析晶和性能的影响,并采用高温黏度计、差式扫描量热、热膨胀分析、X射线衍射和扫描电镜,探讨了对玻璃的高温粘度、核化温度、晶化温度、和微观结构的影响。同时对不同微晶玻璃进行离子交换,通过表面应力仪、显微硬度计对交换后的表面应力、应力深度、硬度等进行表征。通过对各种数据的分析得到最合适的P2O5的引入量,以及对析晶和性能的影响规律。
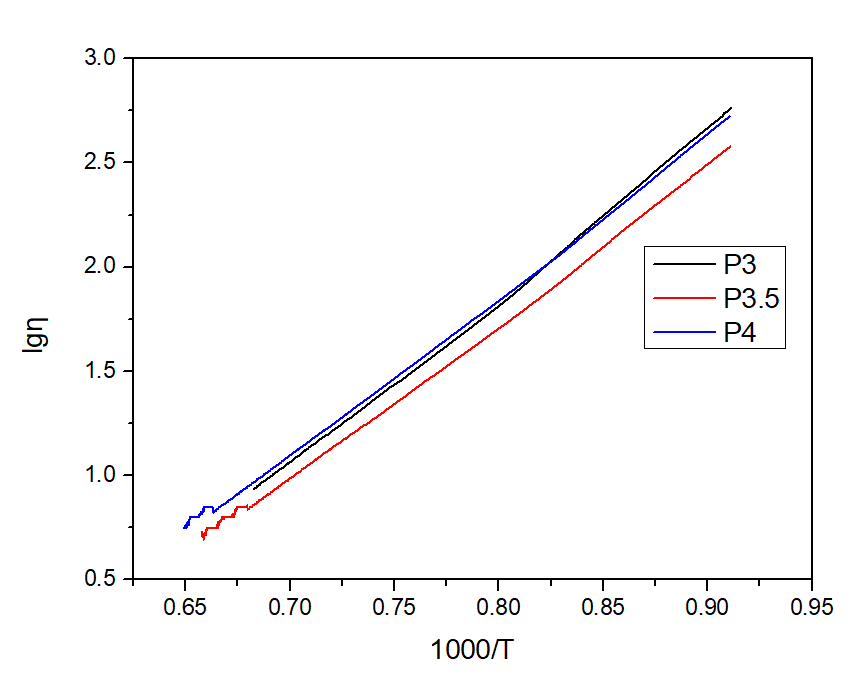
结果研究表明: 通过不同晶化温度之间的微晶玻璃性能对比,可知晶化温度对折射率基本没有什么影响,而断裂韧性随着晶化温度的升高而有所降低。随着P2O5含量的增加,降低析晶界面,在晶化时更容易分相,后续加工时晶化温度上限越来越低。由X射线衍射分析我们可以知道在730℃时没有检测到晶体,但是在扫描图片中,我们可以看到有晶体生成,但粒径很小,所以通过X射线衍射无法检测出来。随着P2O5含量的增加,玻璃粘度下降,P3的粘滞活化能最小为152.84KJ/mol,熔化温度最低为1167.4℃。随着P2O5含量的增加,微晶玻璃表面应力呈上升趋势,应力深度呈减小趋势,硬度总体也呈上升趋势。随着P2O5含量的增加,扩大了网络结构,有利于离子强化。综合上述考虑对晶化工艺和离子强化的影响,P2O5含量在3-4%左右较为合理。
本文特色:通过研究P2O5对铝硅酸盐微晶玻璃粘度、热处理制度、析晶等性能测试,经过数据对比,详细论述了P2O5对铝硅酸盐微晶玻璃的影响,研究了微晶玻璃作为手机屏幕玻璃是否具有可行性。
关键词:铝硅酸盐微晶玻璃,P2O5,离子交换;硬度
Abstract
The hardness and toughness of mobile phone screen glass is more difficult to have, often in the improvement of anti-crushing performance at the same time, scratch resistance has become a short board. Aluminosilicate glass-ceramics have the characteristics of high hardness, outstanding bending strength and impact strength, and low expansion coefficient. Transparent, translucent and opaque products can be prepared by controlling the crystallization process. It has great prospects for mobile phone screens.
In this paper, the effects of P2O5 content on the crystallization and properties of glass-ceramics were studied by means of high temperature viscometer, differential scanning calorimetry, thermal expansion analysis, X-ray diffraction and scanning electron microscope. The effects of high temperature viscosity, nucleation temperature, crystallization temperature and microstructure of glass were discussed. At the same time, the ion exchange of different glass-ceramics was carried out, and the surface stress, stress depth and hardness were characterized by surface stress meter and microhardness tester. Through the analysis of all kinds of data, the most suitable amount of P2O5 is obtained, and the effect on crystallization and properties is obtained.
The results show that the crystallization temperature has little effect on the refractive index, but the fracture toughness decreases with the increase of crystallization temperature. With the increase of P2O5 content, the crystallization interface is reduced, the phase separation is easier during crystallization, and the upper limit of crystallization temperature is lower and lower during subsequent processing. From the X-ray diffraction analysis, we can know that the crystal is not detected at 730 ℃, but in the scanning picture, we can see the crystal formation, but the particle size is very small, so it can not be detected by X-ray diffraction. With the increase of P2O5content, the viscosity of glass decreased, the minimum viscous activation energy of P3 was 152.84KJ / mol, and the lowest melting temperature was 1167.4 ℃.With the increase of P2O5 content, the surface stress of glass-ceramics showed an upward trend, the stress depth decreased, and the hardness increased as a whole. With the increase of P2O5 content, the network structure is expanded, which is beneficial to ion strengthening. Considering the effects of the above considerations on the crystallization process and ion strengthening, it is reasonable for the P2O5 content to be about 3 to 4%.
The characteristics of this paper: through the study of P2O5 on the viscosity, heat treatment system, crystallization and other properties of aluminosilicate glass-ceramics, through the comparison of data, the effect of P2O5 on aluminosilicate glass-ceramics is discussed in detail.The feasibility of glass-ceramics as mobile phone screen glass was studied.
Key Words: aluminosilicate glass-ceramic; P2O5; ion exchange; hardness
目 录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 微晶玻璃 1
1.2 微晶玻璃的种类 1
1.2.1 硅酸盐微晶玻璃 1
1.2.2 铝硅酸盐微晶玻璃 1
1.2.3 硼硅酸盐微晶玻璃 2
1.2.4 磷酸盐微晶玻璃 2
1.3 微晶玻璃的制备 2
1.3.1 整体析晶法 2
1.3.2 烧结法 3
1.3.3 溶胶-凝胶法 3
1.4 玻璃的分相 3
1.4.1 分相 3
1.4.2 玻璃分相的动力学 4
1.5 微晶玻璃的热处理制度 5
1.5.1 阶梯温度制度 5
1.5.2 等温温度制度 5
1.6 微晶玻璃离子强化 6
1.7 立题依据 6
1.8 研究内容 7
第2章 实验 8
2.1 实验原料与仪器设备 8
2.2 实验过程 9
2.2.1 玻璃组分 9
2.2.2 玻璃的熔制 10
2.2.3 样品切割磨抛 10
2.2.4 微晶玻璃离子强化 10
2.2.5 性能测试 10
2.3 测试及表征方法 11
2.3.1 差式扫描量热分析(DSC) 11
2.3.2 X射线衍射定性分析 11
2.3.3 电子探针(EPMA) 11
2.3.4 热膨胀性 12
2.3.5 硬度 12
2.3.6 表面应力与应力深度 12
2.3.7 扫描电镜(SEM) 13
2.3.8 高温粘度 13
第3章 P2O5含量对微晶玻璃的析晶和性能的影响 15
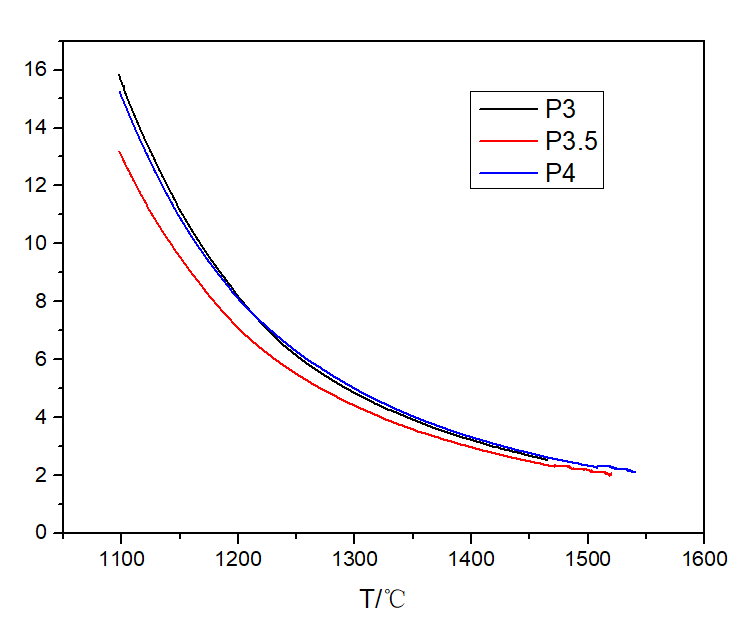
3.1 P2O5含量对玻璃粘度的影响 15
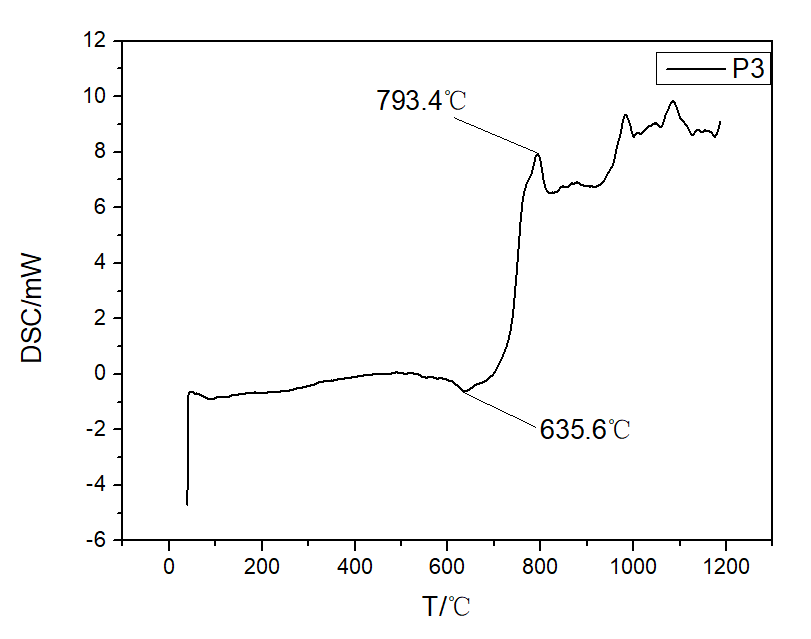
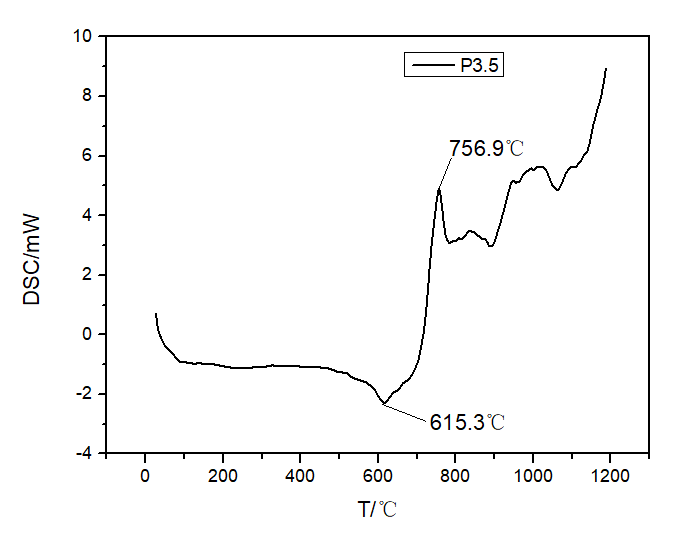
3.2 P2O5含量对析晶温度的影响 16
3.3 晶化制度下得到的微晶玻璃的外观 18
3.4 热处理制度对微晶玻璃析晶的影响 18
3.5 微晶玻璃的晶相形貌 19
3.6 P2O5含量对玻璃折射率的影响 19
3.7 P2O5含量对玻璃断裂韧性的影响 20
3.8 P2O5含量对玻璃硬度的影响 20
第4章 P2O5含量对微晶玻璃离子交换工艺的影响 22
4.1 引言 22
4.2 离子交换工艺 22
4.3 P2O5含量对离子交换微晶玻璃的表面应力的影响 22
4.3.1 不同玻璃的表面应力 22
4.3.2不同玻璃表面应力变化趋势 22
4.4 P2O5含量对离子交换微晶玻璃的应力深度的影响 23
4.4.1 不同玻璃的应力深度 23
4.4.2 不同玻璃应力深度变化趋势 23
4.5 P2O5含量对离子交换微晶玻璃硬度的影响 24
第5章 结论 26
参考文献 27
致谢 28
第1章 绪论
1.1 微晶玻璃
玻璃是一种非晶态固体。从热力学观点上来说,它是一种相较于晶态具有较高的内能的亚稳态,在一定条件下可转变为结晶态。从动力学观点上来说,玻璃溶体在冷却过程中,晶核的形成和长大由于粘度的急剧增加而被抑制,使其难以转化为晶态。微晶玻璃是一种充分利用玻璃的热力学上的优势而制备的全新材料。微晶玻璃在1957年由美国康宁公司研制出。这种材料具有优异的物理化学和力学性能,因此在随后的70多年里得到了迅速的发展[1]。微晶玻璃一般定义为通过对某些特定组成的基础玻璃,通过控制核化和晶化的热处理制度,制得含有大量晶相及玻璃相的多晶固体材料[2-3]。微晶玻璃的结构和性能既有玻璃的特点,又有陶瓷的特性,因此也被称为玻璃陶瓷。
玻璃虽然易制备成几乎没有气泡的透明产品,但是其热稳定性差,脆性大;陶瓷材料虽然硬度好、强度高、耐磨性能优,但是有气孔,透明度低。微晶玻璃的热膨胀系数可以通过设计生成的晶相在很大范围内去调整;机械强度高,硬度大,并且具有良好的热稳定性和化学稳定性,电绝缘性优良,接电损耗小,介电常数稳定。因此微晶玻璃作为一种具有广泛的应用前景的全新材料。
1.2 微晶玻璃的种类
按照基础玻璃的组成成分,将微晶玻璃分为硅酸盐系微晶玻璃、铝硅酸盐系统微晶玻璃、硼硅酸盐系统微晶玻璃和磷酸盐系统微晶玻璃。
1.2.1 硅酸盐微晶玻璃
简单硅酸盐微晶玻璃主要由碱金属和碱土金属的硅酸盐晶相组成,主要包括硅酸锂(Li2SiO3, Li2Si2O3) 、顽辉石(MgSiO3) 、透辉石(CaMgSi2O3) 和硅灰石(CaSiO3) 等[6], 这些晶相也决定了微晶玻璃的性能。光敏微晶玻璃和矿渣微晶玻璃属于硅酸盐微晶玻璃,其主晶相为二硅酸锂,具有骨架结构,易于被氢氟酸腐蚀,被刻蚀为磁头基板、射流原件等电子元件。矿渣微晶玻璃的晶相主要为透辉石[CaMg(SiO3)2]和硅灰石(CaSiO3)。其制备原料主要有高炉矿渣、磷渣、钢渣、硼镁渣、钛渣、铬渣以及放射性废渣。
1.2.2 铝硅酸盐微晶玻璃
这类材料具有优良的热稳定性、抗冲击性及化学稳定性,是一种十分重要的商业化微晶玻璃。其中主要有: Li2O-AI2O3-SiO2系、CaO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2系、MgO-AI2O3-SiO2系和ZnO-Al2O3- SiO2系微晶玻璃。Li2O-AI2O3-SiO2 系微晶玻璃最主要的特性是热膨胀系数在很大范围内可调,且同时具有强度高、易成型和硬度大等特点,可用于制造耐热炊具、加工刀具、滚珠轴承、天文望远镜、烧嘴等[9]。MgO-Al2O3-SiO2系微晶玻璃中最重要的是堇青石型微晶玻璃, 这种材料具有低介电系数、高力学性能、低膨胀系数、电绝缘性良好及抗热震性等特性,广泛应用于如雷达绝缘体、天线罩、电容器、整流罩、混频器和滤波器、微电子基板封装等[10]。ZnO-Al2O3-SiO2系微晶玻璃分为三类主晶相分别是:锌尖晶石、硅锌矿以及以β-石英固溶体或者透锌长石。这类材料不仅膨胀系数低、电阻高而且具有优良的化学稳定性,可以用于电磁灶面板和电气元件等方面[11]。
1.2.3 硼硅酸盐微晶玻璃
硼酸盐/硼硅酸盐微晶玻璃因为具有较低的熔融温度和热膨胀系数、较好的化学稳定性和介电性能而得到广泛应用,尤其是在电子领域。这类微晶玻璃主要有: CaO-B2O3-SiO2、ZnO-B2O3、PbO-ZnO-B2O3、ZnO-B2O3-SiO2、B2O3-Al2O3-SiO2等体系。PbO-ZnO-B2O3系微晶玻璃易熔,可作为电子技术和真空技术中的密封材料,也可作为釉和涂层覆盖在陶瓷、玻璃和金属表面[12]。ZnO-B2O3-SiO2系微晶玻璃具有膨胀系数低,击穿电压高等特性,钝化封装结构致密,相较于树脂类封装材料散热性能好的多,并且有与单晶硅及接线匹配性好、耐高温、体积小、耐疲劳性好,能有效消除外界杂质的影响,降低Na 离子的迁移率等优点,能够大幅提高器件的可靠性,是一种比较理想的钝化封装材料。
1.2.4 磷酸盐微晶玻璃
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
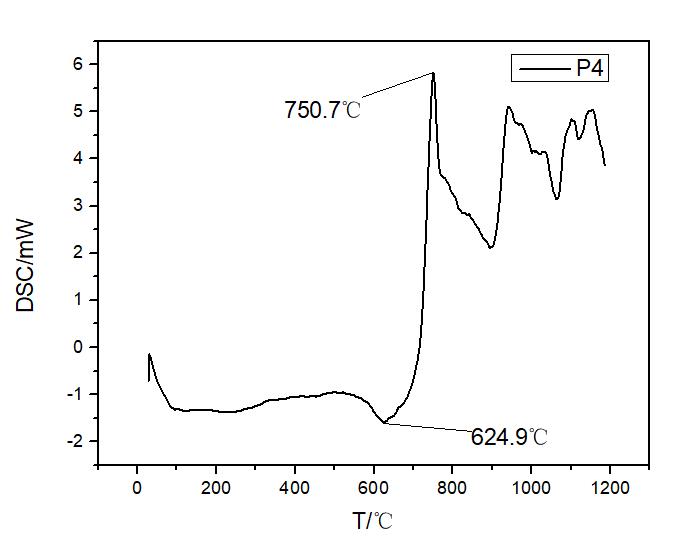
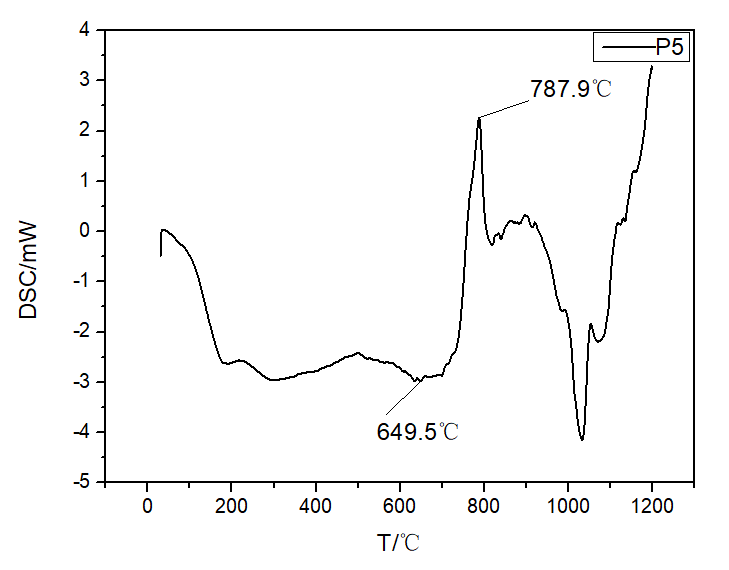
相关图片展示: