TiS2机械剥离工艺对TiS2-AgSnSe2复合热电材料性能的影响毕业论文
2020-06-14 16:30:23
摘 要
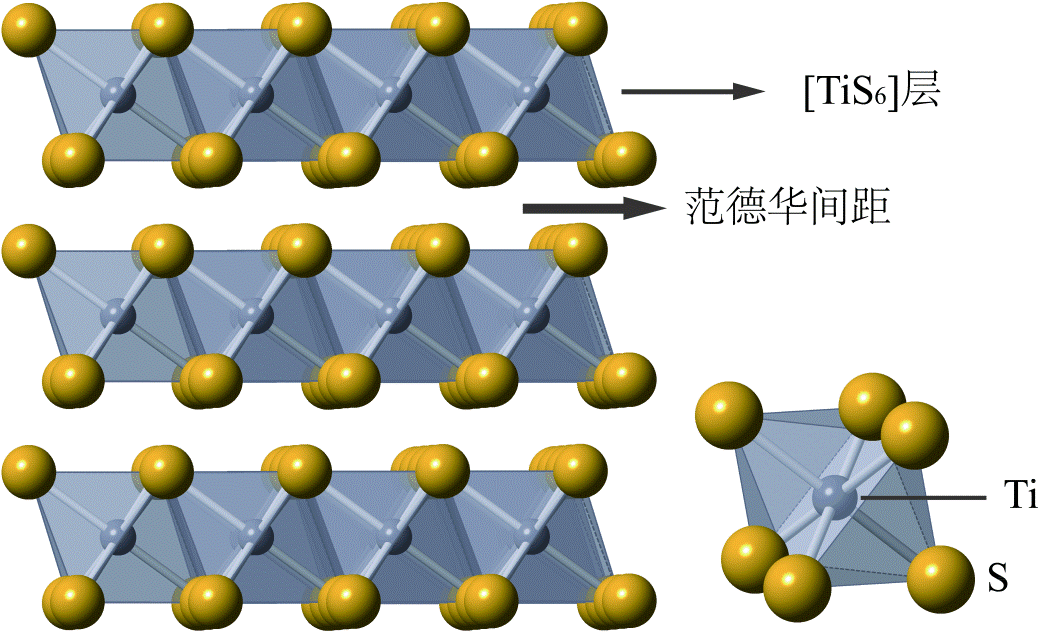
层状二硫化钛(TiS2)导电性好、赛贝克系数高,功率因子能与目前最好的热电材料媲美,但其热导率较高,热电优值ZT相对偏低。本实验旨在采用低温高速剪切手段,细化晶粒以降低热导率,同时避免传统高能球磨导致非晶化和电输运性能降低的现象;另外通过复合AgSnSe2纳米相,引入能量过滤效应,在维持较高功率因子的同时降低电子热导、增加声子散射,从而降低总热导率,最终进一步提升ZT值。
结果表明:
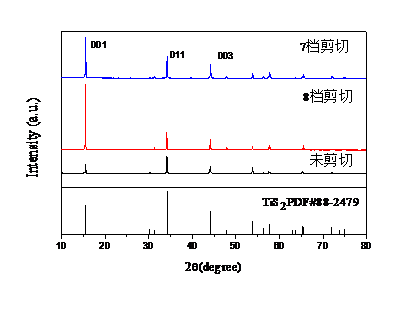
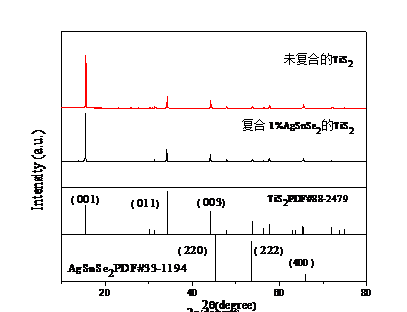
(1) 经高速剪切,可获得结晶度高(由XRD高强度衍射峰推断)、粒度分布宽(纳米级-数微米)的TiS2粉体;
(2) 最佳情况下,由高速剪切处理后的TiS2粉体、经放电等离子烧结制得的致密块体样品(简称剪切样)仍具有较高电导率和赛贝克系数,与未剪切粉末制得的块样(简称未剪切样)相比,323 K和773K对应功率因子(2.2mW/mK2和1.2mW/mK2)分别提高近1倍和50%;同时,剪切样的晶格热导率大幅度降低,使总热导率比未剪切样降低近50%,这应与显微结构中存在大量细小颗粒、增强了声子散射,而高结晶度确保了电输运性质有关。剪切样ZTmax值相比于未剪切样的提高了一倍,在773K时达最高值1.02,验证了剪切对提高ZT值的显著作用;
(3) 随着AgSnSe2复合量增加,TiS2-xAgSnSe2复合材料的电导率有所增加而赛贝克系数快速降低,导致功率因子较未复合剪切样大幅下降,可能是由于AgSnSe2与剪切后的TiS2发生插层反应导致载流子浓度增大有关。尽管热导率基本与未复合样品相近,但热电优值ZT未能获得提升;
关键词:TiS2; 高速剪切处理; TiS2-xAgSnSe2复合材料; 热电性能;
ABSTRACT
Layer-structured TiS2single crystalhas a high electrical conductivity and a large Seebeck coefficient, with a high power factor comparable to those of the state-of-the-art thermoelectric (TE) materials. However, due to its high thermal conductivity,its TE figure of merit (ZT) is rather low compared to the best TEs.The aim of this research is to reduce the thermal conductivity by refining the grain size through a high speed shearing process at room temperature, which would help avoid the severe amorphizationand thus the large degradation of the electrical properties that encountered in the conventional high-energy milling process. Besides, nano-sized AgSnSe2was added into the TiS2matrix, attempting to enhance the power factor through intensified electron scattering or namely the energy filtration effect. Results showed that,
(1) The high-shear treated TiS2 powder covered a rather wide size distribution from nanoscale to several microns, while still with high crystalinity (as evidenced by the high diffraction intensity in XRD data);
(2) As the best case, the pellets sintered by spark plasma sintering using high-shear treated powder (hereafter HS-TiS2) showed an unexpectedly increased electrical conductivity and Seebeck coefficient, leading to a rather large power factor which is almost doubled at 323 K (2.2mW/mK2) and improved by 50% at 773 K(1.2mW/mK2), as compared with the non-sheared samples (hereafter NHS-TiS2). More strikingly, the lattice thermal conductivity in HS-TiS2 decreased almost by half compared to NHS-TiS2. Consequently, the ZTmaxof HS-TiS2 hit a record of 1.02 at 773 K, almost doubled compared to that of NHS-TiS2;
(3) For the HS-TiS2-xAgSnSe2 composites, however, possibly due to the intercalation reaction of AgSnSe2 in TiS2 matrix, electrical conductivity was increased with the amount of x, while Seebeck coefficient decreased largely, leading to a large drop of power factor, and the ZT values were not improved as a result despite the low thermal conductivity close to that of the HS-TiS2 samples.
KEY WORDS: TiS2;high speed shearing;TiS2-AgSnSe2 composite; thermoelectric;
目录
摘要 I
ABSTRACT II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1热电材料研究背景 1
1.2热电材料 1
1.2.1Seebeck效应 1
1.2.2热电性能参数 2
1.2.3提高ZT值的方法 2
1.3 TiS2及AgSnSe2热电材料的研究现状 3
第二章 实验部分 7
2.1实验原理 7
2.2研究内容 8
2.3实验原料及仪器 8
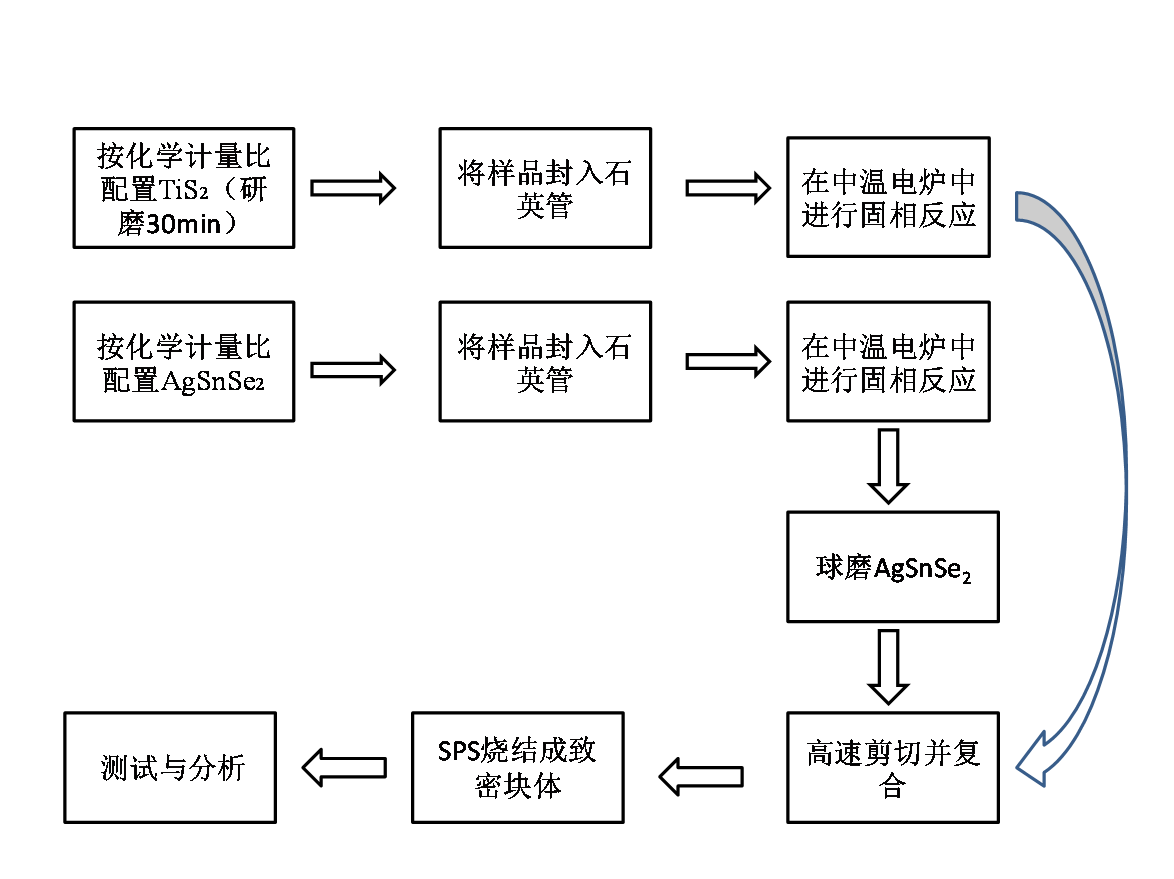
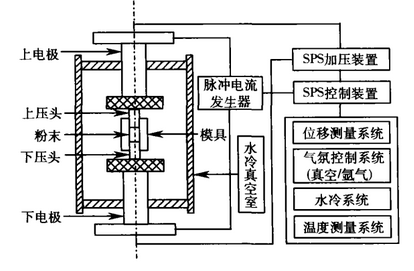
2.4实验流程 9
第三章结果与讨论 12
3.1 XRD分析 12
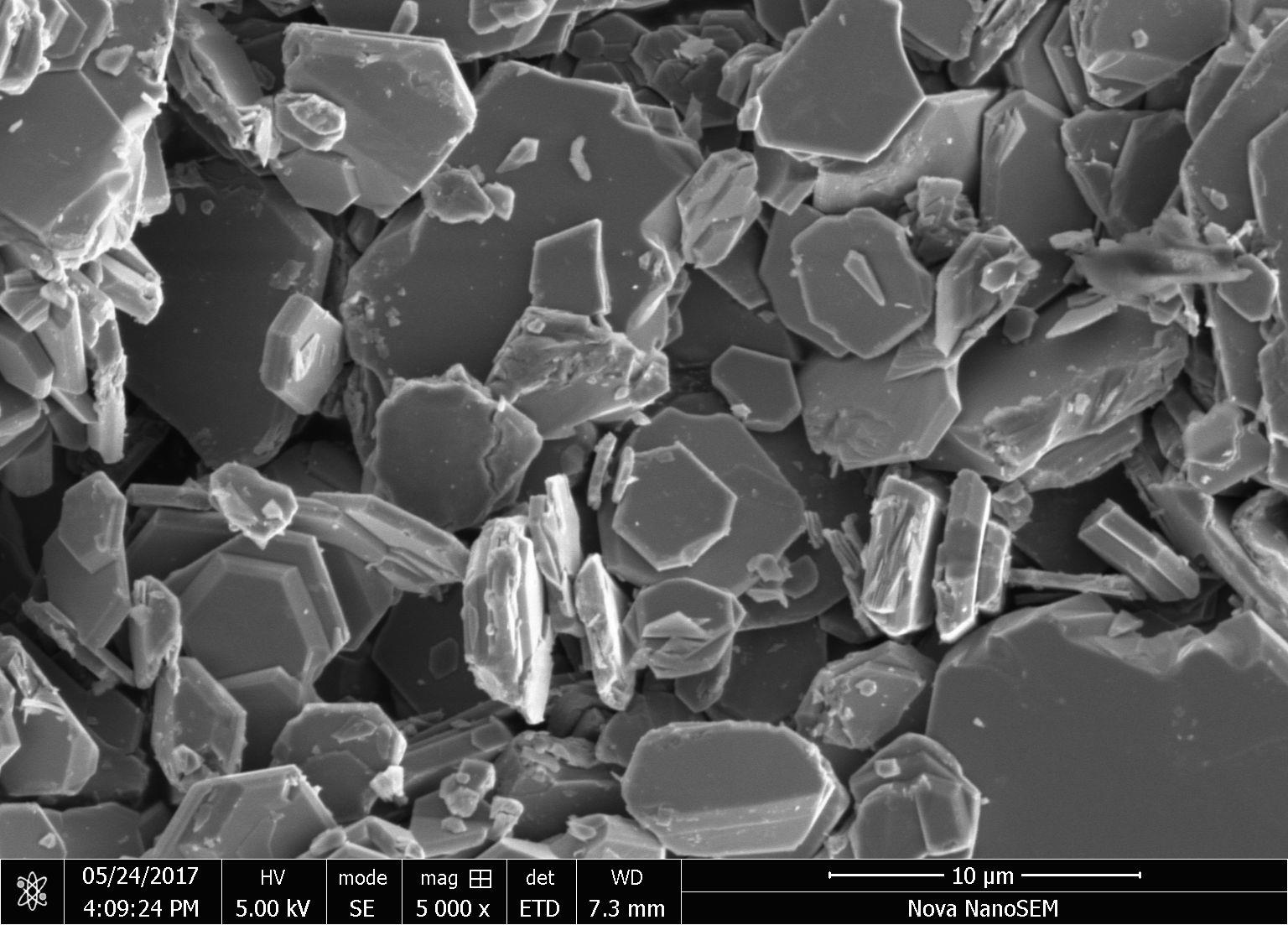
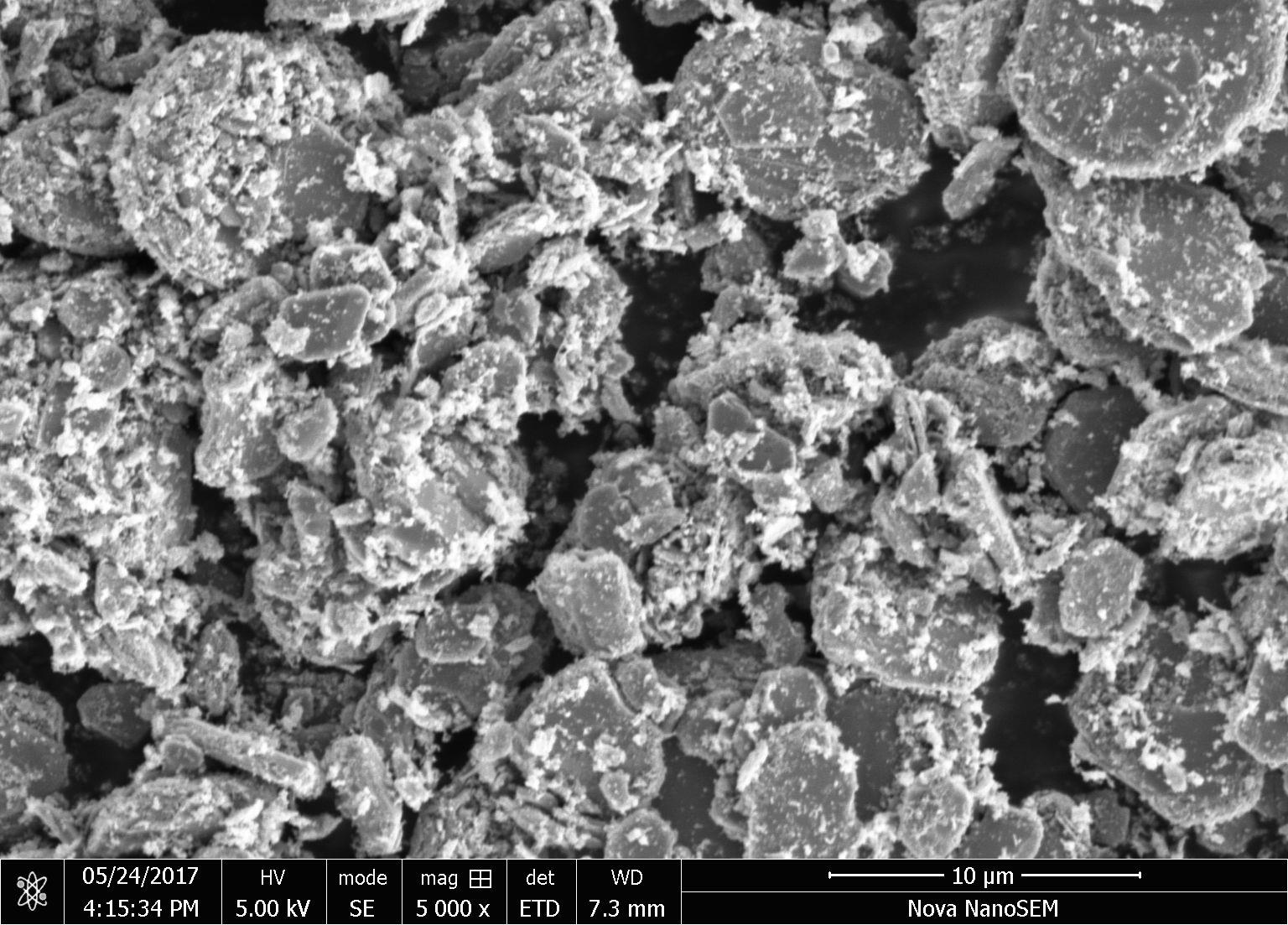
3.2扫描电镜分析 14
3.3烧结温度对TiS2样品的影响 15
3.4剪切对TiS2热电性能的影响 17
3.5 复合对TiS2热电性能的影响 19
3.6热学性能 21
3.7 ZT值 23
第四章 结论与展望 25
参考文献 26
致谢 28
第一章 绪论
1.1热电材料研究背景
随着生态环境日益恶化,化石能源不断消耗,人们迫切希望寻找到新型材料解除危机。热电材料因为具有能将热能和电能相互转换的特性,从而走入人们视线。它可以吸收废热,提高了能源利用率,缓解能源危机,并且热电材料有着很多其他材料没有的优点,比如不产生化学污染物,不需要复杂的机械运转设备。因此,热电材料将会是未来新型材料发展的一个热点。[1; 2]
1.2热电材料
1.2.1Seebeck效应
1821年,德国科学家塞贝克发现,当不同的两段导体组合成一个闭合回路时,加热导体一端,会形成一个ΔV的电动势。[3]我们称这一现象为塞贝克效应。而当温度差ΔT较小时, ΔV与ΔT成正比, 其系数称为Seebeck系数 (单位为 V/K), S = ΔV/ΔT (ΔT → 0),Seebeck效应实现了热能与电能的相互变换, 为热电偶测温和热电发电机的诞生提供了理论依据。[4]
产生Seebeck效应是的原因是载流子的定向移动。载流子从热端移动到冷端,形成电流。例如p型半导体,空穴大都分布于热端,然后由于浓度差,空穴开始运动,会从浓度高的向浓度低的方向移动,也是从高温传递到低温,当回路开路,由于空穴的移动会产生电荷积累,此时高温端呈正,低温端为负。[5]当达到稳定状态,即扩散作用与电子漂移相对稳定时,就会在导体的两端形成电动势,而这个是由于温差产生,所以又叫温差电动势。[6]
相关图片展示: