自动驾驶汽车横向控制方法及模型构建毕业论文
2020-02-17 17:10:09
摘 要
随着世界汽车保有量的不断增长,道路拥堵以及交通安全问题日益严重,世界卫生组织的研究报告指出,交通安全问题每年夺走近130万人的生命。而这些安全问题中,90%以上的交通事故是由于驾驶员的操作不当导致的,95%以上的交通事故的发生与驾驶员有直接关系。由于驾驶员的经验不足、注意力不集中等因素导致的交通安全问题可以通过自动驾驶技术得到解决。自动驾驶车辆是未来智能交通系统的重要组成,而横向控制在自动驾驶车辆控制中占有十分重要的地位。轨迹跟踪控制是横向控制过程中的基本控制问题之一,它要求自动驾驶车辆在指定的时间到达指定的目标处。目前绝大部分轨迹跟踪算法仅考虑了车辆在低速行驶工况下的非完整约束,而并未考虑车辆在高速及低附着系数路面行驶情况的车辆完整约束,这显然无法满足未来自动驾驶车辆的高速行驶控制需求。在高速行驶时,汽车的紧急转向或低附着路面上紧急避障通常会使得轮胎附着力达到饱和,轮胎侧偏力接近附着极限,而导致车辆行驶偏离甚至甩尾的失稳现象,这种情况下,即便是驾驶经验丰富的驾驶员也难以控制汽车的稳定性。因此,本研究将针对这一问题,开展针对高速及低附着系数路面行驶情况的自动驾驶车辆的横向控制问题,主要从以下几个方面展开:
首先阐明自动驾驶车辆横向控制问题的研究背景及意义,了解本研究的主要目的,并深入研究国内外相关研究的发展状况,通过对众多研究的深入研究,明确目前主流的轨迹跟随控制方法,并分析各种方法的优劣之后选择模型预测控制理论作为本研究的轨迹跟踪控制方法。
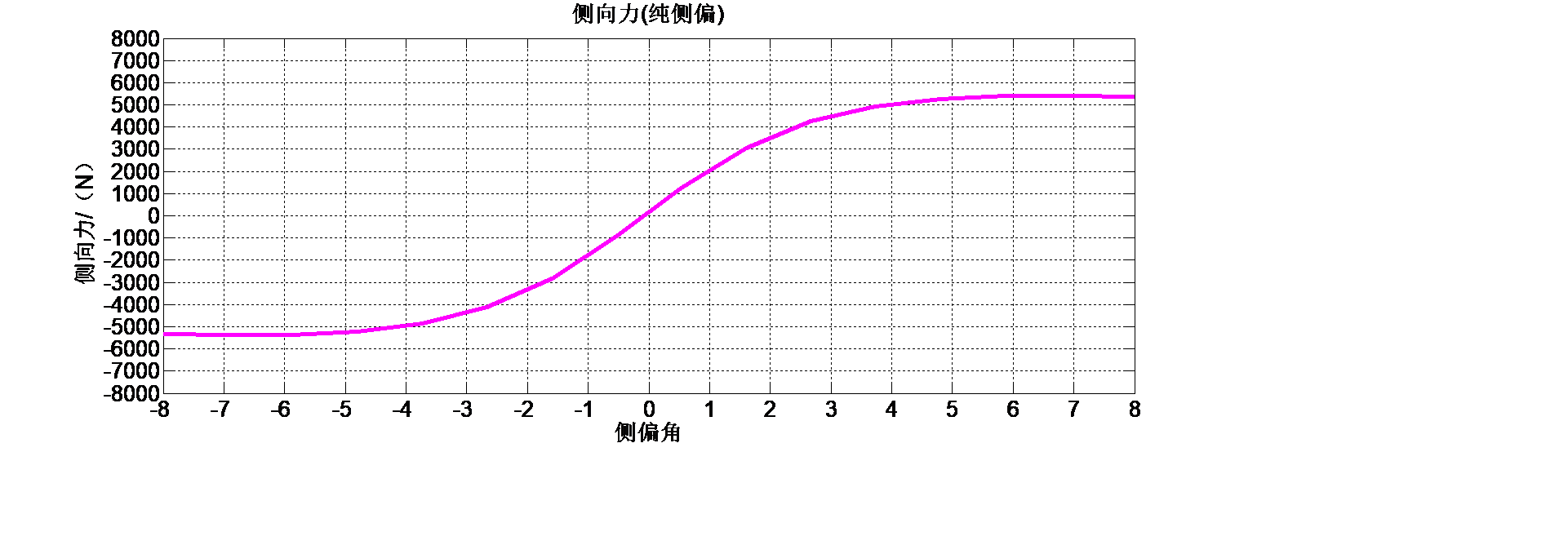
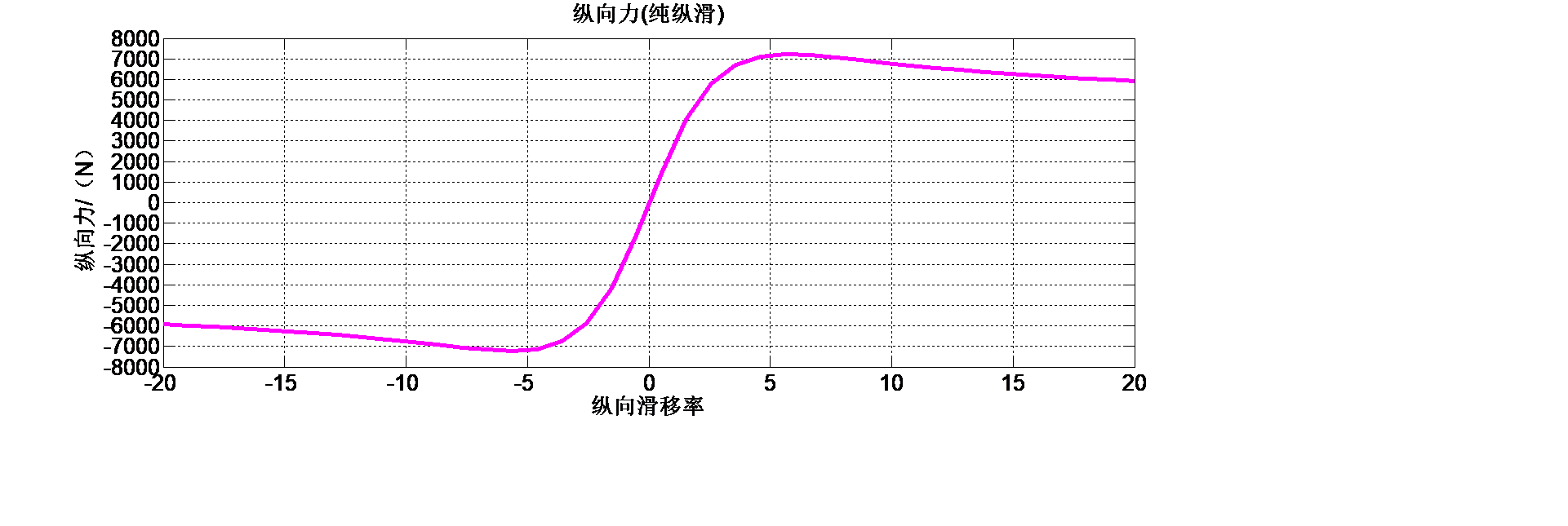
然后是建立被控对象的数学模型,包括车辆动力学模型与轮胎模型的构建。首先分析对比目前主流的轮胎模型优劣,并最终选择魔术公式作为本研究采用的轮胎模型,研究魔术公式轮胎模型的特性,得到准确的数学表达式,然后分析本研究中车辆跟踪控制需要考虑到的横向位移、纵向位移以及横摆转向的自由度,搭建起基于三自由度的车辆动力学模型。
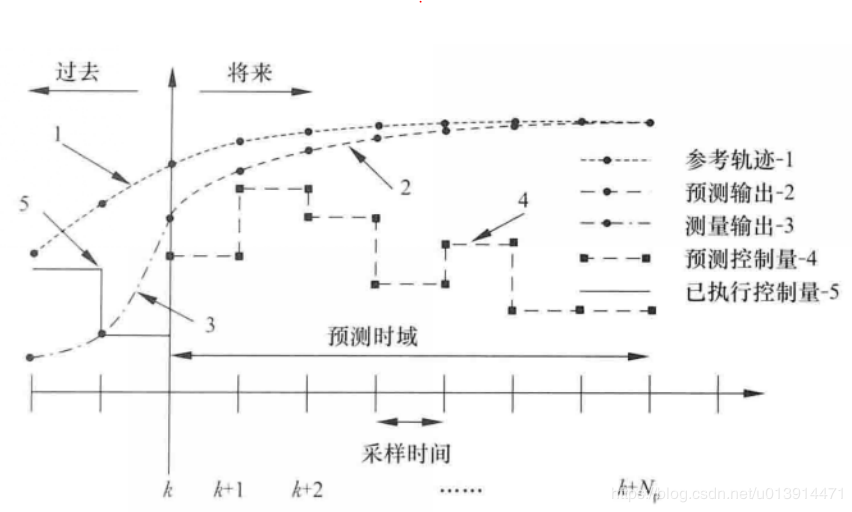
接着对模型预测控制(MPC)理论进行了简要介绍。阐述模型预测控制的基本原理,为控制器的设计提供理论依据。然后选择基于状态空间模型作为本研究的预测模型,着手解决基于状态空间模型下的预测方程的推导问题,并提出对被控系统的合理约束,将带约束的车辆轨迹跟踪最优控制问题转化为便于计算机求解的二次规划问题。
最后在Simulink/Carsim联合平台进行仿真实验,并与基于驾驶员模型的最优预瞄控制器进行对照试验,分析对两种控制器的性能优劣。
关键词:自动驾驶汽车;轨迹跟踪控制;模型预测控制;Simulink/CarSim联合仿真平台
Abstract
With the increasing number of cars in the world, road congestion and traffic safety problems becoming more and more serious, the research report of the world health organization points out that traffic safety problems claim nearly 1.3 million lives every year. Among these safety problems, more than 90% of traffic accidents are caused by improper operation of drivers, and more than 95% of traffic accidents are directly related to drivers. Traffic safety problems caused by drivers' inexperience and inattention can be solved by self-driving technology.
Autonomous vehicle is an important component of intelligent transportation system in the future, and lateral control plays a very important role in autonomous vehicle control. Trajectory tracking control is one of the basic control problems in the lateral control process. At present, most of the trajectory tracking algorithms only consider the non-holonomic constraints of vehicles under low-speed driving conditions, and do not consider the vehicle holonomic constraints under high-speed and low-adhesion road conditions, which obviously cannot meet the high-speed driving control requirements of future autonomous vehicles. At high speed, vehicle emergency or low adhesion road emergency obstacle avoidance often makes tire adhesion saturated, tire cornering force close to the limit, causes the vehicle deviates from the spin instability phenomenon, even in this case, even experienced driver also difficult to control the car driving stability. Therefore, aiming at this problem, this study will carry out the lateral control of self-driving vehicles on the road with high speed and low adhesion coefficient, mainly from the following aspects:
Clarified first autonomous vehicle lateral control problem of the research background and significance, understand the research purpose of this study, in-depth study and development status of related research at home and abroad, through the in-depth study of many studies, clear the current mainstream of trajectory tracking control method, and analyze the advantages and disadvantages of various methods after selection model predictive control theory as the research method of trajectory tracking control.
Then, the mathematical model of the controlled object is established, including vehicle dynamics model and tire model. Firstly analyzed the current mainstream of tire model, and finally choose the magic formula as we adopt the tire model, study the characteristics of the magic formula tire model, get the exact mathematical expressions, and then analysis of vehicle tracking control need to be considered in this study to the lateral displacement, vertical displacement and horizontal pendulum to degrees of freedom, set up based on the three degrees of freedom vehicle dynamics model.
Then the theory of model predictive control (MPC) is briefly introduced. The basic principle of model predictive control is expounded, which provides theoretical basis for the design of controller. Then, the state-space model is selected as the prediction model in this study to solve the derivation of the prediction equation based on the state-space model, and the reasonable constraints on the controlled system are put forward to transform the optimal control problem of vehicle trajectory tracking with constraints into a quadratic programming problem that is convenient for computer solution.
Finally in the Simulink/Carsim platform based on model predictive control theory and wide use of automatic vehicle trajectory tracking controller for double line condition simulation experiments, in order to compare the performance of the designed controller, with the Carsim own optimal prediction based on pilot model aiming controller control test under the same conditions, the analysis of two kinds of controller performance. The simulation results show that the designed controller can achieve better trajectory tracking under the condition of maintaining the stability of the vehicle when driving at high speed on the road with low adhesion coefficient compared with the optimal preview controller of the driver model which is built in Carsim.
Keywords: special scene; Self-driving cars; Trajectory tracking control; Model predictive control; Simulink/CarSim co-simulation platform
目录
第一章 绪论 1
1.1研究背景及意义 1
1.2国内外外自动驾驶汽车研究现状 2
1.2.1国外研究现状 2
1.2.2国内研究现状 5
1.3自动驾驶汽车轨迹跟踪控制策略概述 7
1.4目前存在的问题 8
1.5本研究研究内容及研究方法 9
第二章 车辆动力学模型和轮胎模型的建立 11
2.1 轮胎模型的建立 11
2.2 基于三自由度的车辆动力学模型的建立 15
2.3本章小结 18
第三章 模型预测控制理论基础 20
3.1模型预测控制理论介绍 20
3.2 基于状态空间方程的MPC轨迹跟踪算法 21
3.2.1 状态空间方程模型 21
3.2.2MPC轨迹跟踪控制器预测方程 22
3.2.3 优化问题求解 24
3.3本章小结 27
第四章 轨迹跟踪控制器设计 27
4.1 MPC控制器设计 28
4.1.1 被控对象的建立 28
4.1.2约束条件建立 31
4.1.3带约束优化求解 32
4.2 轨迹跟踪控制器仿真 34
4.2.1 仿真平台概述 34
4.2.2 联合仿真平台搭建 35
4.2.3 参考轨迹的选择。 37
4.3 控制器A:预瞄跟踪最优控制 38
4.3.1 仿真工况1:速度为10m/s 39
4.3.2 仿真工况2:速度为15m/s 41
4.3.3 仿真工况3:速度为20m/s 42
4.4控制器B :MPC控制器 44
4.4.1 仿真工况1:速度为10m/s 45
4.4.2 仿真工况2:速度为15m/s 46
4.4.3 仿真工况3:速度为20m/s 48
4.5控制器性能分析 50
4.6 本章总结 52
第五章 全文总结与展望未来 52
5.1 全文总结 53
5.2 研究展望 54
参考文献 54
致谢 57
第一章 绪论
1.1研究背景及意义
1886年1月29日,世界第一台汽车诞生于德国。130多年来,汽车极大提高了人们的交通效率,推动社会进步,使人们的生活得到了极大的改善。然后,随着工业化进程的推进,世界汽车的保有量不断增长,使得道路等基础交通设施难堪重负,交通拥堵和交通安全问题日益严重;汽车尾气排放的不断增加,给环境造成了巨大的损害;而有限的化学染料也无法满足不断增长的能源需求。在众多问题之中,最为严重的问题就是交通安全问题。世界卫生组织的研究报告指出,交通事故在所有导致死亡的原因中居第9位,其每年夺走近130万人的生命,占全球死亡人数的2.2%,而且是 15-29 岁人群的主要死亡原因。而通过对这些交通事故的研究发现,90%的交通事故时由于驾驶员的不当操作造成的,95%以上的交通事故与驾驶员有关。因此,解决这个问题的关键在于将驾驶员从传统的驾驶任务中解放出来,用自动驾驶技术代替驾驶员完成复杂的驾驶操作。
美国加利福尼亚州制定的关于自动驾驶的法案指出,自动驾驶汽车是指利用计算机、传感器以及其他技术和设备,使得汽车在没有驾驶员的主动控制和连续监测的情况下能够安全行驶的机动车辆。自动驾驶汽车是一个复杂的智能系统[1],包含Client端、算法端以及云端。其中Client端是指硬件平台以及机器人系统;算法端的作用包括传感、感知和决策等,根据传感器感知的数据提取出有用信息并依据此做出决策;云端则是数据存储以及深度学习平台,可以在云平台进行对地图、算法、模型的更新和训练。
可以看出,自动驾驶汽车的发展离不开计算机技术、传感器技术以及车辆控制技术的发展,而其核心的主动控制安全技术也必将是未来智能汽车的核心技术之一。可以预见,自动驾驶技术将在缓解交通拥堵、增加高速安全、减少环境污染等领域发挥出重要作用。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: