初始粉末粒经配比对于3D打印TC4合金的电化学性能影响毕业论文
2020-04-26 12:56:05
摘 要
由于3D打印能够快速成型,且打印出的合金广泛应用于航空及医学领域,所以在使用过程中必须考虑合金的耐蚀性能。本文以具有不同粉比例的3D打印TC4合金和普通轧制TC4合金为研究对象,研究不同粉末粒径合金的微观组织与电化学性能之间的关系,建立初始粉末粒径比3D打印轧制组织-电化学性能之间相互作用的关系曲线。从金相显微组织看出3D打印(SLM成型)TC4合金的微观组织主要为针状α’马氏体和β相柱状晶,轧制TC4主要是呈网状分布的α相和β相组织。由实验结果得电化学测试得出粒径为0-53 μm 的3D打印TC4合金表现出最优异的耐腐蚀性能,而轧制TC4的耐腐蚀性能最差。结合金相组织发现耐蚀性能的提高是由于激光融化快冷产生的α’马氏体组织以及激光融化造成的组织高度细化。后通过硬度测试,表面接触角数据计算表面能也同样得出粒径为0-53 μm 的3D打印TC4合金的耐蚀性能最好的结论。
关键词:3D打印技术 TC4合金 电化学 微观组织
Abstract
3D printings are precise ways for rapid prototyping. The 3D-printed alloys are widely used in aerospace and biomaterials, the corrosion resistance of these alloys have to be considered. In this paper, 3D printing TC4 alloys with three powder ratios and ordinary rolled TC4 alloy were studied. The effects of the as-printed alloys on their electrochemical properties were investigated, and relationships between the initial powder ratios, the metallographic structure and electrochemical properties of 3D- printed alloys was established. From the metallographic microstructure, the microstructure of 3D printing (SLM molding) TC4 alloy is mainly constituted of needle-type α' martensites and β-phase columnar crystals. The as-rolled TC4 alloys haves network structure which mainly composed of α and β phases. According to the results of electrochemical experiments, the 3D-printed TC4 alloys with a particle size of 0-53 μm exhibit the best corrosion resistances, while the rolled TC4 has the worst corrosion resistance. The improvement of the corrosion resistance is considered to be due to the α' martensite structure generated by the rapid cooling during 3D printings and the high grain refinements caused by laser melting. After the hardness test and calculating surface energy by surface contact angle data also obtained the best corrosion resistance of 3D printed TC4 alloys with particle size of 0-53 μm.
Keywords: 3D printing technology; TC4 alloy; electrochemistry; microstructure
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 3D打印 1
1.2 TC4钛合金(Ti-6Al-4V) 1
1.2.1 简介 1
1.2.2 3D打印TC4合金粉末 2
1.3金属粉末的制备方法 2
1.3.1雾化法 2
1.3.2等离子体法 3
1.3.3等离子熔丝法 3
1.4 3D打印TC4的电化学行为 3
1.5 选题意义、目的及研究内容 4
第二章 实验材料和方法 6
2.1实验材料 6
2.2实验设备与药品 6
2.3实验内容 7
2.3.1样品准备 7
2.3.2组织成分观察和分析 8
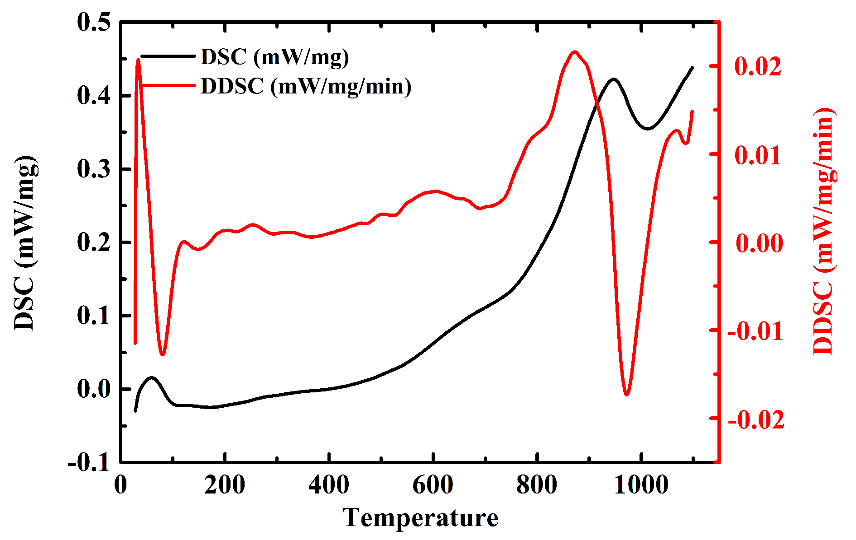
2.3.3 相变点分析 9
2.3.4力学分析 9
2.3.5表面能分析 9
2.3.6电化学分析 9
2.3.7浸蚀试验及形貌观察 11
第三章 实验结果与分析 12
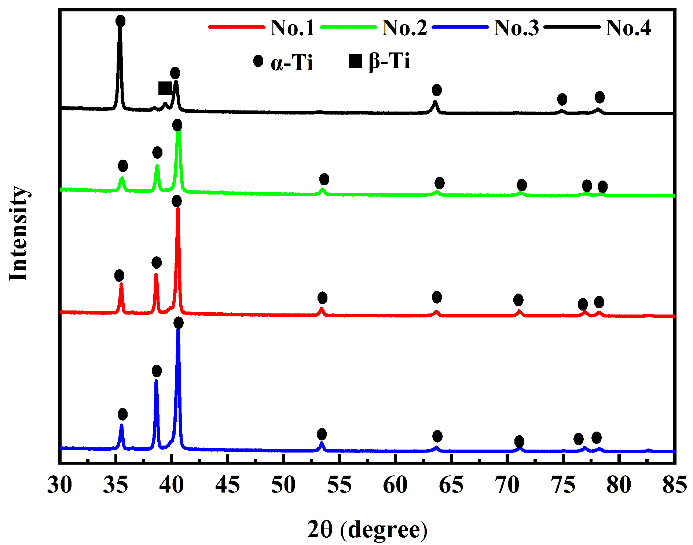
3.1 XRD分析 12
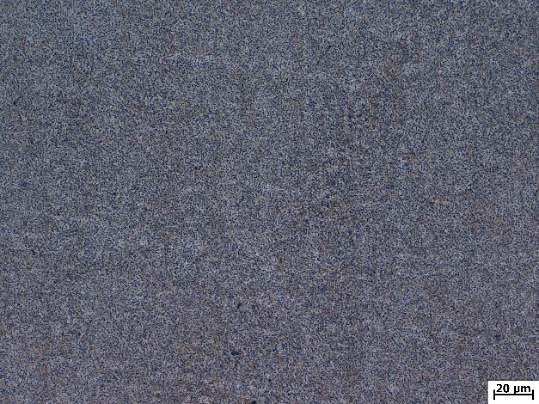
3.2 3D打印成型的TC4合金组织的金相观察 12
3.3 DSC实验 14
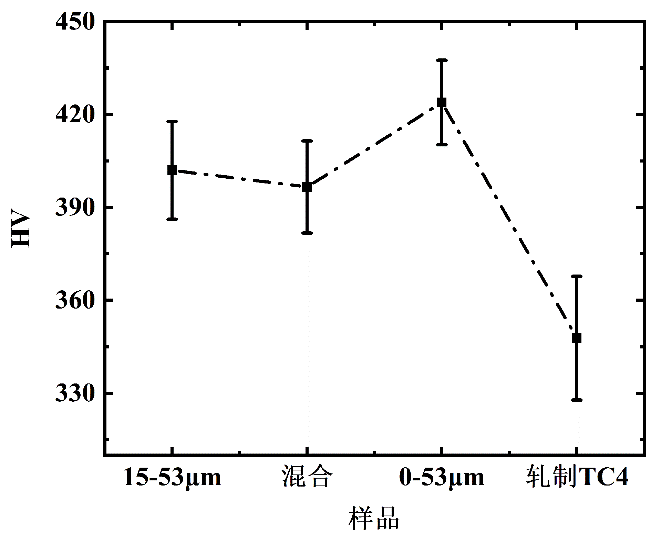
3.4合金维氏硬度测试 14
3.5接触角实验结果 16
3.6极化曲线(动电位扫描)的测定结果 17
3.7电化学阻抗(EIS)实验结果 21
3.8形貌侵蚀实验 23
第四章 结论与展望 28
4.1结论 28
4.2展望 29
参考文献 30
致谢 32
目录
第一章 绪论
1.1 3D打印
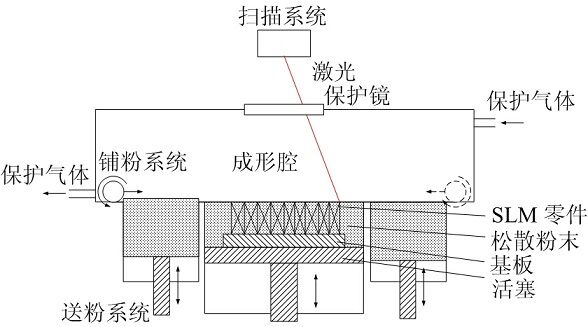
3D打印是一种以软件模型为基础的快速成型方法。3D打印通过使用金属或者塑料粉末并利用计算机软件达到“分层制造,逐层叠加”,能最好构建出完整的实物,是一种“自下而上”材料累加的制造方法。3D打印有着非常明显的优点:1)复杂零件能够快速成型;2)高度自动化生产过程;3)生产成本低;4)广泛的材料选择;5)原料使用少,余料能继续使用[6]。
最常用的金属3D打印技术包含几种:选择性激光熔化技术(SLM),电子束选区熔化技术(EBSM)以及近净成形技术(LESN)[1,2]。打印方法不同形成的样品在各方面的性能也有所不同,本次实验的样品采用SLM技术成型。
相关图片展示:




您可能感兴趣的文章
- 元素对Ti-xAl-yMo-zV和Ti-xAl-yMo-zCr β-Ti合金应变速 率敏感性的影响外文翻译资料
- 复合工艺提高先进钠离子电池的电位窗口外文翻译资料
- 氧化还原催化辅助下的高稳定钒氧化还原流电池外文翻译资料
- 用于高压可伸缩储能的电解锌锰电池外文翻译资料
- 表面活性剂改性疏水性Cu2O量子点作为高效钙钛矿太阳能电池顶部空穴传输材料外文翻译资料
- Nb 和 Ni 共掺杂 Mg(0001)氢解离扩散的理论研究:外文翻译资料
- 低温固相法制备锂离子电池正极材料LiFeSO4F毕业论文
- 锂空气电池新型正极催化剂Gd2Zr2O7的制备与性能研究毕业论文
- 酸类添加剂对beta”-Al2O3电泳沉积成型法的影响毕业论文
- CuZr非晶合金中短程有序结构及其与玻璃形成能力的关系研究毕业论文




