氮掺杂介孔碳储钠性能研究毕业论文
2020-07-07 21:35:22
摘 要
伴随着人类社会经济的飞速发展,人们也加快了对未知领域探索的脚步。由于电子终端设备更新换代的速度越来越快,当今社会人们对储能元件的性能要求也日益提高。而在大规模的二次储能电池领域的研究中,对储能元件主要有两方面的性能要求:具有较为稳定的电化学性能,同时成本低廉并且可以大量制造。已经成功商业化的锂离子电池由于资源储备不足,制约了其进一步的发展,而以资源储备相对更丰富、分布广泛、更廉价的的钠元素制造钠离子电池便成为了这个研究领域的热门。
但是钠离子较大的半径导致在电极材料中进行可逆脱嵌过程有一定的困难,从而影响了钠离子电池的电化学性能,这也是制约钠离子电池进一步发展的一个关键难题。因此,研究如何制备出性能良好的新型电极材料变成了钠离子电池研究的主要课题。
本课题采用溶液凝胶法,合成存在大量介孔和一定量氮元素的掺氮介孔碳材料,以这种材料作为钠离子电池负极材料。合成采用F127为模板,以尿素为氮源加入掺杂元素氮,使溶液发生酚醛缩聚反应得到酚醛树脂碳前躯体,经过碳化后便得到氮元素掺杂的介孔碳材料。进一步研究显示,适当比例的氮元素掺杂增加了材料的比容量,改善了材料的导电性,试样中的氮也为钠离子脱嵌过程提供了更多活性位点,使离子传导速率变快。这种钠离子电池负极材料的循环稳定性也得到了相当的改善。
关键词:钠离子电池 介孔碳 氮元素掺杂
The storage capacity of nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon
Abstract
With the rapid development of social economy, the progress of science and technology has also accelerated. In today's society, the performance requirements of energy storage components are also increasing. In the research of large-scale secondary energy storage batteries, the performance requirements for energy storage components mainly include two aspects: relatively stable electrochemical performance and resource cost. The degree of impact on the environment. Lithium-ion batteries that have been successfully commercialized have limited further development due to insufficient resource reserves. The relatively more abundant, widely distributed, and cheaper sodium-ion batteries have become popular in this research field. However, the larger ionic radius leads to some difficulties in the reversible deintercalation process in the electrode material, which affects the electrochemical performance of the sodium ion battery, which is also a key problem that restricts the further development of the sodium ion battery. Therefore, the study of how to prepare a new type of electrode material has become a major research topic for sodium ion batteries.
This project adopts the solution gel method to synthesize nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon material with a large number of micro mesopores. Use this material as a negative electrode material for sodium ion batteries. Using F127 as a template, urea is used as a nitrogen source to add the nitrogen of the doping element, and the phenolic resin carbon precursor is obtained by the phenolic polycondensation reaction on the surface. After carbonization, a nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon material is obtained. Further studies have shown that an appropriate proportion of nitrogen doping increases the specific capacitance of the material, improves the electrical conductivity of the material, and also provides more active sites for the sodium ion deintercalation process, making the ion transport rate faster. The cycle stability of this cathode material for sodium-ion batteries has also been considerably improved.
Key words: sodium-ion batteries mesoporous carbon nitrogen-doped
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1引言 1
1.2钠离子电池工作原理和研究前景 1
1.3钠离子电池负极材料 3
1.3.1嵌入类材料 3
1.3.2 合金类材料 4
1.4氮掺杂介孔碳材料的特点 5
1.4.1掺杂对碳基材料性能的影响 5
1.4.2介孔碳材料 5
1.5介孔碳的合成 5
1.5.1催化活化法 5
1.5.2溶液-凝胶法 6
1.6氮掺杂介孔碳储钠性能研究进展 6
第二章 实验内容 7
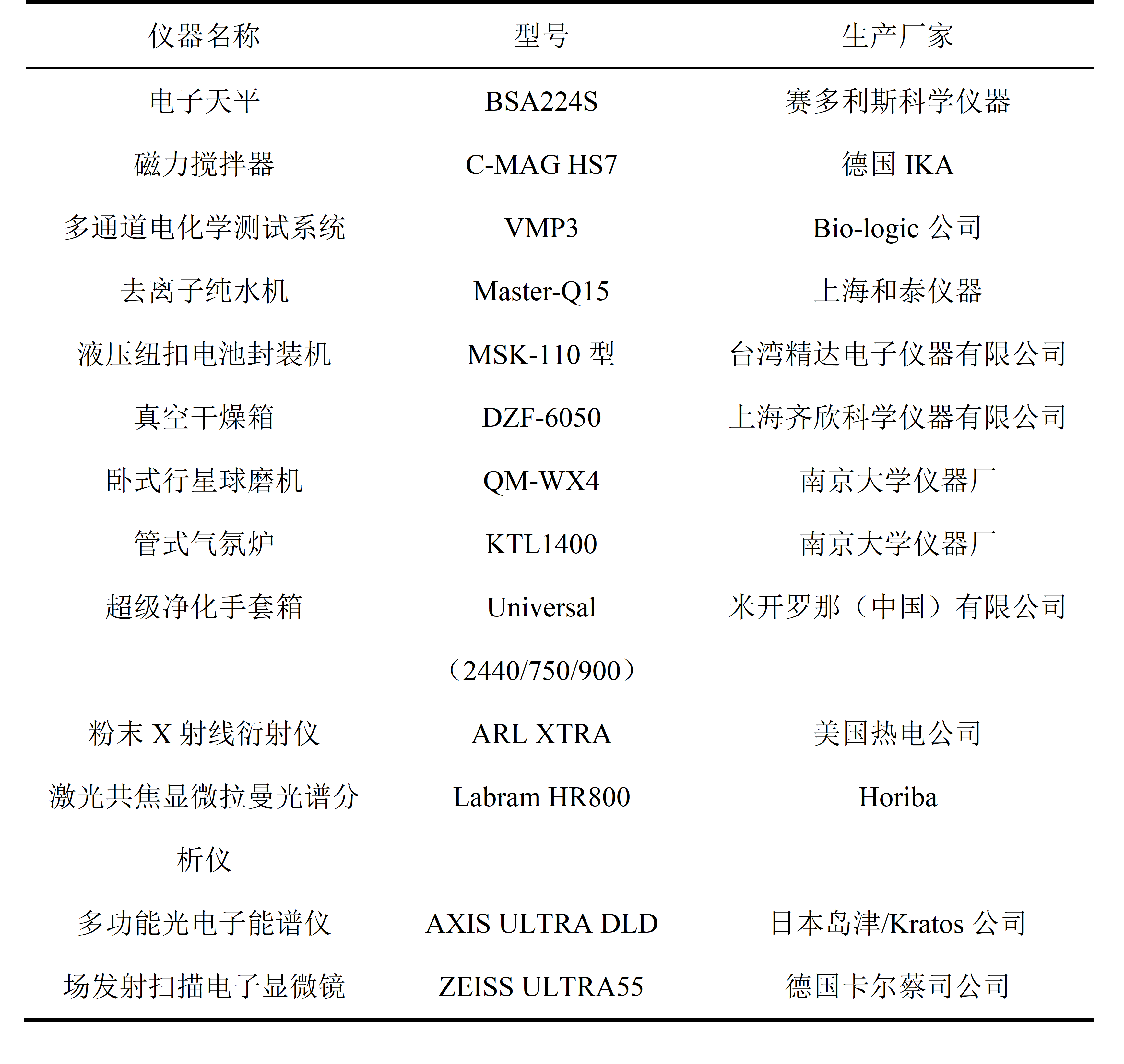
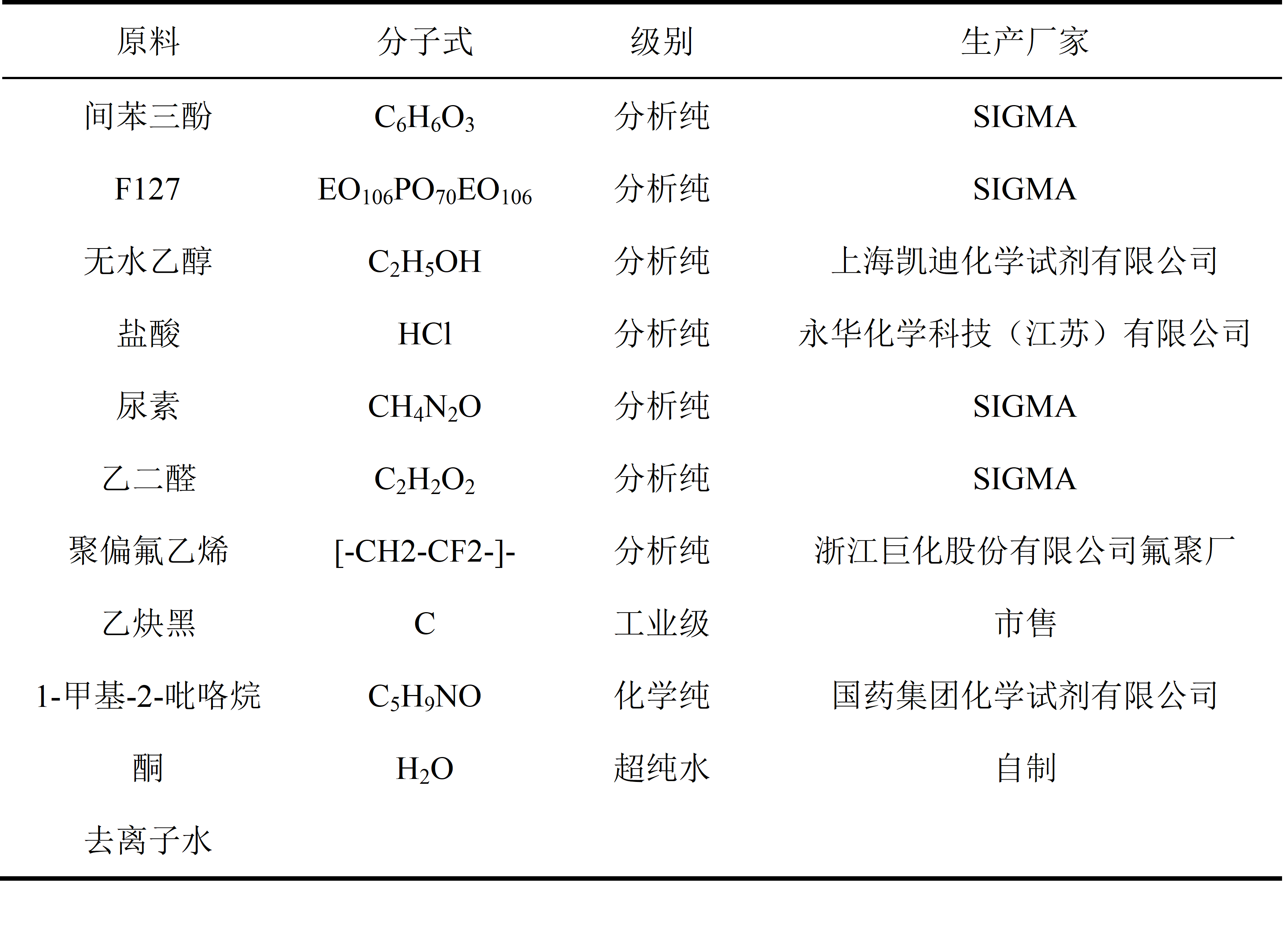
2.1实验主要仪器和药品 7
2.2实验方案 8
2.3 材料表征方法 8
2.4电池组装 9
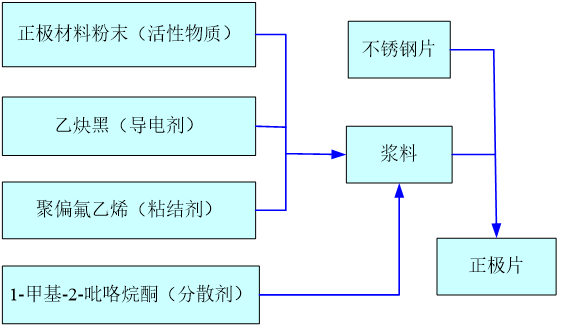
2.4.1正极电极片的制备 9
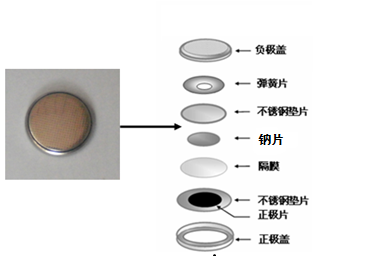
2.4.2纽扣电池的组装 10
第三章 实验结果与讨论 11
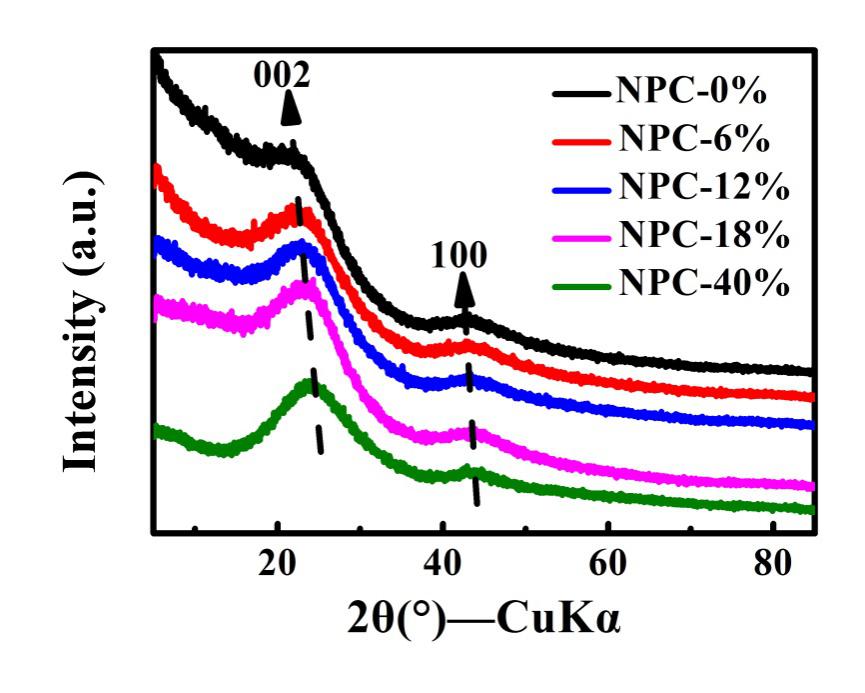
3.1 XRD 分析 11
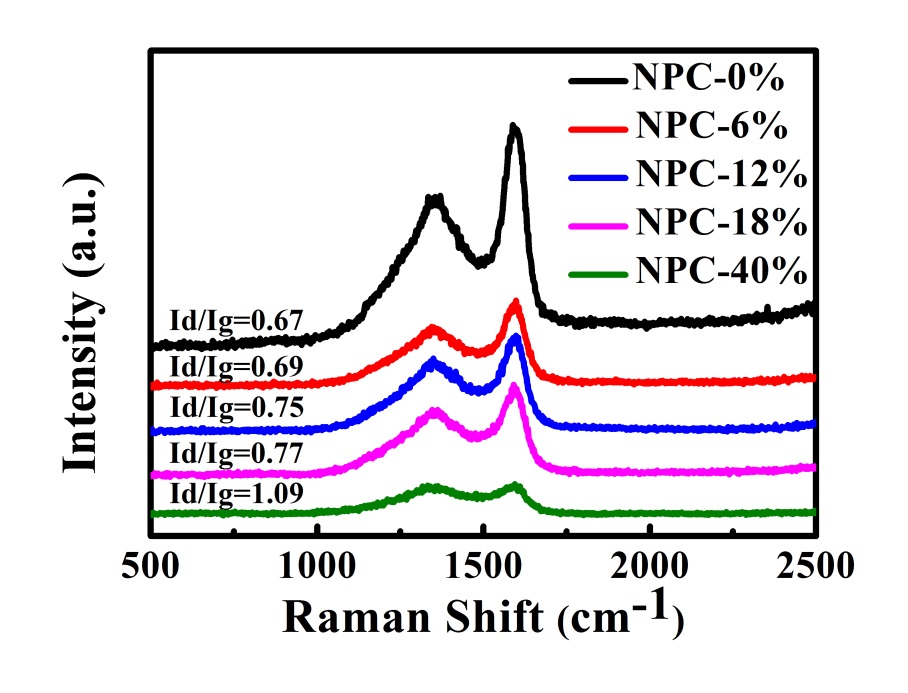
3.2 拉曼光谱分析 11
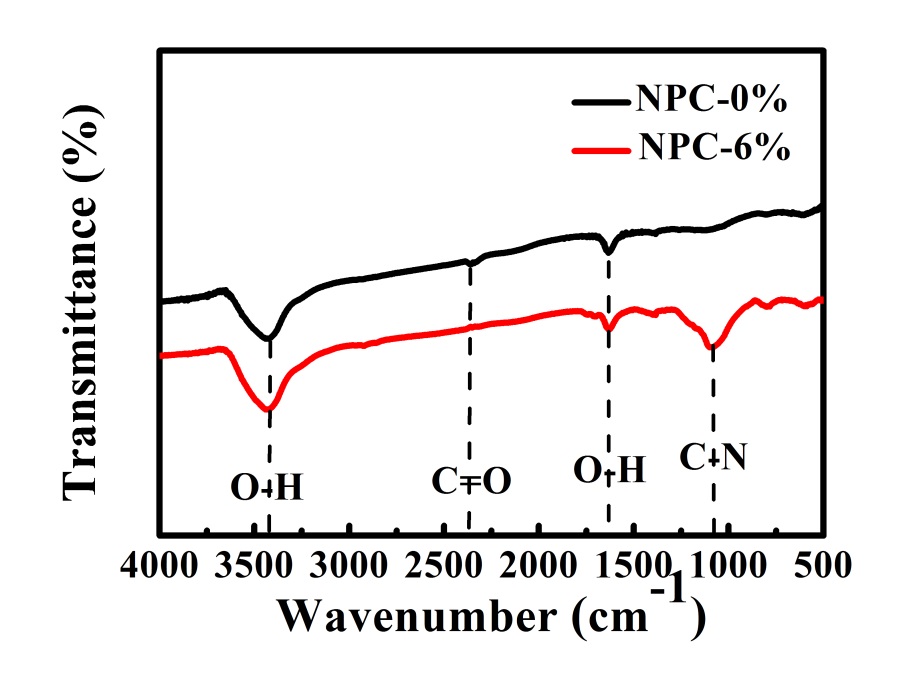
3.2 傅立叶变换光谱分析 12
3.3 电化学性能测试 13
3.4 XPS分析与元素分析 18
第四章 结论 20
参考文献 21
致 谢 24
第一章 绪论
1.1引言
随着社会经济与科技的发展,电子产品飞速更新换代,人们对储能元件的性能要求和需求也在同步提升。同时新能源汽车、二次电池等领域成为热门方向,而这些领域进一步发展的关键就是能否制造出性能更优异,成本更低廉的电池。目前成功商业化并大量应用的代表性储能元件是锂离子电池,其具有能量密度高,循环性能优越等优点,但由于锂元素储量不丰富,且分布不均衡等因素,制约了其进一步的发展。因此与其原理相似的钠离子电池便重新成为了较热门的研究方向。
由于钠元素在地壳中储量较为丰富,且钠与锂性质相近,因此制造钠离子电池能在一定程度上参考较为成熟的锂电池技术。同时钠的价格更为低廉,相比锂元素,这些优点使钠离子电池有良好的研究前景。目前制约其进一步发展的关键因素是没有得到较适宜的钠离子电池电极材料,当然钠离子电池有着价格低廉,储量更丰富的优势,这意味着钠离子电池有希望替代如今市场主流的锂离子电池,得到广泛的应用。
1.2钠离子电池工作原理和研究前景
钠离子电池的研究可追溯到20世纪80年代,由于锂离子电池首先商业化成功,人们对钠离子电池的研究便逐渐放慢了脚步。因为钠与锂是同主族元素,所以它们有着相近的化学性质(表格1),同时两者的充放电原理也很接近(图1)。以钠离子电池为例,其充电过程中,从正极材料(例如NaMnO2)中释放出Na ,通过电解液转移至负极材料(例如硬碳),而电子则从外电路转移至负极,两者维持电荷平衡;反之即是放电过程。相较锂离子电池,钠离子电池优点有:首先地壳中钠资源较丰富(地壳元素储量为2.64%),同时钠元素具有廉价,广泛分布的优点,这使钠离子电池大规模应用成为了可能。当然它也有缺点,由于钠离子具有与锂离子相比较更重的质量和较大的半径(钠:0.102 nm ,锂0.069 nm),使得其在电极材料中脱嵌速度慢,这相当程度上影响了钠离子电池的性能。同时,Na /Na比Li /Li的标准电极电位高0.3 V,意味着钠离子电池本身不具备锂离子电池的高能量密度[1-3]。
相关图片展示:
您可能感兴趣的文章
- 元素对Ti-xAl-yMo-zV和Ti-xAl-yMo-zCr β-Ti合金应变速 率敏感性的影响外文翻译资料
- 复合工艺提高先进钠离子电池的电位窗口外文翻译资料
- 氧化还原催化辅助下的高稳定钒氧化还原流电池外文翻译资料
- 用于高压可伸缩储能的电解锌锰电池外文翻译资料
- 表面活性剂改性疏水性Cu2O量子点作为高效钙钛矿太阳能电池顶部空穴传输材料外文翻译资料
- Nb 和 Ni 共掺杂 Mg(0001)氢解离扩散的理论研究:外文翻译资料
- 低温固相法制备锂离子电池正极材料LiFeSO4F毕业论文
- 锂空气电池新型正极催化剂Gd2Zr2O7的制备与性能研究毕业论文
- 酸类添加剂对beta”-Al2O3电泳沉积成型法的影响毕业论文
- CuZr非晶合金中短程有序结构及其与玻璃形成能力的关系研究毕业论文




