基于高拉伸导电水凝胶的传感器的开发毕业论文
2020-04-22 19:35:31
摘 要
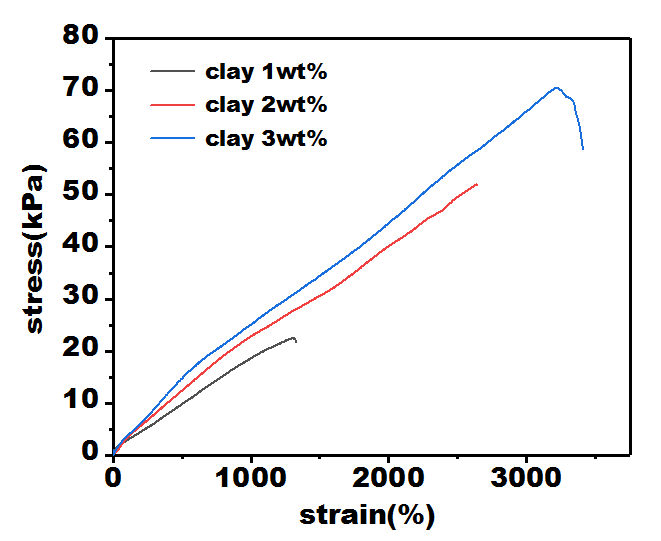
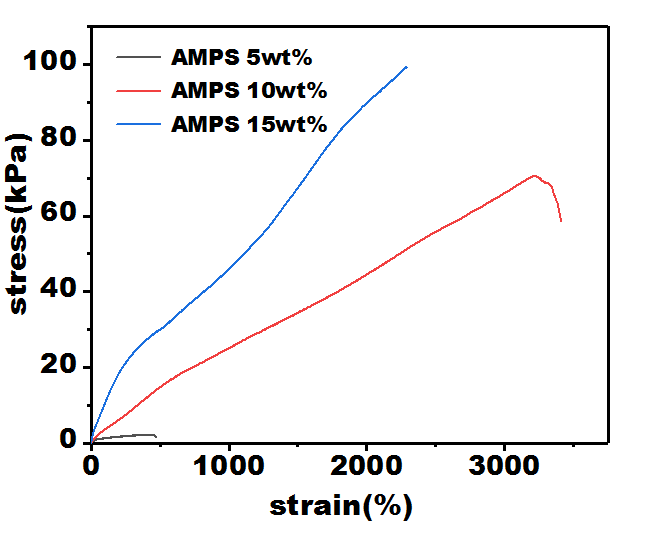
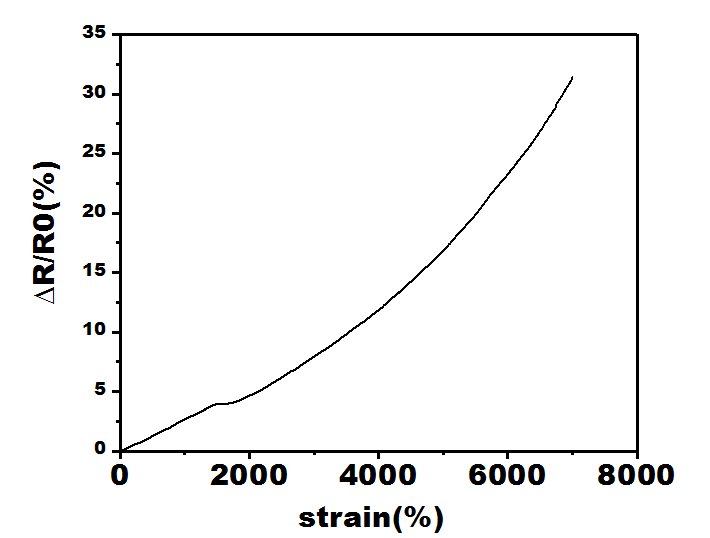
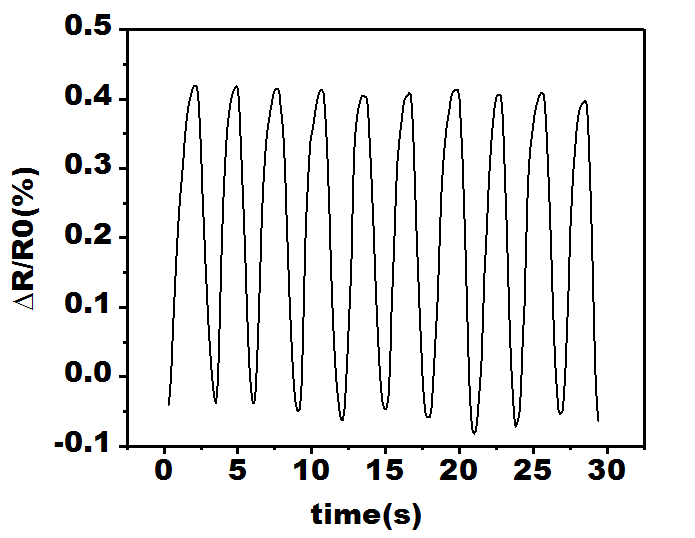
近年来,柔性传感器的使用愈发普及,已经成为水凝胶材料领域重点研究方向,在实际使用中对水凝胶应变灵敏度要求较高,在设备中使用纳米离子水凝胶需要它们力学性能优秀,要有较不错的传感性能。以N,N-二甲基丙烯酰胺和2-丙烯酰胺基-2-甲基-1-丙烷磺酸为单体尝试配制一种可作为传感器材料的水凝胶。通过多键交联具有广泛可调的力学性能。同时,AMPS部分的赋予了水凝胶坚韧和导电的性能。这项工作不仅提供了一个简单的策略来制造良好拉伸性能的和优秀传感性能的纳米黏土水凝胶还具有水凝胶的多功能特性,实现设备的灵活应用,具有巨大的开发潜力。在本次实验中主测试纳米水凝胶中单体与纳米粒子配比以达到良好的力学性能及传感性能,以N,N-二甲基丙烯酰胺(DMA)阳离子单体,使用2-丙烯酰胺基-2甲基-1丙烷磺酸(AMPS)为阴离子单体形成共聚,纳米clay为交联剂,用过硫酸钾(KPS)作引发剂。探讨了单体和黏土配比对水凝胶成胶性能的影响。着重对该纳米水凝胶传感及力学性能进行评价。本文通过控制引发剂(KPS)不变的情况下,先后改变单体及黏土比例,实验数据表明,当DMA、AMPS、黏土比例为20:15:3性能最为优异。
关键词:传感器 水凝胶 纳米水凝胶 力学性能 传感性能
Abstract
Nowadays, the application of stretch conductive sensor is more and more extensive, and the development of such sensor is more and more important.In practical use, hydrogels require high mechanical and sensing properties. The use of hydrogels in equipment requires excellent mechanical properties and good sensing performance. N, N-dimethylacrylamide and 2-acrylamide-2-methyl-1-propane sulfonic acid were used as monomers to prepare a hydrogel which could be used as sensor material. Multi-bond crosslinking has a wide range of adjustable mechanical properties. At the same time, the AMPS part gives the hydrogel toughness and conductivity. This work not only provides a simple strategy to fabricate nano-clay hydrogels with good tensile properties and excellent sensing properties, but also has multifunctional properties of hydrogels, which has great potential for development. Realize flexible equipment application. In this experiment, the ratio of monomers and nanoparticles in nanohydrogels was tested to achieve good mechanical properties and sensing properties. N, N-dimethylacrylamide (DMA) and 2-acrylamide-2-methyl-1 propane sulfonic acid (AMPS) were used as monomers, nanoclay was used as crosslinking agent, and potassium persulfate (KPS) was used as initiator. The effects of the ratio of monomer to clay on the gelling properties of hydrogels were discussed. The sensing and mechanical properties of the nano-hydrogel were evaluated emphatically. In this paper, the ratio of monomer to clay is changed successively by controlling the constant KPS. The experimental data show that when the ratio of DMA, AMPS and clay is 20:15:3, the performance is the best.
Keywords:Sensor ;Hydrogel;Nanohydrogel;Mechanical;Properties;Sensing Properties
目 录
摘要 I
Abstract I
第一章 文献综述 1
1.1 纳米clay水凝胶 1
1.1.1 聚合物水凝胶 1
1.1 成分简介 1
1.2.1 单体DMA 1
1.2.2 AMPS 1
1.3 高分子纳米复合凝胶研究进展 1
1.4 本文研究内容 1
第二章 水凝胶的制备与表征 1
2.1本文研究内容 1
2.1.1 实验主要原料 1
2.1.2 实验仪器与设备 1
2.2 实验部分 1
2.2.1 DMA凝胶的制备 1
2.3 实验相关表征与主要测试手段 1
第三章 结果与讨论 1
3.1 水凝胶的形成和结构分析 1
3.2 红外分析 1
3.3 凝胶的拉伸性能 1
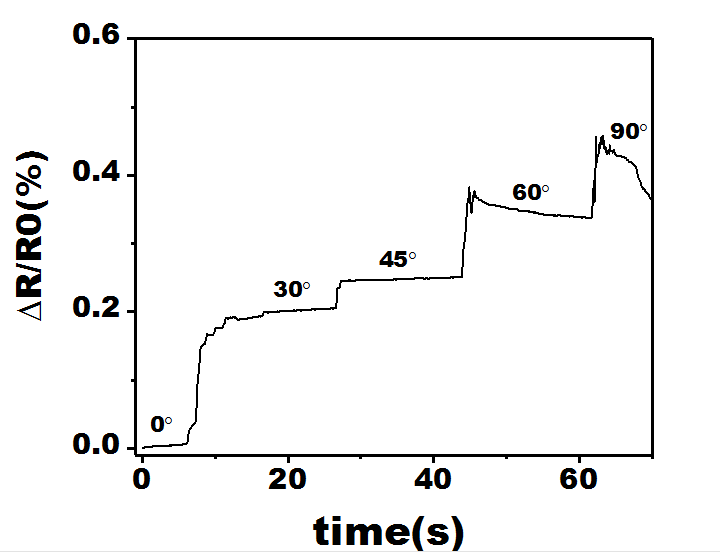
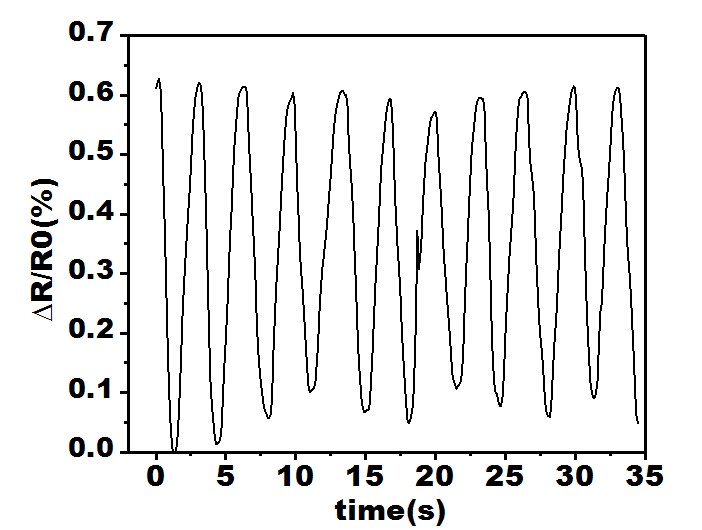
3.4 凝胶的传感性能 1
第四章 结论与展望 1
4.1 结论 1
4.2 展望 1
参考文献 1
致谢 1
第一章 文献综述
1.1 纳米clay水凝胶
1.1.1 聚合物水凝胶
水凝胶是一种自身拥有充足水分,却不溶于水。这是一种为生物特别是人类而开发的材料。水凝胶在与液体组织接触时会有较优秀的相容性,它不会对生物的代谢进行影响,在人体组织中,大部分都属于水凝胶结构。生物用水凝胶通常是两相系统,由微米或纳米级纤维增强[1]。水凝胶在柔性装置中的新兴应用要求其具有多功能特性,包括在各种变形或外部环境下的稳定机械和功能。高应力导电材料广泛用于应用电子皮肤、人机界面、生物医疗设备、人类活动监视器和可穿戴电子设备等。对雨水的线性和高灵敏度,以及所需的应变。最灵活的传导器是液体弹性体和金属颗粒的组成金属、碳、离子液体或导电聚合物许多较低含量和较低断裂应变(lt;100%)由更高的材料相容性引起。具有高延伸性和稳定性的柔性导电体传导性传感器和装置的大应变高阻和高阻。
1.1.2 纳米水凝胶
相关图片展示: