巯基化透明质酸和丙烯酰化聚乙二醇水凝胶的制备和性能研究毕业论文
2020-07-05 17:26:10
摘 要
随着当今社会科技的不断进步发展,世界各国的科学家们不断地致力于医学创新,企图治愈那些医学上的疑难杂症,而随着3D打印的问世,科学家们立刻将它关联到医学上来。
在2010年时,美国公司研发出了一种3D生物打印机,可以制作仅用于研发无法实际应用的生物组织。2014年,同一家公司又推出了用于商务的可打印人体肝脏组织的三维生物打印机,用于药物在进入市场前的测试。在2013年5月,有人在新英格兰医学杂志发表了一篇新闻。科学家表示已经完成了第一例人体植入,成功地将3D打印器官支架植入婴儿体内,治好了婴儿的先天性支气管炎。此后,三维生物印刷的实际应用正式出现。在中国,第一台三维生物材料打印机是在2013年8月7日发明的。利用生物医用高分子材料或活细胞,科学家成功地印刷了人体的软骨、内脏等。
在3DP领域里,生物墨水被作为印刷材料,它是一种可调节性能的印刷生物材料,可能含有细胞,生长因子和药物,应用于各种生物医学应用领域。尽管在这方面取得了进展,但在生物医学中应用3DP技术仍然存在挑战,开发适合作为生物墨水的材料尤其具有挑战性。这里我要研究的是一种透明质酸和聚乙二醇为基底的可打印水凝胶油墨,通过透明质酸的巯基化改性,能够有效降低体内透明质酸酶对透明质酸的降解,而以聚乙二醇为基底的水凝胶无毒,生物相容性好,且可以降解吸收,是一种智能水凝胶,而将末端的羟基活化后能与蛋白质相结合,抑制血小板的沉积,有效遏制出血。复合后的水凝胶它既包括剪切变薄,又包括通过客体-宿主键自愈合的行为,以及共价交联,用于光聚合进行稳定化的连接。无论当客体-主体程序集或共价交联单独使用,长期稳定。由于网络松弛,结构没有形成。在印刷或分散之前油墨长丝特别稳定。
关键词:3D生物打印、生物墨水、透明质酸、聚乙二醇、水凝胶
Preparation of thiol hyaluronic acid and acylated polyethylene glycol hydrogel
Abstract
With the development of modern social science and technology, scientists all over the world are constantly committed to medical innovation, trying to cure those medical problems, and with the advent of 3D printing, scientists immediately linked it to medicine.
In 2010, American companies developed a 3D bio-printer that could be used to produce only 1 of biological tissue that could not be physically applied. In 2014, the same company launched a three-dimensional bio-printer for commercial printing of human liver tissue for testing drugs before entering the market. In May 2013, a news article was published in the New England Journal of Medicine. Scientists say the first human implant has been completed, and the successful placement of the print organ stent into the baby's body has cured the baby's congenital bronchitis. Since then, the actual application of three-dimensional biological printing has been formally appeared. In China, the first three-dimensional bio-material printer was invented on August 7, 2013. Using biomedical polymer materials or living cells, scientists successfully printed the human body's cartilage, internal organs, and so on .
In the 3DP field, bio-ink is used as a printing material, it is an adjustable performance of the printing of biological materials, may contain cells, growth factors and drugs, applied to various biomedical applications. Despite the progress made in this regard, the application of 3DP technologies in biomedicine continues to be a challenge, especially for developing materials suitable for use as biological inks. Here I want to study is a hyaluronic acid and polyethylene glycol as the base of the printable hydrogel inks, by sulfhydryl modification of hyaluronic acid, it can effectively reduce the degradation of hyaluronic acid in vivo, and the hydrogel with polyethylene glycol as substrate is non-toxic, good biocompatibility, and can degrade and absorb, it is an intelligent hydrogel, The activation of the hydroxyl group can be combined with the protein, inhibit the deposition of platelet and effectively restrain the bleeding. The composite hydrogel comprises both shear thinning and the behavior of self healing through the object-host bond, and covalent cross-linking for stabilization of optical polymerization. No matter when the object-principal assembly or covalent cross-linking is used alone, long-term stability. Because of the network slack, the structure is not formed. The ink filament is particularly stable "3" before printing or dispersing.
Key words: 3D bio-printing, bio-ink, hyaluronic acid, polyethylene glycol, hydrogel
目录
摘要 1
Abstract 2
第一章 前言 6
1.1课题背景 6
1.2 3D打印的技术难题 6
1.3 水凝胶在3D生物打印中的应用 7
1.4 水凝胶材料的分类 8
1.5 透明质酸简介 9
1.6 透明质酸在生物医学上的应用 9
1.7 聚乙二醇简介 10
1.8 聚乙二醇在生物医学方面的应用 11
1.9 透明质酸和聚乙二醇的改性化处理及复合水凝胶的合成 12
13
第二章 HA-Cys与PEGDA的制备与检测 15
2.1 实验材料与仪器 15
2.1.1原料 15
2.1.2设备 15
2.2巯基化透明质酸的合成 15
2.2.1实验配方 15
2.2.2实验步骤 16
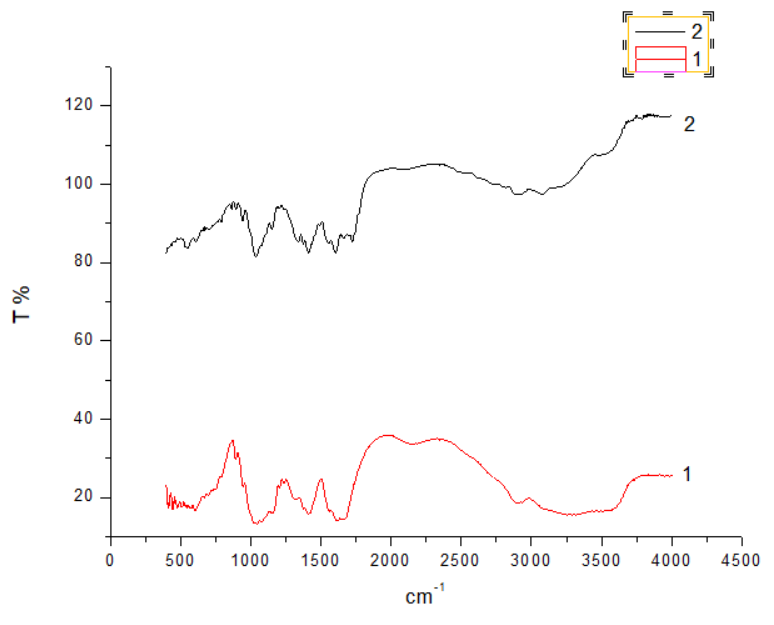
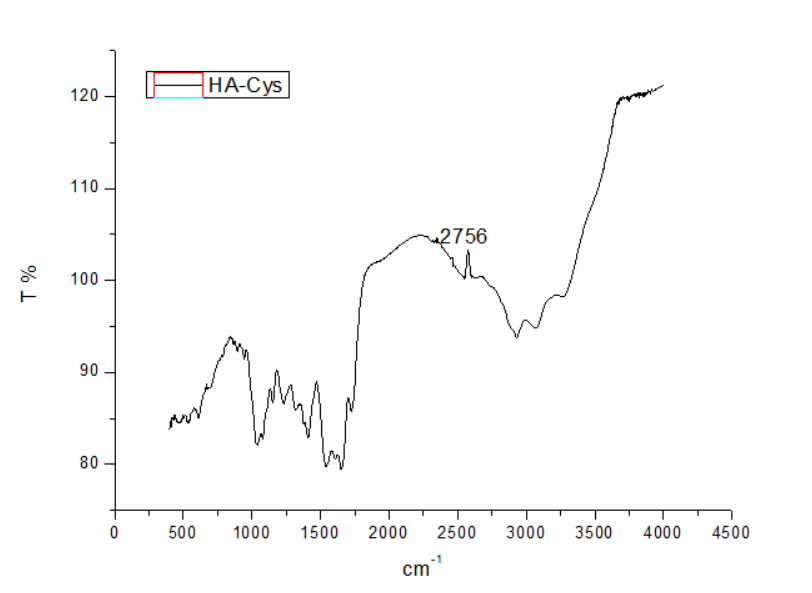
2.2.3测试与表征 16
2.2.4总结 18
2.3丙烯酰化聚乙二醇的合成 18
2.3.1丙烯酰化聚乙二醇的合成步骤 18
2.3.2表征与测试 19
2.4小结 21
第三章 巯基化透明质酸和丙烯酰化聚乙二醇复合水凝胶的合成 22
3.1实际用量的筛选 22
3.1.1HA-Cys浓度的筛选 22
3.1.2 PEGDA浓度的筛选 22
3.1.3交联剂用量的筛选 23
3.2实验过程 23
结果与展望 24
参考文献 25
致谢 27
第一章前言
1.1课题背景
当今世界,科技不断创新,自从3D打印技术面世以后,便有人提出了将它用于生物医药方面,3D生物打印的概念由此而来。各国都十分重视这项技术,被视为未来发展过程中不可或缺的一项技术,相信首先掌握这项技术的国家一定能在医学领域超越他国一大步【1】。组织器官的移植一直是医学上的一个难题,并且联合国已经通过法律,唯一承认的组织器官来源就是公民的自愿捐献,但是这根本满足不了医学上那大量的需要移植器官的需求,所以这也导致了器官移植手术的天价费用,而有了三维立体打印技术后,科学家们立刻想到,如果能用3D打印来打印人体组织器官,不就能缓解当前所面临的组织器官紧缺的危机了吗,于是,三维立体生物打印的观点应运而生,3D生物打印这一技术概念最早是由美国某大学的教授在2000年左右提出,2003年又有两位科学家在Trends in Biotechnology杂志系统提出用3D打印来打印器官的想法【2】。在中国,几乎在同时,清华大学颜教授率先在国内进行了三维生物打印的研究。
1.2 3D打印的技术难题
目前的3D生物打印技术还不够成熟,还有很多难点没有克服,主要的难点在以下几个方面:
细胞技术:人体,或者扩大来说,整个生物圈中的生物,他们的每一个组织和器官都很重要,并且它们都具有不同的属性,不存在用同一个细胞来打印出所有器官的方法。人体的不同组织都是由不同的细胞组合而成,神经中有神经细胞,肌肉组织中存在肌肉细胞,表皮上主要有各种上皮细胞。但是即使有了组织所特有的细胞,也不一定能在人体外分离培养出来,而且最重要的是,即使能打印出来,想要在打印完后还能保持如人体内一般的生物活性也是难上加难。所以要想3D生物打印能够成功,首先要解决的就是将不同的细胞分开培养,使之能成功的增殖,保持细胞活性。
相关图片展示: