基于弯曲元的干砂剪切波动力响应研究毕业论文
2020-02-16 23:43:53
摘 要
土体小应变参数作为岩土工程动力响应中的重要参数,在岩土工程中土体变形预测、灾害防治等研究领域中有着重要意义。岩土体的小应变在一般情况下可当作是线弹性的。其中小应变的剪切模量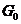 是重要的小应变参数之一,通过测定剪切模量
是重要的小应变参数之一,通过测定剪切模量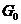 可以获得土体的其他小应变弹性参数。因此,寻找到简单快捷准确地测量土体的小应变剪切模量的方法是十分有意义的。现在主流的剪切波速室内试验测量方法是共振柱试验和压电弯曲元试验。共振柱方法测试土体小应变剪切模量的可靠性在国际上已经得到公认,弯曲元设备操作简单、成本较低、便于安装移植等特点,被广泛应用于测定土体的最大剪切模量。但对于压电弯曲元测量剪切波速方法,存在的最大问题就是剪切波的初达时间确定上仍存在一定的分歧。
可以获得土体的其他小应变弹性参数。因此,寻找到简单快捷准确地测量土体的小应变剪切模量的方法是十分有意义的。现在主流的剪切波速室内试验测量方法是共振柱试验和压电弯曲元试验。共振柱方法测试土体小应变剪切模量的可靠性在国际上已经得到公认,弯曲元设备操作简单、成本较低、便于安装移植等特点,被广泛应用于测定土体的最大剪切模量。但对于压电弯曲元测量剪切波速方法,存在的最大问题就是剪切波的初达时间确定上仍存在一定的分歧。
本文在总结以往研究的基础条件上,以福建标准砂和石英玻璃珠为研究对象,在公认可靠性的共振柱仪的基础上,尝试将弯曲元件与之耦合,开发得到弯曲元—共振柱联合试验仪,并采用该仪器对弯曲元试验结果进行标定,找到确定剪切波初达时间的准确方法。另外,本文在石英玻璃珠的弯曲元室内试验基础上,通过离散元(DEM)软件PFC3D来再现室内弯曲元试验的全过程,通过离散元模拟与物理试验的对照,从细观角度对颗粒材料中剪切波传播过程进行了探讨。具体研究内容如下:
1.对弯曲元与共振柱仪的试验原理及构造进行了介绍,总结了两种试验方法各自的不足,为弯曲元与共振柱进行耦合进行打下了理论基础。
2.实现了弯曲元—共振柱联合试验仪的改造,对带有弯曲元的共振柱进行了重新标定。使用弯曲元—共振柱联合试验仪,分别对福建标准砂干砂试样和石英玻璃珠进行了相同密实度、两个不同围压条件下,开展了剪切波速测量试验,明确了采用初达波法确定剪切波传播时间的可靠性,同时发现选取最大波峰前一波峰的零电位点作为剪切波的初达点最合适,与共振柱试验的标定值最接近。对于两种不同试验材料的试验表明,这种方法对于不同形状尺寸的材料具有普遍适用性。
3.为对剪切波在土体介质中的传播过程进行细观的探讨,在室内弯曲元石英玻璃珠的剪切波速测量试验的基础上,利用颗粒流软件PFC3D进行模拟。通过接触本构模型的选择、细观参数的选择、建模、运行程序等几个步骤中实现。最终将模拟的弯曲元试验结果与室内试验结果对比,寻找宏观波动响应与细观传递机制的联系。
通过上述研究得到结论:采用弯曲元—共振柱联合试验仪来测量土体剪切波速具有必要性,利用可靠的共振柱仪对弯曲元的缺陷进行了弥补,同时验证了用初达波法测量剪切波速的合理性;对于离散元模拟的接触本构模型的选择中,发现选择Hertz-Mindlin模型较为合理。通过将模拟得到的剪切波形与物理试验的波形对比,发现在同一激发频率下两方法测量得到的剪切波波形十分相近。观察发现力的传递规律表现出与剪切波波形具有相同的趋势,即如波浪形由上顶部往下底部发展。在位移的分布规律上,整个试样中的颗粒位移有明显的随时间增长,发生向下波动传递的过程。且传播的进行过程中,位移场逐渐变小,弹性波的波幅与传播距离大小呈负相关,这和真实的剪切波在土体中的传播特征一致。
关键词:小应变;剪切模量;弯曲元;共振柱;离散元;剪切波
Abstract
As an important parameter in the dynamic features of soil of geotechnical engineering, small-strain parameter is of great significance in the research fields of soil deformation prediction and disaster prevention and control. The small-strain of soil can generally be regarded as linear elastic. The shear modulus of small-strain is one of the important parameters of small-strain. Therefore, it is important to find a simple, fast and accurate method to measure the small-strain shear modulus of soil. The main methods of measuring the velocity of shear wave are resonant column method and bender element method. The reliability of the resonance column method for testing the small-strain shear modulus of soil has been recognized widely. However, there are some disputes on how to accurately determine the arriving time of shear wave by using bender element method.
In this paper, on the basis of previous research conditions, the Fujian standard sand and quartz glass beads were taken as the research object. Based on the accepted reliability of the resonance column instrument, a set of bender element- resonance column tester was developed by combining the bender element and the resonant column instrument, and found the method to determine the initial arriving time of shear wave accurately. In addition, based on the laboratory test of the bender element of quartz glass beads, this paper reproduces the whole process of the laboratory test of bender element test through the DEM software PFC3D, and discussed the process of shear wave propagation in granular materials from the perspective of microscopy comparing the difference between DEM and physical method. The following research contents are as follows:
1. The test principle and structure of the bender element and resonant column instrument are introduced, and the disputes of the two test methods were summarized, expounded the theoretical foundation for the combining of the bender element and the resonant column.
2. The joint equipment of bender element and resonant column was reformed, and the resonant column with bender element was re-calibrated.Fujian standard sand dry sand and quartz glass beads were investigated respectively by using bender elements-resonant column joint tester.They were investigated under the same sample compactness, two different confining pressure conditions.The reliability of the initial wave method to determine the propagation time of the shear wave is verified. At the same time, the take-off point of the peak located before the main peak of the received wave (the maximum peak of the amplitude) is the most accurate point, which is consistent with the value of the resonance column test.Experiments on two different materials show that this method is applicable to materials of different shapes and sizes.
3. In order to investigate the propagation process of shear wave in soil particles, PFC3D was used to simulate the velocity of shear wave measurement test of bender element test in the laboratory.It is realized through following steps:contact constitutive model selection, mesoscopic parameter selection, modeling and running program.Finally, the simulated bending element test results are compared with the laboratory test results to find the connection between macro wave response and mesoscopic transmission mechanism.
The conclusion is drawn from the study: it is necessary to use the bender element- resonance column tester to measure the velocity of shear wave of soil.In the selection of contact constitutive model for discrete element simulation, it is found that hertz-mindlin model is more reasonable.By comparing the simulated waveform with the physical test waveform, it is found that the waveform measured by the two methods is very similar under the same excitation frequency.It is observed that the law of force transfer shows the same trend as the shear wave shape, that is, the wave shape develops from top to bottom.In terms of the distribution of displacement, the particle displacement in the whole sample increases obviously with time, and the process of downward fluctuation transfer occurs.In the process of propagation, the displacement field gradually decreases, and the amplitude of elastic wave is negatively correlated with the propagation distance, which is consistent with the propagation characteristics of real shear wave in soil.
Key Words: small-strain; shear modulus; bender elements; resonant column; discrete element methods; shear wave
目 录
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景 1
1.2 土体小应变模量 2
1.3 小应变剪切模量的测量方法 3
1.4 本文研究内容 5
第二章 试验设备改造与实现 7
2.1试验设备简介 7
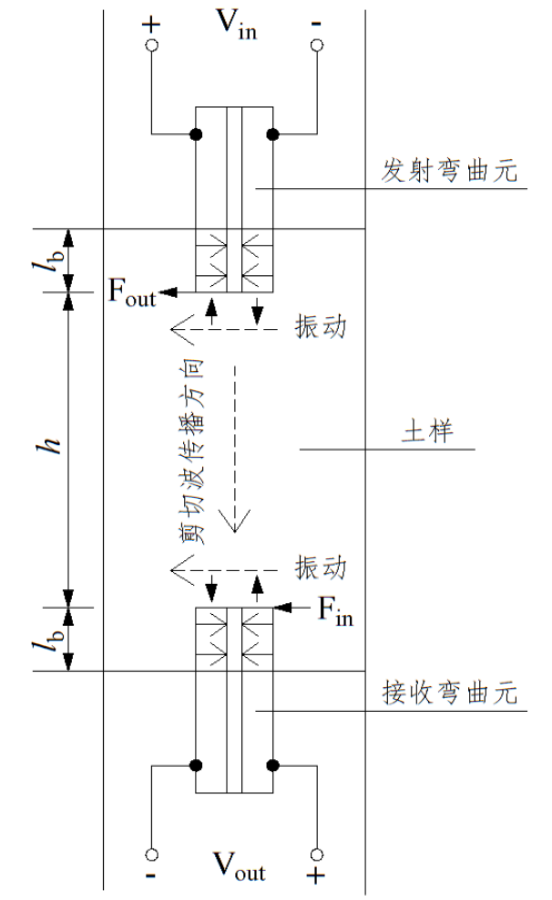
2.1.1 弯曲元原理简介 7
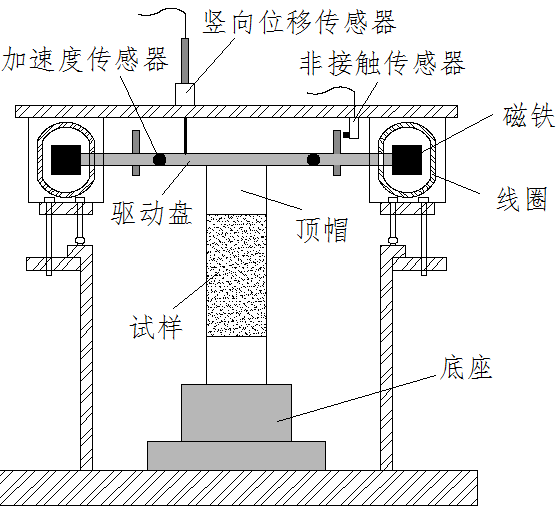
2.1.2 共振柱原理简介 9
2.2试验原理 11
2.2.1 剪切波初始到达时间的影响因素及解决办法 12
2.2.2 剪切波到达时间的判定方法 12
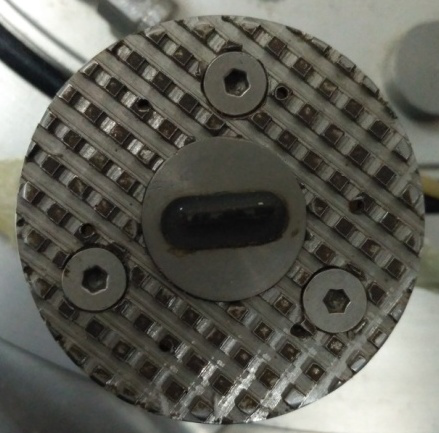
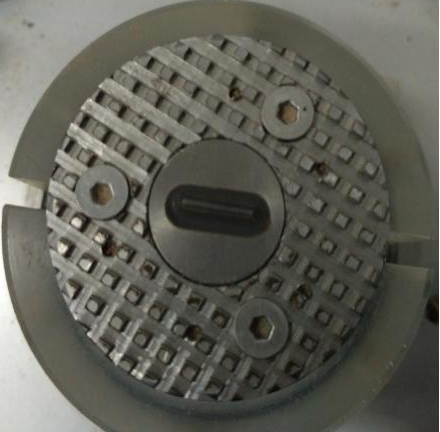
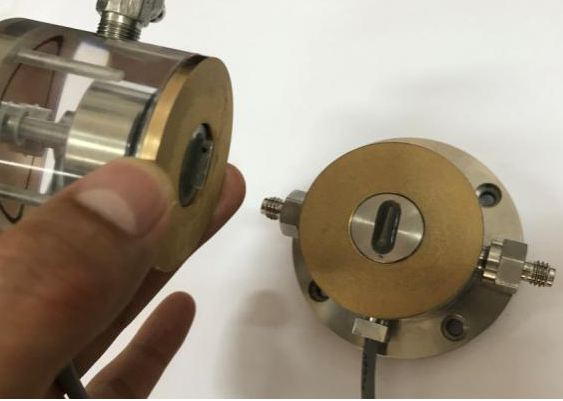
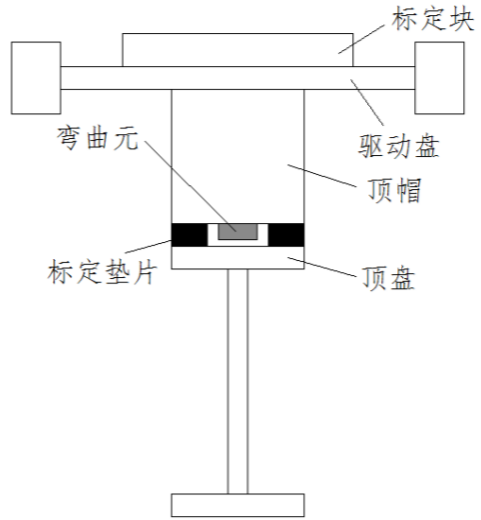
2.3共振柱—弯曲元联合试验装置的开发及标定 13
第三章 共振柱—弯曲元联合测试试验 17
3.1 试验材料 17
3.1.1福建标准砂 17
3.1.2 石英玻璃珠 18
3.2 试验方案 19
3.3 试验结果对比 20
第四章 弯曲元剪切波的离散元模拟 22
4.1 离散元模拟介绍 22
4.1.1离散元基本原理和应用 22
4.1.2接触本构模型 22
4.2 建模过程 23
4.2.1 三轴室的生成 24
4.2.2 颗粒的生成 24
4.2.3 加载过程及激发剪切波过程 25
4.2.4 接触本构模型的选择 28
4.3 参数的选取、标定 29
4.4 数值模拟与物理试验对比 30
4.5 剪切波细观传播特性分析 32
4.5.1 力的传递规律 32
4.5.2 位移分布规律 33
第五章 结论与展望 35
5.1 本文主要结论 35
5.2 进一步研究建议 36
参考文献 37
致 谢 40
第一章 绪论
1.1 研究背景
土体小应变特性参数是岩土工程动力响应问题分析中重要的参数,在工程中土体变形、地震场地分析和基础设计等领域中意义重大。但是有关土体小应变的研究历史并不长,一方面由于以往实验仪器不够精确无法测得土体中的小应变状态,另一方面研究者们也未对土体中的小应变起到足够的重视,认为工程实际中土体的应变范围应该较大,小应变特性的研究对整体变形意义不大[1]。
但是经过大量的工程实例经验及测试结果表明,有很大一部分的地下结构土体在荷载状态下的应变状态是小应变状态。Jardin等[2]于1986年通过工程实例发现,大部分工程中非基坑、基础周围的土体的整体变形量级均在0.01%-0.1%的范围内。Burland等[3]于1989年发现在荷载作用下的深基坑周边土体应变小于0.1%但大于0.05%。罗国富等[4]在进行地铁天安门西站的开挖工作时,工程实测数据也与上述结论类似土体应变在0.1%-0.01%之间。Izumi等[5]于1997年提出在对彩虹大桥建设过程中的监测中发现,地基土和基础土的应变小于等于0.01%,这也基本符合上述土体小应变范围。不同荷载条件下岩土体的应变范围如图1.1所示[6]:
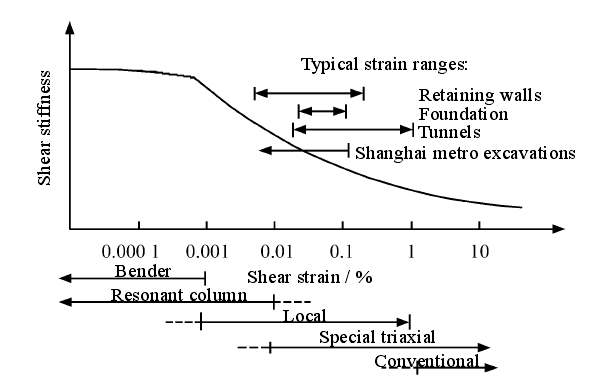
图1.1 各荷载条件下岩土体的应变范围 (汪中卫等[6],2007)
有关岩土体的小应变特性的研究工作展开起步于上世纪70年代年左右,研究者们在岩土工程中发现一个重要的问题即室内试验的得到的土体刚度与现场原位测试得到的结果差距较大。研究者对这种现象给出了各种分析和解释[7-8],认为与土体试样的影响因素较多有关,并没有认识到土体的小应变特性的重要。而实际上,各类地下工程周围土体处于小应变状态,这对岩土体变形规律研究有着重要的意义。
Atkinson等[9]于1991年定义了不同的应变范围:非常小应变(lt;0.001%)、小应变(0.001%-1.000%)和大应变(gt;1%)三个范围。Jardin等[10]在1992年总结了,土体在某一小应变的区域内,土体呈现线弹性状态的,而一旦应变稍大一些超过这一区域,应变则会是非线性的。因此,总体上而言在岩土体应变小于10-5的情况下,通常可认为是线弹性的。如何有效地对土体的基本弹性参数快速准确地确定对于土体变形预测等岩土工程问题十分重要。
1.2 土体小应变模量
土体的弹性参数主要包括剪切模量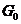 ,杨氏模量
,杨氏模量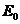 ,体积模量
,体积模量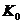 和侧限模量
和侧限模量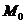 等,下式(1.1)为这些参数之间的关系:
等,下式(1.1)为这些参数之间的关系:
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: