深色有隔内生真菌Exophiala salmonis与纳米CuO的相互作用研究毕业论文
2020-02-17 09:02:34
摘 要
在现代科技飞速发展的同时,纳米材料的发展引起了全球范围内生物、物理化学、工业和农业等领域的重大变革。纳米材料独特的理化特性使其被广泛应用于人类社会生活的许多领域。作为使用最广泛的纳米材料之一,金属纳米材料进入环境后会经历分散团聚沉降、生物摄取累积等一系列变化,从而会对周围的生态系统产生负面影响。自然界中有许多微生物对纳米金属材料具有良好的抵抗性和富集特性,因此用微生物法治理纳米金属材料污染具有远大的前景。
深色有隔内生真菌(Dark Septate Endophytes, DSE)是一种定殖于植物根部且组成和生态学功能多样化的小型内生真菌,广泛分布于各种逆境胁迫的地区。本文以沙门外瓶柄霉(Exophiala salmonis)为试验菌种,以纳米CuO为污染物,研究了不同粒径(40和150 nm)的纳米CuO胁迫对沙门外瓶柄霉生长、营养代谢、抗氧化酶活性的影响,以及沙门外瓶柄霉对纳米CuO的吸附与富集特性,并取得如下结果:
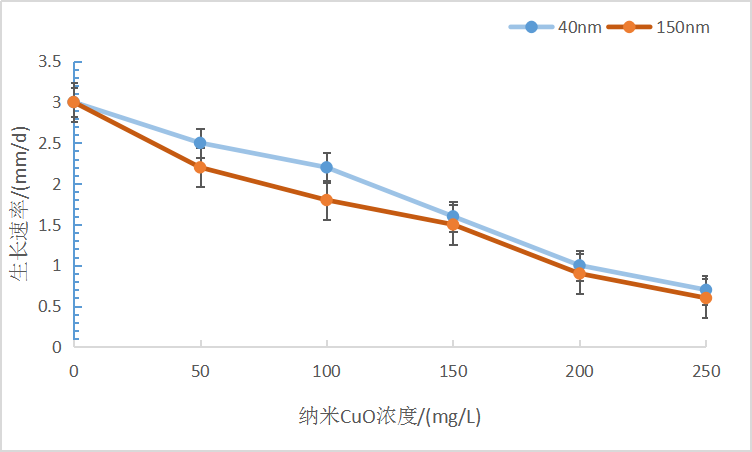
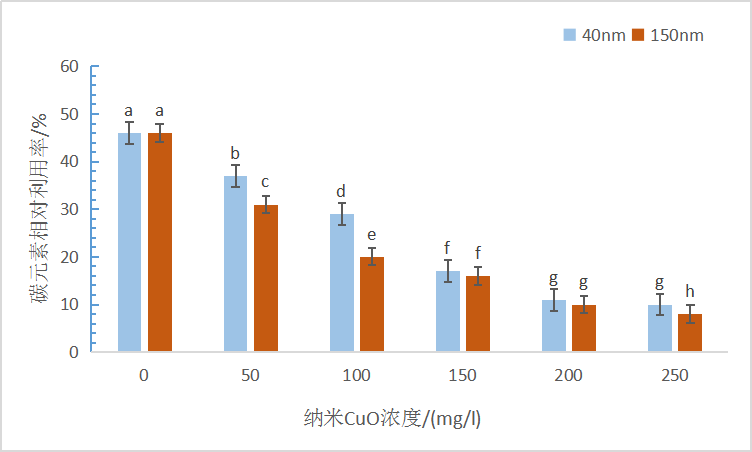
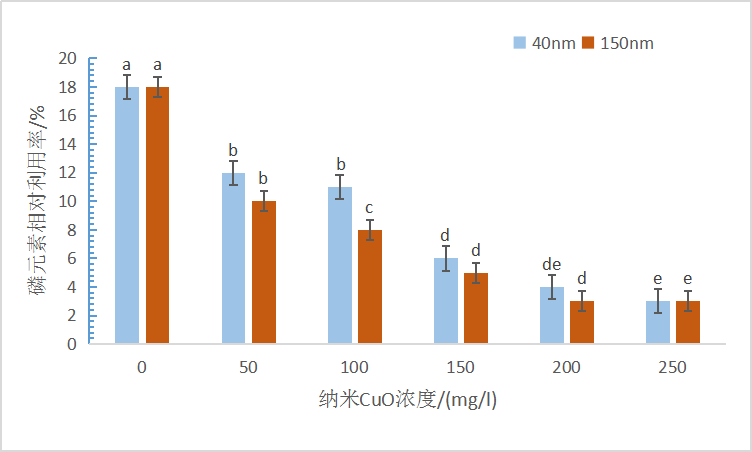
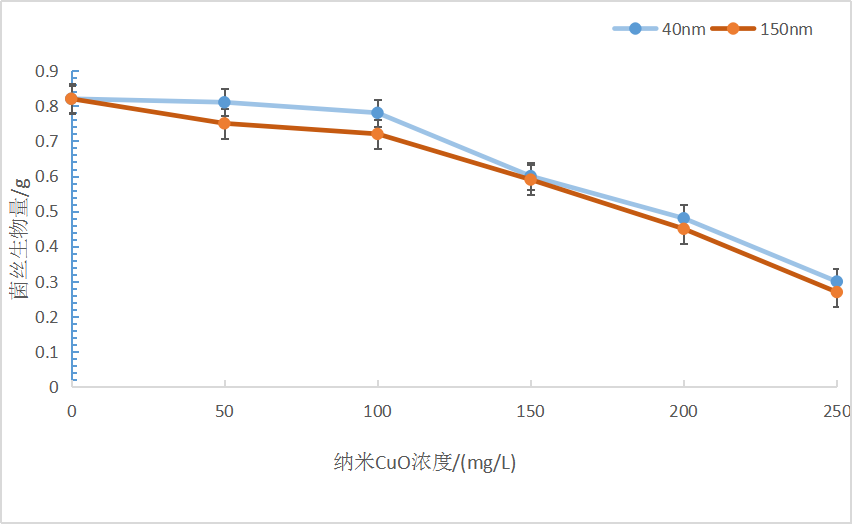
(1)沙门外瓶柄霉生长、碳、磷代谢和不同粒径纳米CuO浓度呈现显著相关性,在40 nm粒径的纳米CuO胁迫下,低浓度(10-100 mg/l)胁迫时沙门外瓶柄霉菌丝生长和碳磷利用受抑制程度不显著,高浓度(150-250 mg/l)胁迫时相比于对照受抑制程度显著(P<0.05);在150 nm粒径的纳米CuO胁迫下,低浓度(10-100 mg/l)和高浓度(150-250 mg/l)胁迫均显著抑制了沙门外瓶柄霉的生长(P<0.05)。
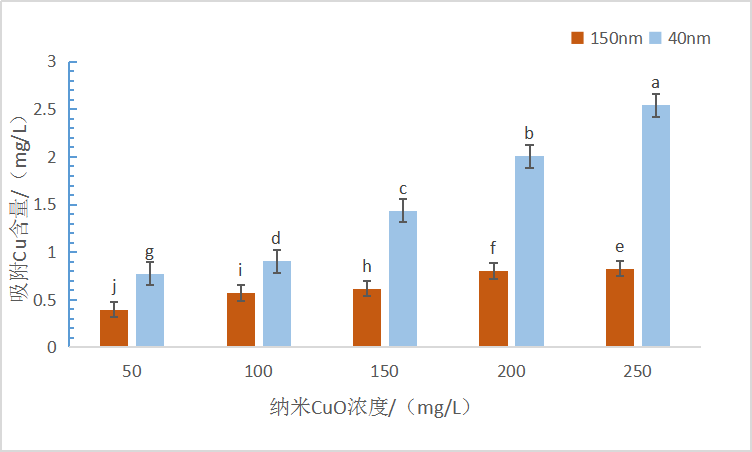
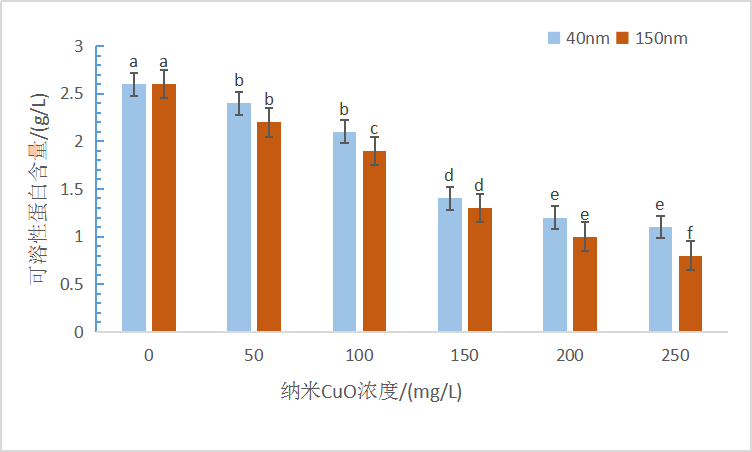
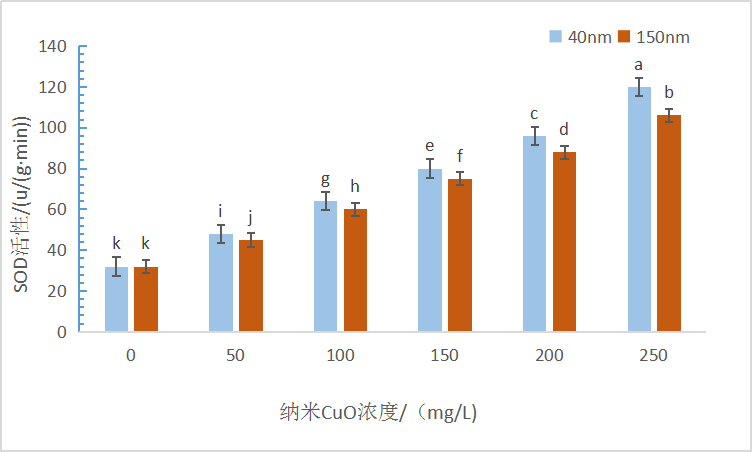
(2)高浓度(150-250 mg/l)的纳米CuO胁迫下,沙门外瓶柄霉可溶性蛋白含量减少,超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)、过氧化物酶(POD)和过氧化氢酶(CAT)活性随着纳米CuO浓度的增加而显著提高。相比于150 nm粒径,40 nm粒径的纳米CuO胁迫时沙门外瓶柄霉抗氧化酶活性更高,表明沙门外瓶柄霉对40 nm粒径的纳米CuO抗性更强。
以上研究结果表明,沙门外瓶柄霉对纳米CuO有较强的耐受能力,尤其对小粒径的纳米CuO抗性更强,而抗氧化酶活性的提高是沙门外瓶柄霉降低纳米CuO毒性的重要机制。
关键词:深色有隔内生真菌;沙门外瓶柄霉;纳米氧化铜;营养代谢;抗氧化酶
Abstract
With the rapid development of modern science and technology, the development of nanomaterials has caused significant changes in fields of biology, physical, chemistry, industry and agriculture all over the world. Nanomaterials are widely used in many fields of human social life because of their unique physical and chemical characteristics. As one of the most widely used nanomaterials, metal nanomaterials will undergo a serious of changes such as dispersion, agglomeration, sedimentation, biological uptake and accumulation after they are discharged into environment, thus result in negative effects on ecosystem around. Many microorganisms in nature have good resistance and enrichment characteristics to metal nanomaterials, therefore, there is a great prospect to treat metal nanomaterials pollution with the method of microbial remediation.
Dark septate endophytes (DSE) are one kind of small endophytic fungi with diverse composition and ecological functions, which are widely distributed in the roots at various of stressed habitats. In this study, the effects of nano-copper oxide with different particle sizes (40 and 150 nm) on the growth, nutrient metabolism and antioxidant enzyme activities of Exophiala salmonis were studied. In addition, the adsorption and enrichment characteristics of E. salmonis nano-copper oxide were also studied. The results obtained were listed as following:
- The growth and metabolisms (carbon and phosphorus) of E. salonis was significantly correlated with the concentrations of nano-copper oxide with different particle sizes. Under 40 nm nano-copper oxide stress, the mycelial growth, carbon and phosphorus utilization of E. salmonis were inhibited less under mild stress (10-100 mg/l) than under severe stress (150-250 mg/l). Under 150 nm nano-copper oxide stress, the mycelial growth, carbon and phosphorus utilization of E. salmonis were significantly (P<0.05) inhibited both at mild stress (10-100 mg/l) and severe stress (150-250 mg/l).
2)High concentration (150-250 mg/l) of nano-copper oxide significantly inhibited the growth of E. salmonis, resulting in the decrease of soluble protein content. The activities of superoxide dismutase, peroxidase and catalase increased significantly with the increase of nano-copper oxide concentration. Compared to 150 nm nano-copper oxide, the enzyme activities of E. salmonis under 40 nm nano-copper oxide stress increased significantly, which indicated that E. salmonis showed more resistance to 40 nm nano-copper oxide.
The above results show that E. salmonis has a strong tolerance to nano-copper oxide, especially to small-sized nano-copper oxide. The increase of antioxidant enzyme activities is an important mechanism of E. salmonis reducing the toxicity of nano-copper oxide.
Key words: dark septate endophytes, Exophiala salmonis, nano-copper oxide, nutritional metabolism, antioxidant enzymes
目 录
第一章 绪论..................................................................................................................................1
1.1金属纳米材料概述..............................................................................................................1
1.1.1 金属纳米材料定义.................................................................... .................................1
1.1.2 金属纳米材料的应用..................................................................................................1
1.1.3 金属纳米材料的危害与治理.......................................................................................1
1.2深色有隔内生真菌(DSE)的研究进展...........................................................................1
1.2.1 DSE的形态特征...........................................................................................................2
1.2.2 DSE的分布...................................................................................................................2
1.2.3 DSE的生态学功能.......................................................................................................2
1.3微生物对金属纳米污染物富集特性...................................................................................3
1.4微生物对金属纳米污染物的抗性机制...............................................................................3
1.5研究内容..............................................................................................................................3
第二章 纳米CuO对沙门外瓶柄霉生长及营养代谢的影响......................................................4
2.1 材料与方法.........................................................................................................................4
2.1.1 实验材料........................................................................................................................4
2.1.2 仪器设备........................................................................................................................4
2.1.3 沙门外瓶柄霉的生长曲线和生长速率测定................................................................4
2.1.4 沙门外瓶柄霉对碳、磷的相对利用率.........................................................................4
2.1.5 液体培养下沙门外瓶柄霉的生物量............................................................................6
2.1.6 数据统计方法................................................................................................................6
2.2 结果与讨论.........................................................................................................................6
2.2.1 纳米CuO胁迫对沙门外瓶柄霉的生长曲线和生长速率的影响................................6
2.2.2 纳米CuO胁迫对沙门外瓶柄霉碳、磷相对利用率的影响........................................9
2.2.3 纳米CuO胁迫对沙门外瓶柄霉的生物量积累的影响..............................................10
2.3 本章小结..........................................................................................................................11
第三章 沙门外瓶柄霉对纳米CuO的吸附作用及响应机制研究.........................................12 3.1 材料与方法.......................................................................................................................12
3.1.1 实验材料....................................................................................................................12
3.1.2 仪器设备....................................................................................................................12
3.1.3 沙门外瓶柄霉对Cu的吸附量..................................................................................12
3.1.4 沙门外瓶柄霉菌丝可溶性蛋白含量测定.................................................................12
3.1.5 沙门外瓶柄霉菌丝SOD活性测定............................................................................13
3.1.6 沙门外瓶柄霉菌丝CAT活性测定............................................................................14
3.1.7 沙门外瓶柄霉菌丝POD活性测定............................................................................14
3.1.8 数据统计方法............................................................................................................15
3.2 结果与讨论.......................................................................................................................15
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: