喷油控制策略对GDI发动机性能影响仿真分析毕业论文
2020-02-18 10:44:39
摘 要
缸内直喷式汽油机在功率和转矩方面所取得的效益,以及在降低油耗和有害物排放方面所存在的巨大潜力,使汽油机缸内直喷成为内燃机发展的必由之路。而内燃机喷油系统对内燃机的主要性能指标具有重要影响,故研究喷油控制策略对GDI发动机性能影响具有较好的理论意义和较强的工程应用价值。
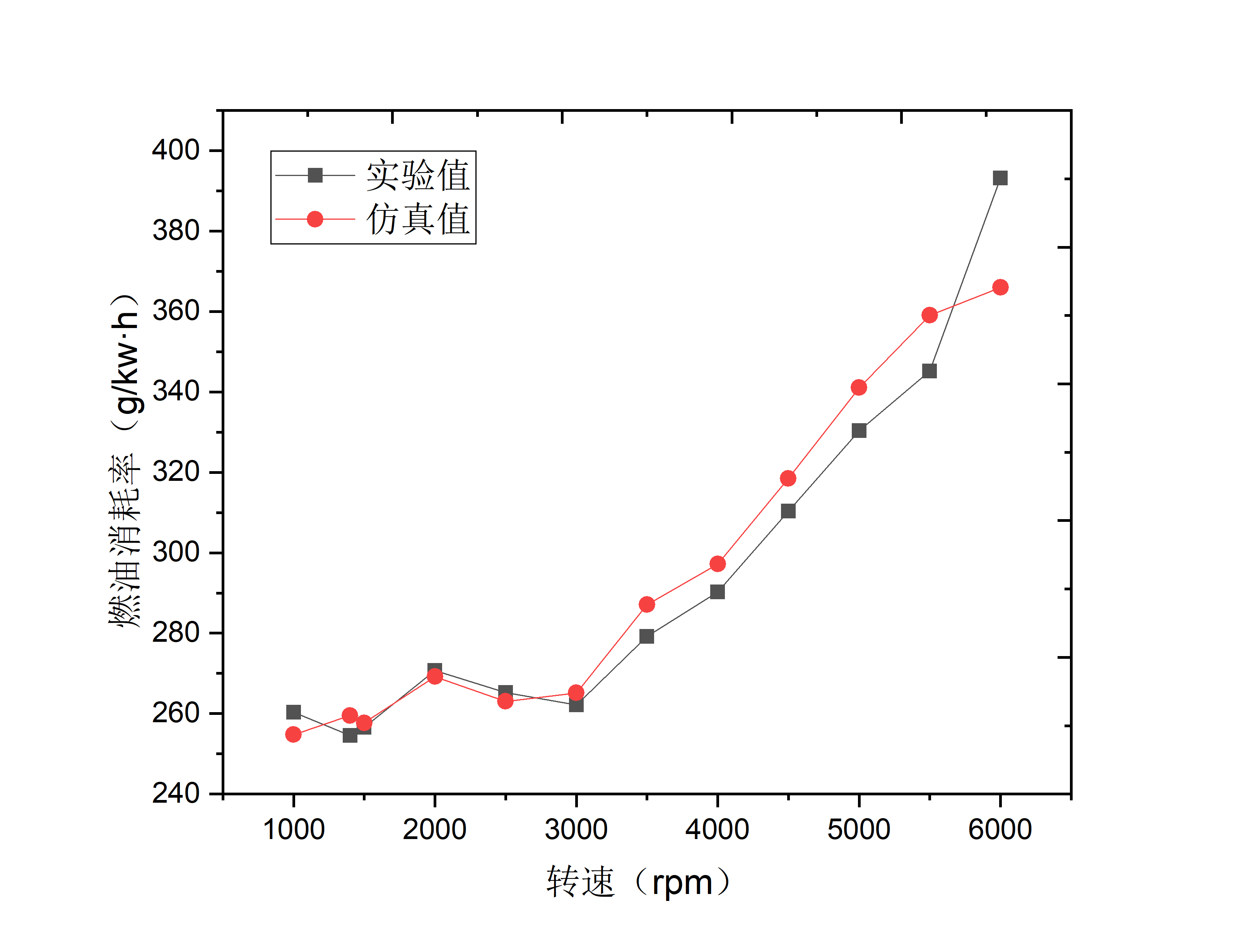
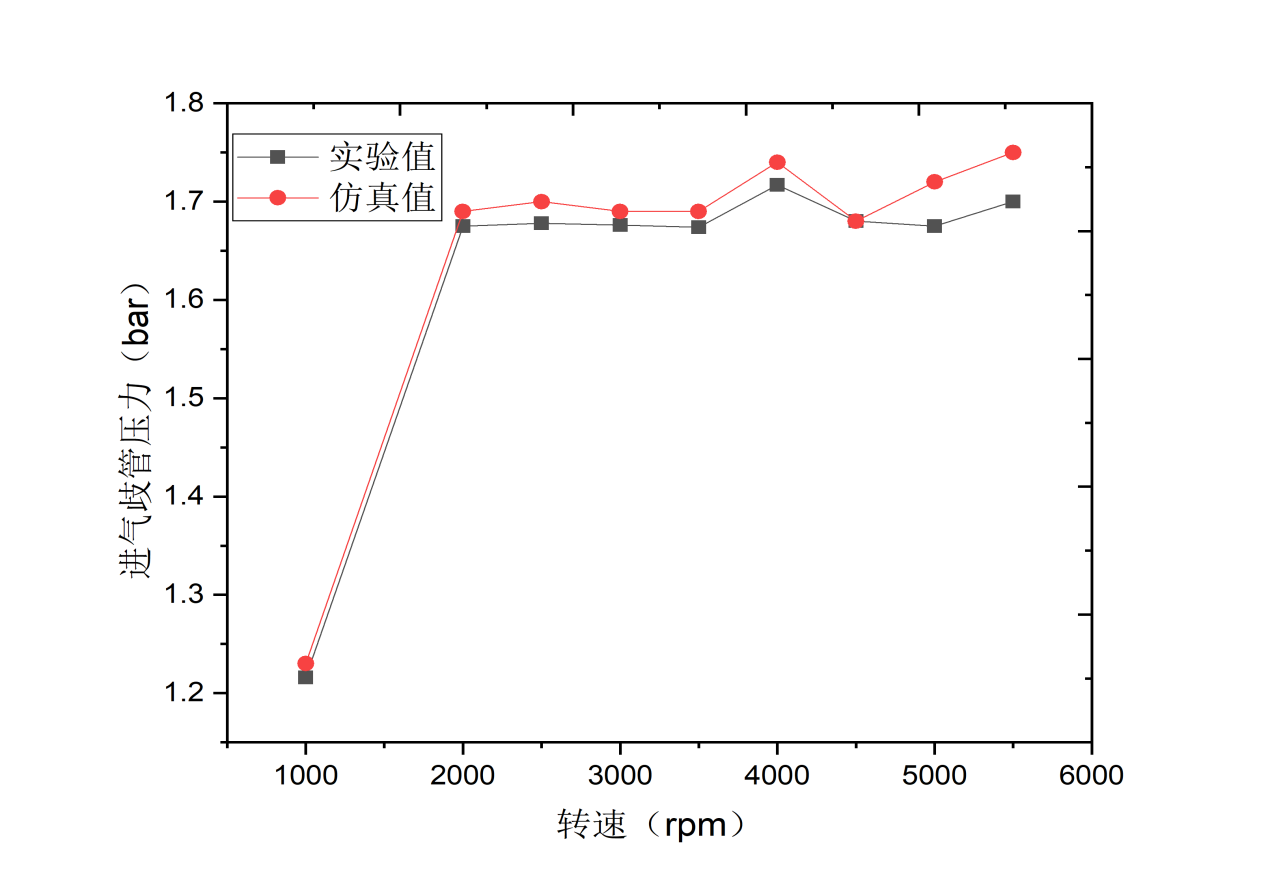
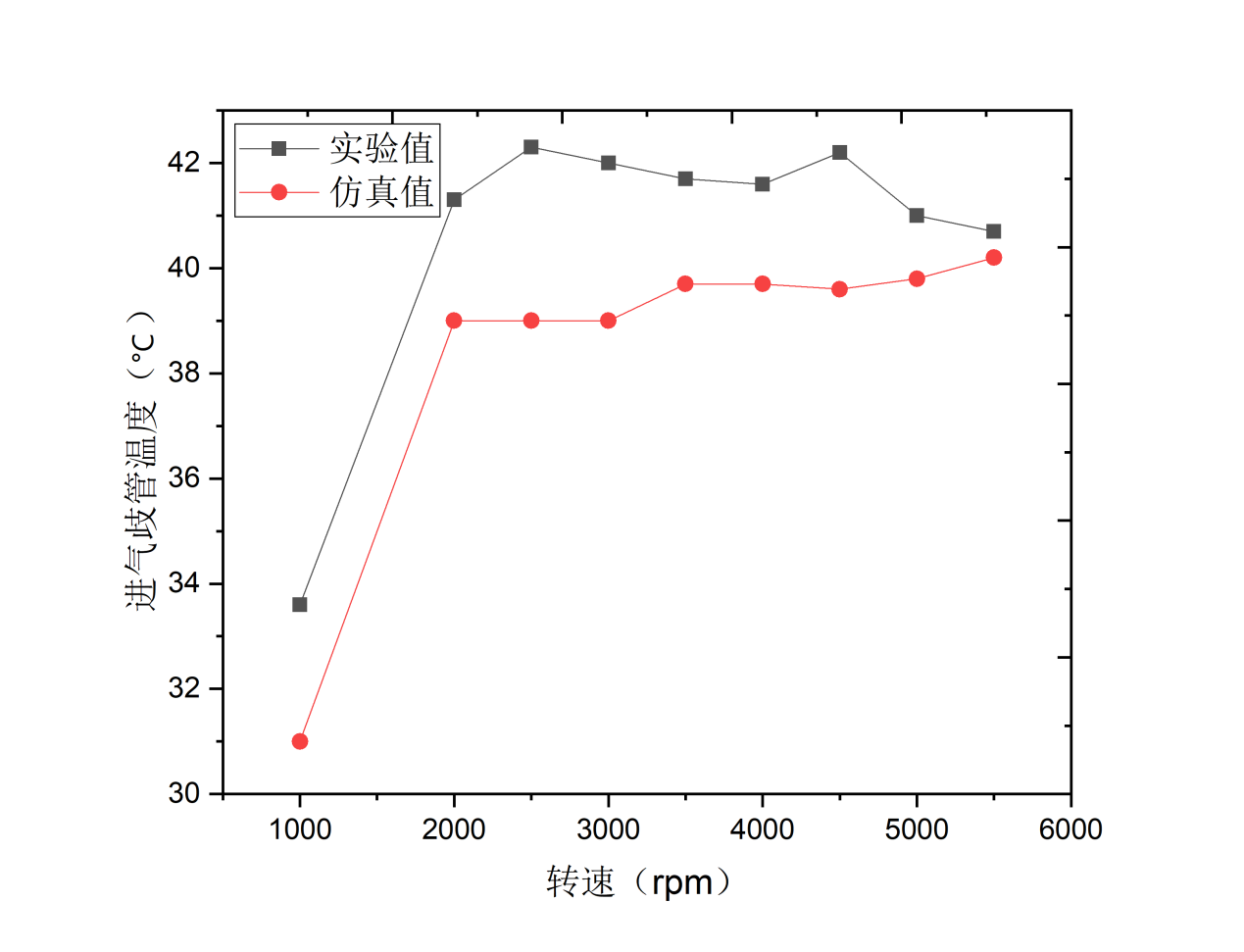
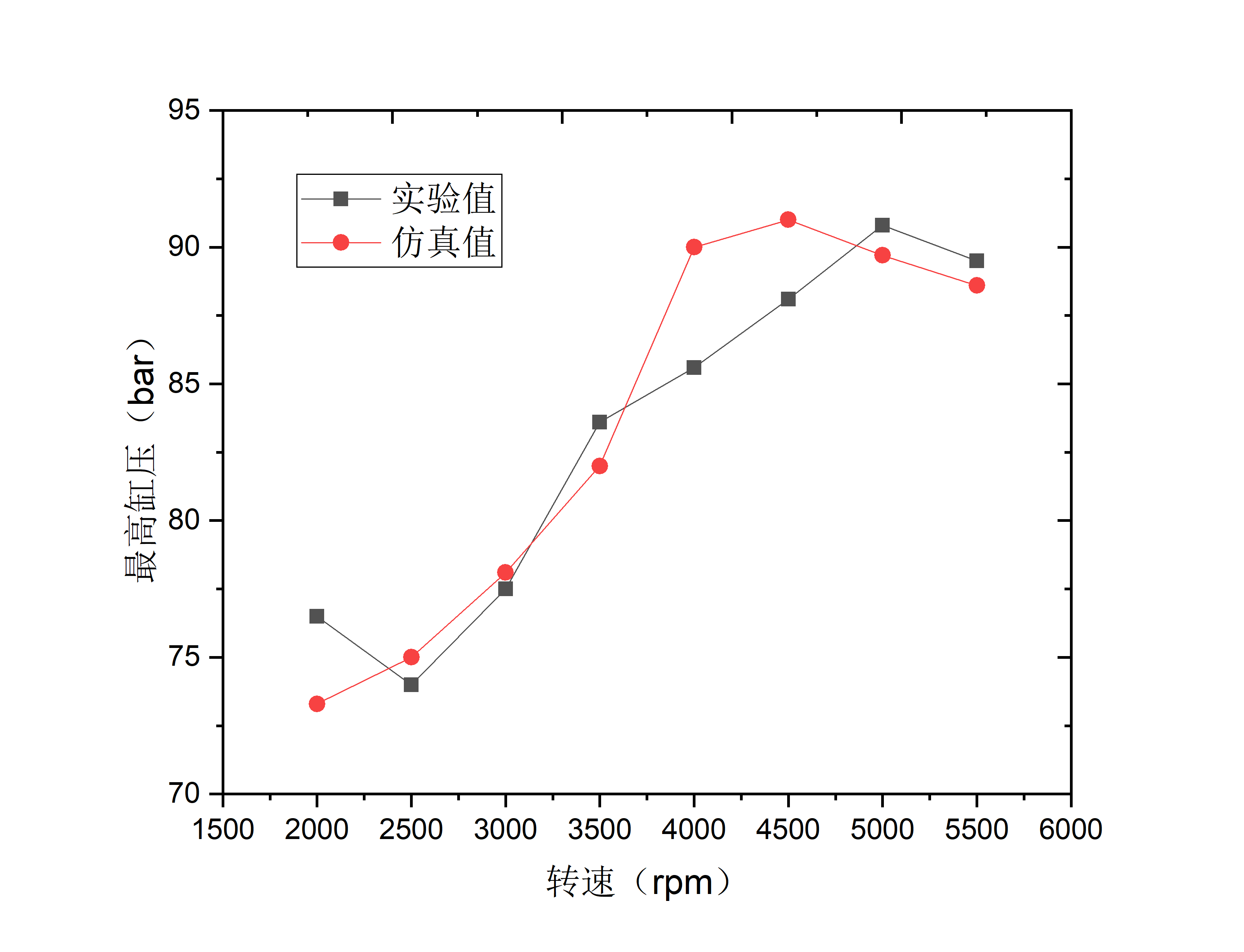
本文首先运用发动机工作过程模拟软件GT-Power建立某1.6T四缸GDI汽油机仿真计算模型,模拟计算结果与原机外特性试验数据基本吻合,大部分转速工况下误差在5%以内,证明了该模型有较高的精度,可用于GDI汽油机性能的研究。
其次分别对该GDI发动机的喷油正时、点火提前角及进气门正时对发动机性能的影响进行了研究,在得到了某一转速工况下的最佳喷油正时的基础上,据此开展点火提前角及进气门正时结合喷油正时对发动机性能影响的研究,结果表明:合适的喷油正时可以达到非常低的HC排放,在全转速工况下随着喷油正时的增大发动机的动力性、经济性及NOx和HC的排放均变好;而CO排放随着喷油正时的增大而增大;在给定的转速工况下,增大点火提前角可以使发动机获得更好的动力性、经济性和更低的CO及HC排放,但会使主要污染物NOx排放增加,说明推迟点火可以使最高燃烧温度降低,NOx的生成减少;同时也会使发动机排气温度升高影响发动机的动力性和经济性;而对于给定的转速工况,当进气门正时增大时,会对发动机的动力性、经济性及排放性造成不同程度的影响,使发动机远离了最佳状态。
最后通过正交试验的设计对发动机的喷油正时、点火提前角以及相位进气门正时的参数值进行模拟研究,并对性能较好的方案进行优化设计。通过模拟结果分析得知,随着转速升高,应加大进气门正时保证发动机的动力性处于高水平,其中在低转速工况下应选择较小的进气门正时角,在中高转速工况下应选择较大的进气门正时角;同时在合适的范围内增大点火提前角可以促使动力性及经济性提高,HC及CO排放减少。但增大点火提前角会使NOx排放增加,而推迟点火可以使发动机排气温度升高,使NOx的生成减少,同时也会有损于发动机的动力性和经济性。在1000r/min到5000r/min工况下优化后的模型有更好的性能,而对于高转速工况下,可采用优化后的模型以适当牺牲一定的动力性及经济性来满足发动机对于低排放的要求;也可采用优化前的模型维持发动机更好的动力性及经济性。
关键词:GDI发动机,喷油正时,单次喷射,排放,GT-power
Abstract
The benefits of in-cylinder direct injection gasoline engine in terms of power and torque, as well as the great potential in reducing fuel consumption and harmful emissions, make in-cylinder direct injection become the only way for the development of internal combustion engine. The injection system of internal combustion engine has an important influence on the main performance indexes of internal combustion engine, so it has good theoretical significance and strong engineering application value to study the effect of fuel injection control strategy on the performance of GDI engine.
In this paper, firstly, the simulation calculation model of a 1.6T four-cylinder GDI gasoline engine is established by using the engine working process simulation software GT-Power. The simulation results are in good agreement with the experimental data of the external characteristics of the original engine, and the error is less than 5% under most speed conditions. It is proved that the model has high accuracy and can be used to study the performance of GDI gasoline engine.
Secondly, the effects of injection timing, ignition advance angle and intake valve timing of the GDI engine on the engine performance are studied, and the optimal injection timing at a certain speed is obtained. Based on this, the effects of ignition advance angle and intake valve timing combined with fuel injection timing on engine performance are studied. the results show that the proper injection timing can achieve very low HC emission. Under the full speed condition, the power performance, economy and NOx and HC emissions of the engine become better with the increase of fuel injection timing, while the CO emission increases with the increase of fuel injection timing. Increasing the ignition advance angle can make the engine get better power, economy and lower CO and HC emissions, but it will increase the emission of the main pollutant NOx, indicating that delaying ignition can reduce the maximum combustion temperature and reduce the formation of NOx. At the same time, the increase of engine exhaust temperature will affect the power and economy of the engine, and for the given speed condition, when the inlet valve timing increases, it will have different effects on the power, economy and emission of the engine. Kept the engine away from its best condition.
Finally, through the orthogonal test design, the fuel injection timing, ignition advance angle and phase intake valve timing parameters of the engine are simulated, and the better performance scheme is optimized. Through the analysis of the simulation results, it is found that with the increase of the rotating speed, the intake valve timing should be increased to ensure that the power performance of the engine is at a high level, and a smaller intake valve timing angle should be selected at low speed. Under the condition of medium and high speed, the larger intake valve timing angle should be selected; at the same time, increasing the ignition advance angle in the appropriate range can improve the power and economy, and reduce the emissions of HC and CO. However, increasing the ignition advance angle will increase the NOx emission, and delaying the ignition can increase the engine exhaust temperature and reduce the formation of NOx. At the same time, it will also damage the power and economy of the engine. The optimized model has better performance under the condition of 1000r/min to 5000r/min, but under the condition of high speed, the optimized model can be used to meet the requirements of low emission of the engine at the appropriate sacrifice of power and economy. The pre-optimization model can also be used to maintain the better power performance and economy of the engine.
Keywords: GDI engine, Injection timing, Single injection, Emission, GT-power
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景和意义 1
1.2 国内外研究现状 1
1.3 主要研究内容 3
第2章 GDI发动机相关理论及GT模型的建立 4
2.1 GDI发动机相关理论 4
2.2 GDI发动机GT仿真模型的建立 4
2.3 本章小结 8
第3章 喷油控制策略对发动机性能的影响 9
3.1 喷油正时对GDI发动机性能的影响 9
3.1.1 喷油正时对GDI发动机动力性的影响 9
3.1.2 喷油正时对GDI发动机经济性的影响 12
3.1.3 喷油正时对GDI发动机排放性的影响 13
3.2 点火提前角对喷油正时及GDI发动机性能的影响 16
3.2.1 点火提前角对GDI发动机动力性的影响 16
3.2.2 点火提前角对GDI发动机经济性的影响 18
3.2.3 点火提前角对GDI发动机排放性的影响 19
3.3 进气门正时对喷油正时及GDI发动机性能的影响 21
3.3.1 进气门正时对GDI发动机动力性的影响 23
3.3.2 进气门正时对GDI发动机经济性的影响 23
3.3.3 进气门正时对GDI发动机排放性的影响 24
3.4 本章小结 26
第4章 GDI发动机喷油控制策略优化分析 27
4.1 正交试验设计方法 27
4.2 综合仿真及分析 28
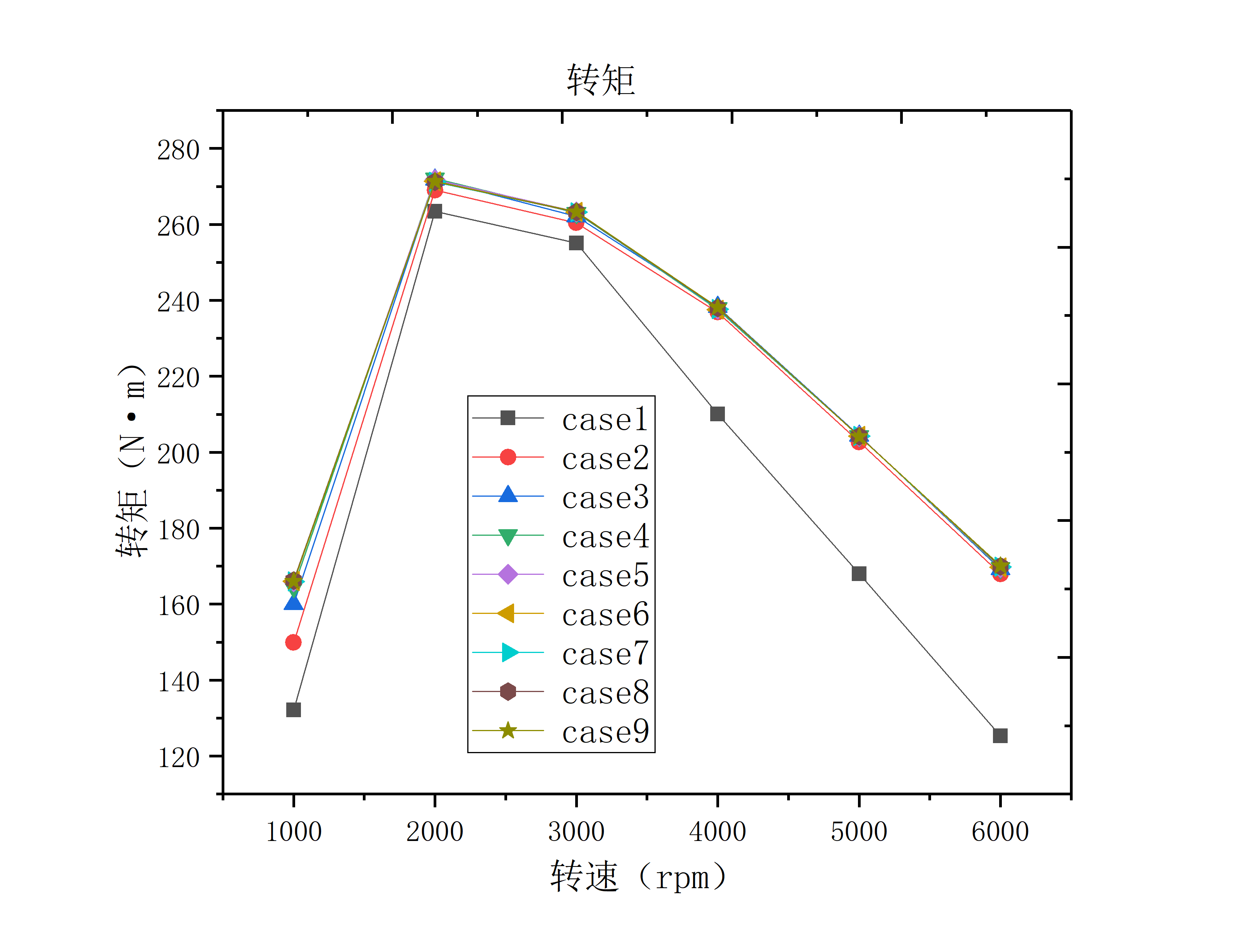
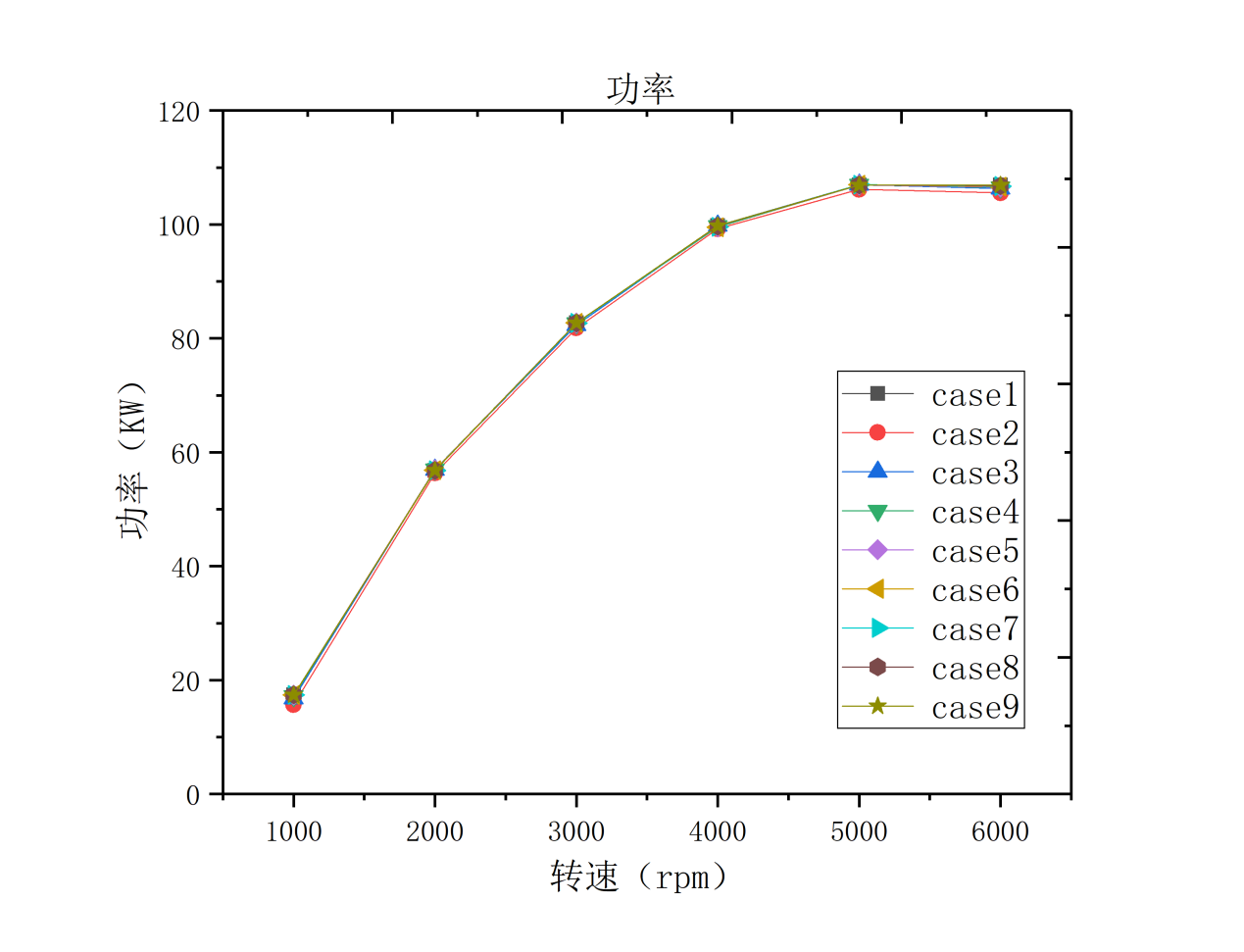
4.2.1 对发动机动力性仿真分析 28
4.2.2 对发动机经济性仿真分析 30
4.2.3 对发动机排放性仿真分析 30
4.3 优化前后发动机性能对比 33
4.4 本章小结 36
第5章 总结与展望 37
5.1 全文总结 37
5.2 研究展望 37
参考文献 38
致谢 40
第1章 绪论
1.1 研究背景和意义
近年来,随着汽车保有量急剧增长,化石能源危机与环境污染问题日益严峻,发展高效率低排放的内燃机已是大势所趋。汽油机作为乘用车的主要动力源,已成为内燃机研究的重点之一。为改善其燃油经济性、提高动力性,汽油缸内直喷技术得到广泛关注。与传统汽油机相比,缸内直喷汽油机(Gasoline Direct Injection)在同时保证动力性和燃油经济性方面有显著的优势,但所带来的颗粒物排放问题也不容忽视。根据不同乘用车发动机和后处理条件的试验结果表明,GDI汽油机的颗粒质量和数量显著高于PFI和带DPF的柴油车。颗粒物的排放与缸内直喷汽油混合气的形成密切相关,喷射时刻和喷油压力等喷射因素均会影响混合气的形成,尤其在喷油可调控范围大的低转速阶段,因此喷油策略对发动机的动力性、燃油经济性、排放性影响显著。
1.2 国内外研究现状
在喷油正时和喷油压力影响GDI发动机经济性和排放性方面,国内外学者做了大量工作:韩文艳[1]等采用AMESim和FIRE软件通过对某涡轮增压缸内直喷汽油机模拟,并借助发动机台架试验中获得的油耗、排放及燃烧数据,研究了喷油开始时刻对发动机性能的影响,得到了不同工况下最佳的喷油时刻。
黄雅卿[2]等采用CFD数值模拟和发动机台架试验相结合的方法,研究了不同的喷射时刻对直喷汽油机混合气形成和颗粒物排放的影响,结果表明:缸内直喷汽油喷雾碰壁形成油膜与颗粒物排放有着直接的关系;在小负荷和中等负荷工况下,喷射时刻的优化能够有效地降低颗粒物数量排放。
叶磊[3]等采用Matlab/Simulink与GT-FUEL联合仿真的方式验证了一种针对GDI发动机轨压控制复合策略的优越性。
钟兵[4]等在一台GDI汽油机上研究了部分负荷下喷油压力、喷油正时和过量空气系数对微粒的粒径分布特性和数量浓度排放的影响。
秦秋实[5]等利用CFD软件建立了缸内直喷(GDI)发动机的缸内分层燃烧过程三维模型,并通过仿真计算研究了喷油时刻与点火时刻对GDI发动机分层燃烧过程的影响,得出了给定工况下相对最佳的喷油、点火相位。
李旻[6]利用整车转鼓试验和发动机台架试验研究了缸内直喷汽油机(GDI)的主要控制参数对发动机颗粒物排放的影响,从而优化了缸内直喷发动机的整车颗粒物排放。
杜家坤[7]等试验研究了不同喷油时刻及喷油压力下的缸内燃烧及喷雾发展特性,分析了燃油喷射控制参数对直喷汽油机缸内喷雾及燃烧的影响规律。Miaomiao Zhang[8]等详细研究了不同工况下喷射正时和喷射压力对喷雾引导的GDI发动机的燃烧和颗粒的影响。
Chongming Wang[9]等在化学计量空燃比下单缸GDI发动机中研究了燃料(汽油与乙醇)和喷射系统(喷射压力和喷射条件)对颗粒排放的影响。
Pablo Santirso[10]等将1-D发动机仿真模型与SIMULINK结合,使用MATLAB将具有Lambert W功能的EOQ添加到模型中以研究GDI发动机的喷油控制策略。汽油喷射控制策略对发动机燃烧至关重要,喷油正时提前或推迟均可导致颗粒物排放增加;增大喷油压力,增大过量空气系数(采用较稀的混合气)等同样可减少颗粒物排放。
二次喷油策略是应用在车用发动机上的一种准均质稀燃技术,也是一种重要的喷油控制策略。国内外学者进行了二次喷射对GDI发动机性能影响的相关研究:陈雨阳[11]等研究了缸内直喷汽油机在不同二次喷射时刻条件下的颗粒物粒径分布特性,试验结果表明:低负荷下,合理优化二次喷油时刻可以降低颗粒物排放;中等负荷时,单次喷射的颗粒物排放远低于二次喷射。
韩文艳[12]等使用FIRE软件对直喷汽油机单段喷射和两段喷射策略进行研究,发现采用两段喷油策略可明显改善燃油碰壁情况。
G. Marseglia[13]等在单次和两次喷射下对GDI发动机进行协同实验和数值分析,同时利用FIRE软件进行模拟研究了不同喷射策略对GDI发动机中混合物形成和燃烧过程的影响。二次喷射较单次喷射相比燃油经济性排放性均更好,且可降低爆燃强度及燃油碰壁情况。
在喷油压力和喷油正时影响发动机爆震及燃油湿壁方面,国内学者完成了如下研究:韩立伟[14]等利用FIRE软件建立并模拟GDI发动机起动时第2缸的喷雾和混合气形成,分析了不同喷油策略下压缩上止点时混合气的空燃比分布和着火情况并指出了第二缸在不同喷油策略下发生自燃、可以点燃和失火的区域。
钱丁超[15]等使用CONVERGE软件建立了定容弹喷雾和发动机缸内流动喷雾的数值计算模型,分析了燃油喷射压力对啧雾贯穿距和索特平均直径及缸内湿壁现象的影响并使用段喷射策略对燃油湿壁问题进行改善。
贾志超[16]等制定了一种考虑发动机实际运行工况的超级爆震的试验测试程序,研究在扫气条件下燃油策略对超级爆震抑制作用及对发动机经济性和排放性的影响。
Lei Zhou[17]等通过实验方法研究了延迟喷射正时对汽油发动机的爆震阻力和循环变化的影响。结果表明:适当降低喷油压力、推迟燃油喷射角可缓解燃油湿壁问题;采用二次喷射、延迟喷油正时可抑制爆震。
1.3 主要研究内容
本次研究利用GT-POWER软件建立GDI发动机模型,完成单次喷射下喷油正时、点火提前角及进气门正时等策略对GDI发动机动力性、经济性、排放性能的影响;调整喷油控制,优化发动机的动力性、经济性、排放性能。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: