CMT和TIG工艺增材制造TC4钛合金组织与性能的研究毕业论文
2020-04-23 20:13:58
摘 要
电弧增材制造是使用焊接当中所产生的电弧热,并使用层层熔化覆盖的方法,通过不断添加焊丝,并且利用设计好的程序控制路径自下而上逐层沉积出金属零件的一种先进数字化制造技术。通过此技术产出的钛合金材料在航空航天以及船舶等领域有着广泛的利用。
此次研究的主要内容是通过CMT与TIG工艺增材制造TC4钛合金,研究这两种焊接工艺的3D打印试样的组织与性能间的差异。首先,经过对TC4钛合金工艺参数的优化,得到了合适的打印参数:TIG打印工艺,送丝速度为2.0m/min,扫描速度为0.008m/s,焊接电流为180A,熔宽7.5mm,熔高1.1mm;CMT打印工艺,送丝速度8.0m/min,扫描速度0.008m/s,熔宽8.5mm,熔高1.5mm。同时为了改善材料内部组织,设计出了三种不同的热处理工艺为:800℃普通退火 空冷,800℃普通退火 炉冷,950℃固溶 550℃时效 空冷。
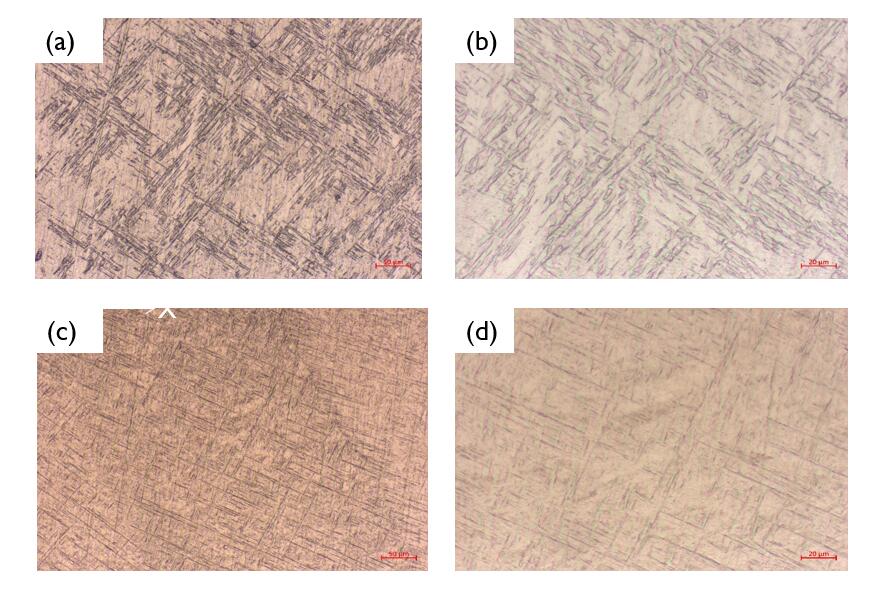
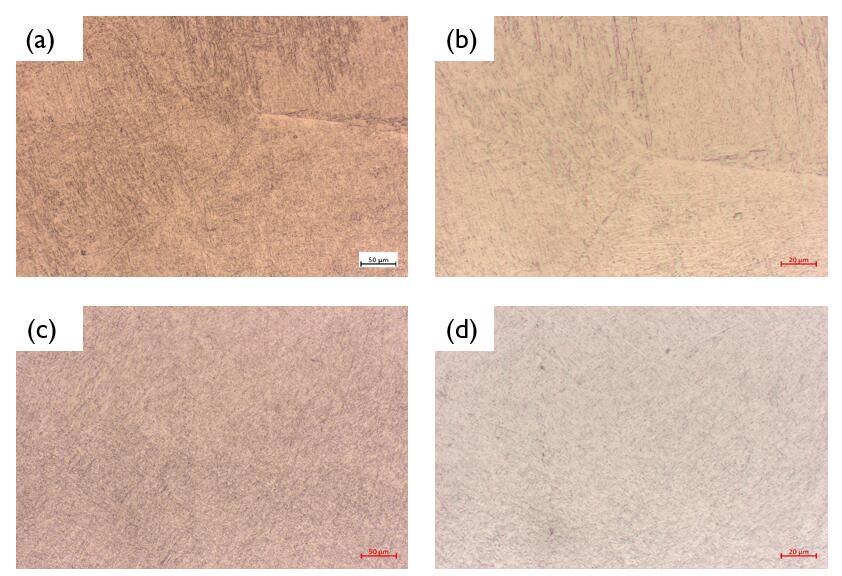
其次,对比研究CMT与TIG两种不同工艺的电弧增材制造试样的金相显微组织。经过研究分析表明:通过CMT与TIG两种焊接工艺打印出来试样的微观组织均表现为细小的网篮状组织;当经过固溶强化的处理后,通过CMT与TIG两种工艺打印试样的显微组织转变为了粗大的网篮状组织;当对打印试样进行退火处理后,再次观察出的试样的网篮组织会转变得细小;对比分析两种打印工艺试样的显微组织,可知TIG工艺打印出的试样使用TIG工艺所打印的试样的针状α组织会比使用CMT工艺所打印出的试样更多,其网篮组织更加致密一些,整体组织相对均匀一些。
最后对比分析了CMT与TIG两种不同工艺的电弧增材制造TC4钛合金的显微硬度及力学性能。硬度分析显示:使用TIG工艺增材制造出的试样硬度明显高于使用CMT工艺增材制造出的样品硬度,通过退火处理会降低试样的硬度,通过固溶时效处理后可以增加试样的硬度。拉伸性能分析表明:经热处理后,试样延伸率提高,塑性得到改善;退火使得试样强度提高,而固溶强化会使强度降低;TIG工艺得到的试样的拉伸性能普遍高于CMT工艺。
关键词:电弧增材制造;TC4钛合金;TIG与CMT;显微组织;力学性能;显微硬度
Study on Microstructure and Properties of TC4 Titanium Alloy Made by CMT and TIG Additions
Abstract
Arc augmentation manufacturing is an advanced digital manufacturing technology, which uses arc heat generated during welding and layer by layer melting and covering method to deposit metal parts from bottom to top by continuously adding welding wire and using the designed program control path.
The main content of this study is to study the differences in the microstructure and properties of 3D printed samples of TC4 titanium alloy manufactured by CMT and TIG process additive. Firstly, by optimizing the process parameters of TC4 titanium alloy, the suitable combination of printing process parameters was obtained: TIG printing process, wire feeding speed of 2.0m/min, scanning speed of 0.008m/s, welding current of 180A, welding width of 7.5mm, welding height of 1.1mm; CMT printing process, wire feeding speed of 8.0m/min, scanning speed of 0.008m/s, fusion width of 8.5mm and fusion height of 1.5mm. Meanwhile, in order to improve the internal structure of the material, three different heat treatment processes were designed: ordinary annealing at 800 plus air cooling, ordinary annealing at 800 plus furnace cooling, solution aging at 950 and air cooling at 550.
Secondly, the metallographic structure of arc-strengthened specimens using CMT and TIG processes was compared. The results show that the microstructures of the samples printed by CMT and TIG welding processes are fine net basket structure; after solution strengthening treatment, the microstructures of the samples printed by CMT and TIG process become coarse net basket structure. The RE of the sample observed again will change. By comparing and analyzing the microstructures of two kinds of printing process samples, it can be concluded that the needle-like alpha structure of TIG process printing samples is denser and more uniform than that of CMT process printing samples.
Finally, the microhardness and mechanical properties of TC4 titanium alloy manufactured by arc augmentation with CMT and TIG were compared and analyzed. The hardness of the samples will be reduced by annealing treatment, and the hardness of the samples can be increased by solution aging treatment. Tensile properties show that after heat treatment, the elongation and plasticity of the samples are improved, the strength of the samples after annealing is increased, and the strength after solution strengthening is decreased. the tensile properties of the samples obtained by TIG process are generally higher than those obtained by CMT process.
Key words: Arc augmentation manufacturing; TIG and CMT; TC4 titanium alloy; Microstructure; mechanical property; Microhardness
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1本课题研究的目的及意义 1
1.2 钛合金 2
1.2.1 钛合金及钛 2
1.2.2 钛合金常见分类 2
1.2.3 TC4钛合金 3
1.3 增材制造技术简述 3
1.3.1 增材制造技术 3
1.3.2 金属增材制造技术分类 3
1.3.3电弧增材制造发展 4
1.4 CMT工艺与TIG工艺 5
1.4.1 CMT工艺概述 5
1.4.2 TIG工艺概述 6
1.5 本课题研究内容 7
第二章 实验准备与研究方法 8
2.1 本章内容概述 8
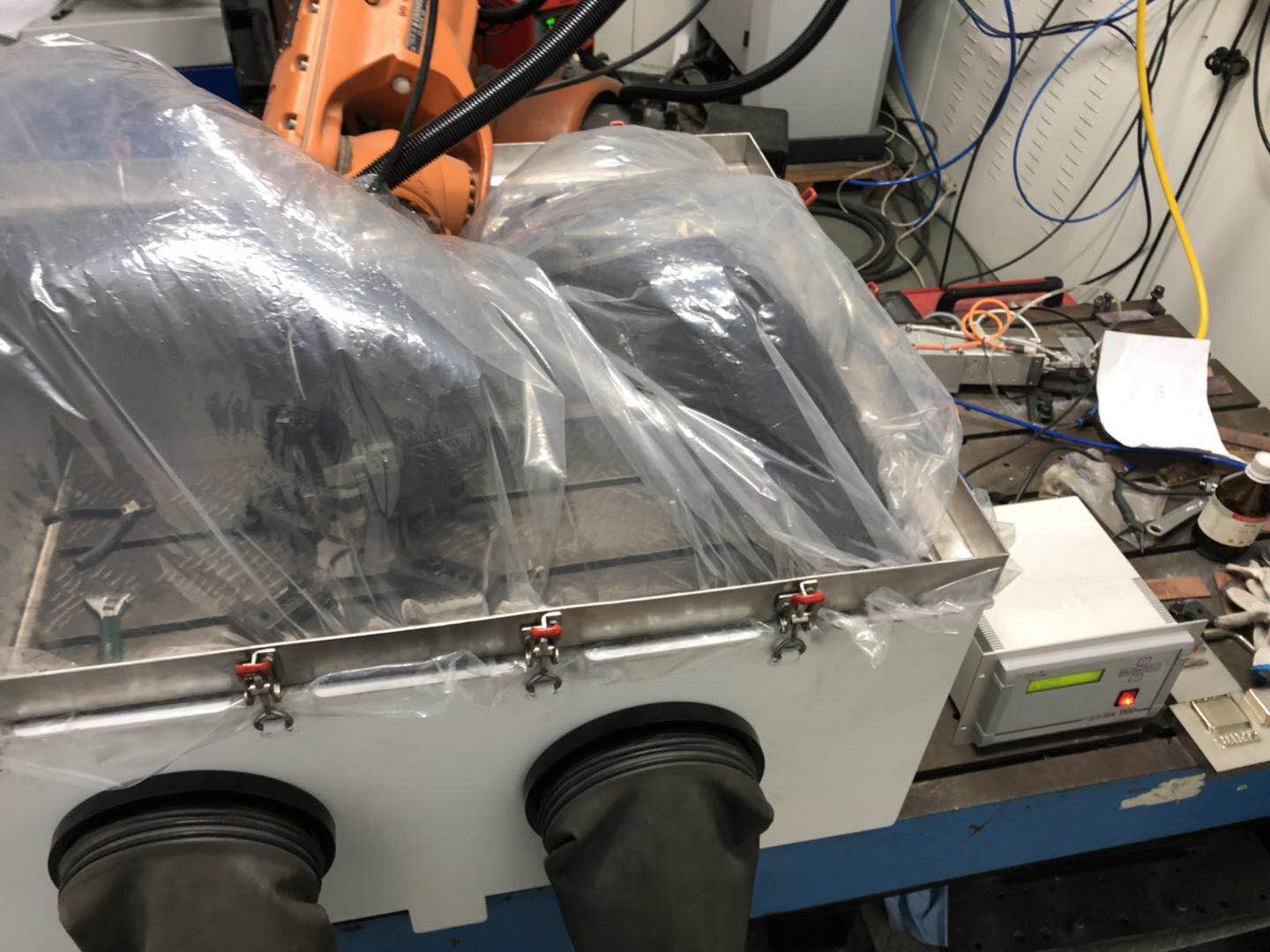
2.2 实验材料与设备简介 8
2.2.1实验材料准备 8
2.2.2 实验设备 8
2.3 实验研究方法 10
2.3.1 实验过程设计及打印工艺参数设置 10
2.3.2 热处理工艺研究 11
2.3.3 力学性能研究 11
2.3.4 TC4钛合金的显微组织研究 12
第三章 实验分析 13
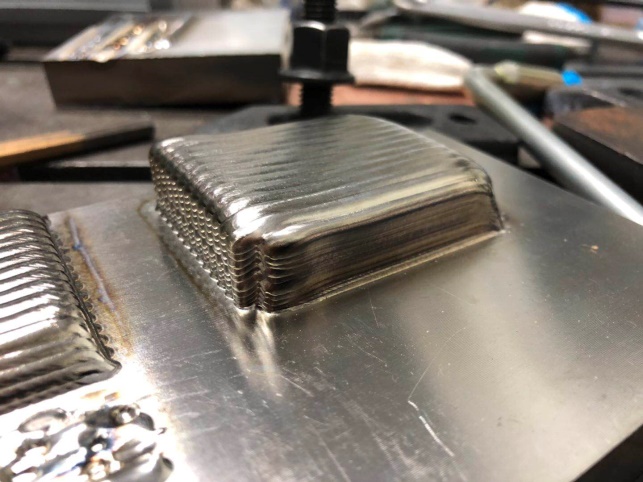
3.1 TIG与CMT电弧增材制造成形工艺研究 13
3.1.1 单道成形及搭接率试验 13
3.1.2 路径规划 13
3.2 TIG与CMT增材制造TC4钛合金显微组织分析 14
3.2.1 沉积态TC4显微组织分析 14
3.2.2 800℃退火 空冷后的TC4钛合金显微组织分析 14
3.2.3 800℃退火 炉冷后的TC4钛合金显微组织分析 15
3.2.4 950℃固溶时效后的TC4钛合金显微组织分析 16
3.3 CMT与TIG增材制造TC4钛合金的硬度分析 17
3.3.1 TIG工艺下不同热处理试样硬度分析 17
3.3.2 CMT工艺下不同热处理试样硬度分析 18
3.3.3 CMT与TIG工艺打印的样品硬度对比分析 19
3.4 CMT与TIG增材制造TC4钛合金拉伸性能分析 20
3.4.1 TIG工艺打印试样的拉伸性能 20
3.4.2 CMT工艺打印试样的拉伸性能 20
3.4.3 TIG工艺打印试样的拉伸断口 21
结论 23
致谢 25
参考文献 26
第一章 绪论
1.1本课题研究的目的及意义
增材制造是一种通过预先编写好的设计打印路径程序而控制打印路径,从而使用一层层添材的方式进行零件制造的技术,实际上就是一种从下而上的材料累积制造方式[1]。经过论文查阅,可以发现经过过去40年来的发展,增材制造技术取得了许多显著的成果,并且广泛应用于工艺生产当中。美国政府早在2012年就提出了该计划,而且还设立了许多增材制造研究中心。紧随其后的欧洲各个国家也建立了自己的增材制造研究中心,在此方面,我国也力争上游,在增材制造技术发展规划上拟定自己的路线图,在各地区频繁的进行展会和研讨会[2]。
随着当今社会的发展进步,新技术、新材料、新工艺不断涌现,作为现阶段一种新的、实用的材料成形技术,增材制造技术将会在制造领域发挥重要作用。增材制造技术变革了传统的机械加工减量成形和锻造等量成形模式, 该技术在制造加工比较复杂的高性能零件中有广泛的应用[3]。
相关图片展示: