双轴载荷下含I-II复合型裂纹CS试样的断裂行为研究毕业论文
2020-04-15 17:39:43
摘 要
工程结构中的缺陷或裂纹往往以复合型方式存在。众多学者对Ⅰ型及Ⅰ-Ⅱ复合型断裂问题展开了广泛深入的研究,为将Ⅰ型及复合型断裂研究成果应用于工程实际中奠定了基础。然而现有的研究成果依然存在不足,无法满足工程需要。因此,为了提供给工程应用更多的参考依据,以及为了Ⅰ-Ⅱ复合型断裂研究进一步的发展,本文通过理论分析以及有限元模拟,对含Ⅰ-Ⅱ复合型裂纹CS试样的断裂行为等问题开展深入的研究和探讨。主要研究工作及成果如下:
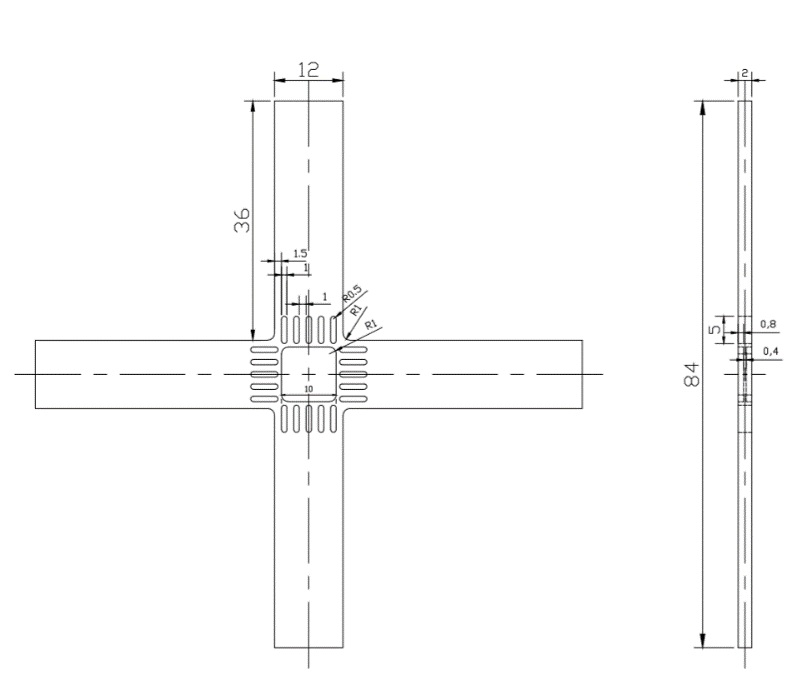
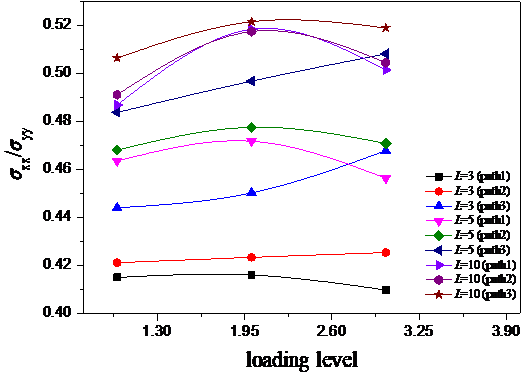
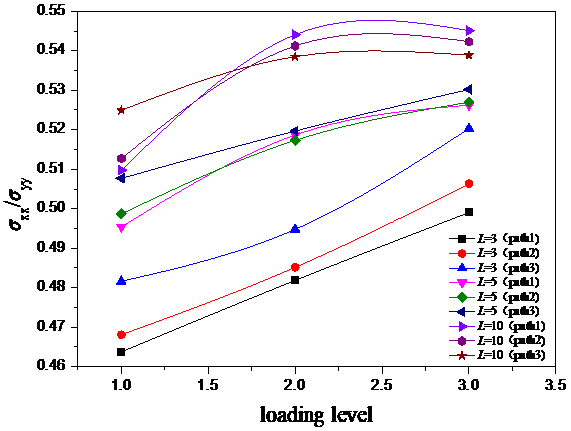
(1)通过有限元方法对无裂纹十字形试样进行了一系列的分析。研究表明:开槽数目及长度对试样中心测试区的应力比有影响。当开槽数目固定时,应力比随槽长的增加而增加;开槽长度一定时,应力比随开槽数目的增加而增加。随着路径的外移应力比逐渐增加。通过计算分析可得到,当槽数为5,槽长为5mm时,中心测试区应力比最接近理论值0.5。
(2)通过理论分析及有限元计算对双轴载荷作用下含Ⅰ-Ⅱ复合型裂纹CS试样裂尖的断裂参数进行了一系列的研究。研究表明线弹性模型数值解与理论解较吻合。T应力值和加载比例系数呈线性关系。在裂纹角0~30°,T应力的值为负,值随裂纹角增加逐渐增加;β=45°时,T应力的值恒等于0;裂纹角60~90°时,T应力的值为正,并且随裂纹角增大逐渐减小。J积分的值随着比例系数的增加逐渐增加,变化幅度随着裂纹角度的增加而增加。
(3)通过有限元方法对含中心裂纹CS试样裂尖J积分、应力三轴度h以及裂尖应力场进行了一系列的分析。研究表明当试样裂尖发生大范围塑性变形时,线弹性断裂理论不再适用。当β=90°时,各试样裂尖J积分随着加载比例的增加逐渐减小。当βlt;90°时,各试样裂尖J积分随着加载比例的增加逐渐增加。相同加载角度下,J积分随着裂纹倾斜角度的减小逐渐增加。当加载比例较小时,应力三轴度随着裂纹倾斜角的增加先减小后增加。当加载比例较大时,应力三轴度随着裂纹倾斜角的减小逐渐增大(除β=0°和15°以外)。应力三轴度随着加载比例的增加逐渐增加(除β=0°和15°以外)。此外,等轴加载作用下,各试样应力三轴度相同,与裂纹倾斜角无关。
关键词: I-II复合型裂纹 有限元 J积分 T应力 拘束度
Abstract
Defects or cracks in engineering structures often exist in a composite mode. Many scholars have carried out extensive and in-depth research on type I and I-II mixed mode fracture, which laid a foundation for applying the research results of type I and composite fracture to engineering practice. However, the existing research results are still insufficient to fulfill the needs of the project. Therefore, in order to provide more references for engineering applications, and to further develop the study of I-II mixed mode fracture, the fracture behavior of CS specimens with I-II mixed mode cracks has been deeply studied and discussed in this paper through theoretical analysis and finite element simulation. The main research work and achievements are as follows:
(1) A series of analysis of crack-free cruciform specimens were carried out by finite element method. The results show that the number and length of grooves have an effect on the stress ratio in the central test area of CS specimens. When the number of slots is fixed, the stress ratio increases with the increase of slot length, and when the slot length is fixed, the stress ratio increases with the increase of slot number. With the outward displacement of the path,the stress ratio increases. Through the calculation and analysis, when the number of grooves is 5 and the length of grooves is 5 mm, the stress ratio in the central test area is the closest to the theoretical value of 0.5.
(2) The fracture parameters of the crack tip of CS specimens with mixed mode I-II cracks under biaxial loading were studied by theoretical analysis and finite element calculation. The results show that the numerical solution of the linear elastic model is in good agreement with the theoretical solution. T-stress value has a linear relationship with biaxial loading ratio λ. When the crack angle is 0°and 30°,the value of T-stress is negative. The value of T-stress increases gradually with the gain of the crack angle; when the crack angle is 45°, the value of T-stress is equal to 0; and the value of T-stress is positive when the crack angle is 60°and 90°. The value of T-stress falls gradually with the increase of the crack angle. The value of J-integral increases with the growth of biaxial loading ratio λ,and the range of variation increases with the raising of crack angle.
(3) The J-integral, stress triaxiality h and stress field at the crack tip of CS specimens with a central crack are analyzed by finite element method. The results show that the linear elastic fracture theory is no longer applicable when the crack tip of the specimen undergoes large-scale plastic deformation. The J-integral of crack tip decreases with the growth of loading ratio when the value of β=90°. The J-integral of crack tip enhances gradually with the increase of loading ratio when βlt;90°. At the same loading angle, J-integral increases with the loss of crack inclination angle. When the loading ratio is small, the stress triaxiality first falls off and then gains with the increase of the crack inclination angle. When the loading ratio is large, the stress triaxiality increases with the reduction of the inclination angle of the crack (except for β=0°and 15°). The stress triaxiality increases with the growth of loading ratio (except for β=0°and 15°). In addition, the stress triaxiality of each specimen is the same under equiaxed loading, which is independent of the crack inclination angle.
Key words: mixed mode I-II crack;finite element;J-integral;T- stress;constraint
目录
摘要 I
Abstract III
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 课题背景及研究意义 1
1.2 I型裂纹问题研究现状 2
1.3 I-II复合型裂纹问题研究现状 3
1.4双轴载荷断裂研究现状 4
1.5研究内容及方法 5
第二章 双轴载荷CS试样的设计 7
2.1 引言 7
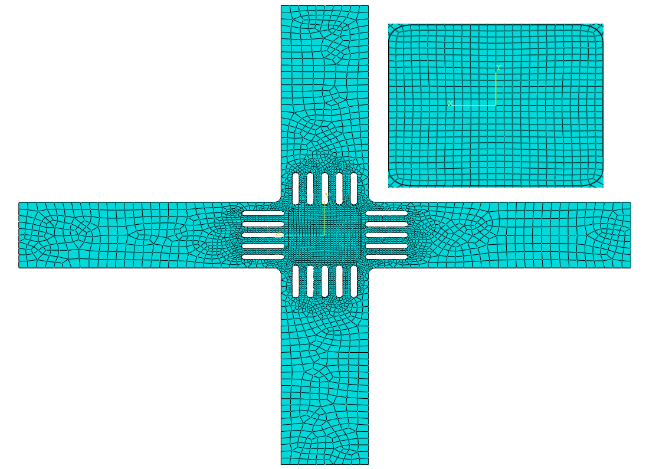
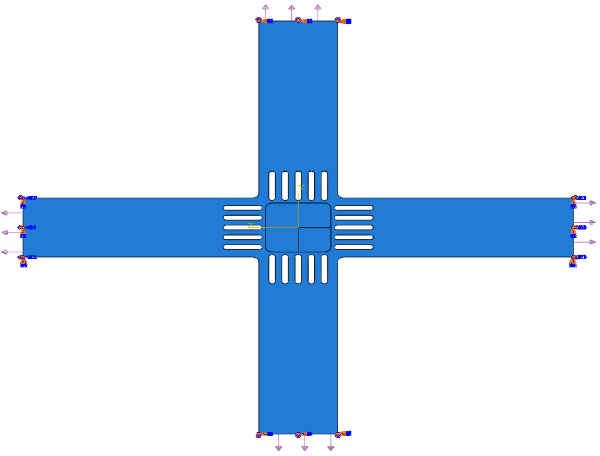
2.2有限元模型 7
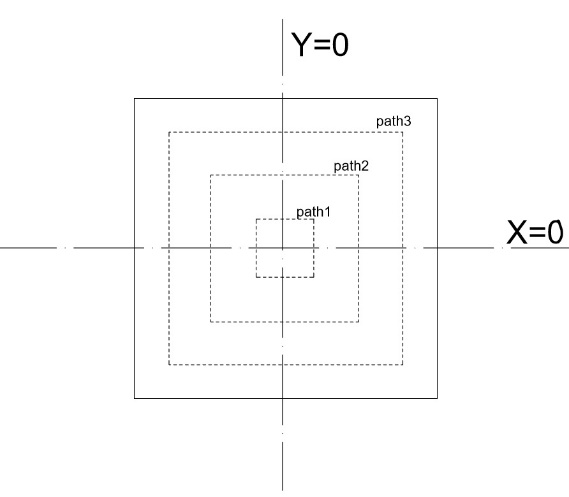
2.3不同因素对中心测试区应力比的影响 10
2.3.1开槽长度的影响 10
2.3.2开槽数目的影响 12
2.4 小结 14
第三章 双轴载荷作用下含I-II复合型裂纹CS试样线弹性断裂行为研究 15
3.1引言 15
3.2有限元模拟 15
3.3含中心裂纹CS试样T应力分析 17
3.3.1 T应力理论解 17
3.3.2 T应力有限元解 18
3.4含中心裂纹CS试样J积分分析 18
3.4.1 J积分理论解 18
3.4.2 J积分模型解 20
3.5含中心裂纹CS试样应力场分析 21
3.6小结 25
第四章 双轴载荷作用下含I-II复合型裂纹CS试样弹塑性断裂行为研究 27
4.1引言 27
4.2有限元模型 27
4.3含中心裂纹CS试样的J积分分析 27
4.4 含中心裂纹CS试样的拘束度分析 28
4.4.1拘束度参数 28
4.4.2 计算结果 29
4.5含中心裂纹CS试样应力场分析 35
4.6 CS试样线弹性及弹塑性断裂参数对比分析 38
4.7 小结 39
第五章 总结与展望 40
5.1 结论 40
5.2 后续工作展望 41
参考文献 42
致谢 46
第一章 绪论
1.1 课题背景及研究意义
承压设备(压力容器和压力管道)在工业经济发展中发挥着重要作用,随着工业技术的不断革新,压力容器也逐渐向大型化发展。在压力容器制造过程中,不可避免的会出现质量问题,裂纹问题是其中重要的一个方面。任何工程材料和构件都会存在裂纹或者类似缺陷,它们可能是材料本身固有的,也有可能是在加工制造过程中及后续使用过程产生的。压力容器常用的各种钢材、钛材及其他金属,都会存在初始的宏观裂纹、微裂纹、微缺陷及其他形式的初始损伤,对容器的制造和使用都会产生影响。压力容器的服役工况较复杂(除了受到与壁面垂直的内外压力外,不同地方的压力容器会受到不同的环境影响,例如风载荷、地震载荷以及温度变化等),在这些作用下,材料所带有的初始宏观裂纹和微缺陷会发展、演化,进而形成断裂。材料的断裂会导致结构产生应力集中,强度下降,会导致承压设备的失效,进一步影响设备的安全可靠性及使用寿命。2016年,全国发生特种设备事故和相关事故233起,死亡269人,受伤140人,与2015年相比,事故起数降低9.34%,死亡人数降低3.24%。按设备类别来划分,锅炉事故17起,压力容器事故14起[1]。安全事故一旦发生,财产损失会高达上亿元。因而,对压力容器及压力管道生产过程、结构技术的安全可靠性要求越来越高,对压力容器的断裂行为进行深入研究是很有必要的。
为了研究含裂纹结构的力学性质和强度特点,在宏观材料力学、弹性力学以及结构力学基础上逐步建立和发展出了一个专门用于研究含裂纹结构力学行为的学科—断裂力学[2]。针对Ⅰ型及复合型裂纹断裂问题展开过广泛深入的研究,其中Ⅰ型裂纹断裂研究已经比较成熟,已有大量的试验标准、理论解析以及应用案例等。然而由于复合型断裂问题的复杂性以及断裂试样的多样性,至今还没有统一的Ⅰ-Ⅱ复合型裂纹断裂试验标准以及断裂参数的解析标准。有必要对复合型裂纹进行深入的研究和讨论。在实际的工程应用中,承压设备(压力容器和压力管道)等一般都处于多向应力状态,同时受两个方向或多个方向力的作用被称为双轴或多轴载荷。对双轴作用下结构的分析评定标准还不太完善。因此对双轴载荷作用下Ⅰ-Ⅱ复合型裂纹的断裂行为进行研究是很有必要的。
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: