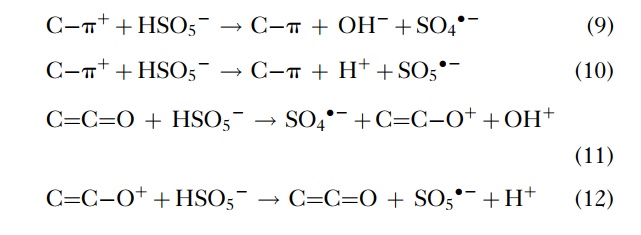氧化钴基双功能纳米反应器及其在燃料降解中的应用研究毕业论文
2020-04-22 19:38:48
摘 要
介孔硅基纳米材料(MSNs)由于其大的孔体积和表面积、规则有序的孔道结构、狭窄的孔径分布、可调控的介观结构和表面化学性质以及良好的生物兼容性等特点,在催化、吸附、分离、传感器、生物医学等领域中展现出重要的应用前景。然而介孔氧化硅的表面惰性特征限制了其各项应用,功能化介孔氧化硅的表面活性物种状态(分布、氧化还原性、酸碱性、润湿性等)将直接决定其各项功能性。尤其在多相催化中,担载于载体上活性组分的状态与其制备引入方法密切相关,因此介孔氧化硅的表面修饰技术无疑是决定它在催化吸附等应用中性能好坏的关键因素。
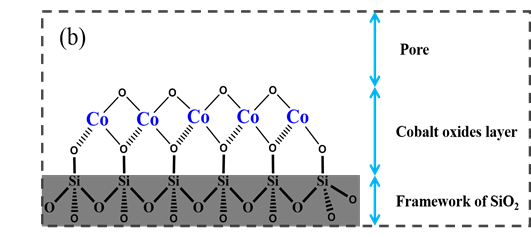
过渡金属是工业催化体系中催化活性来源的主要贡献者,其在催化载体上的状态包括浓度、分布、活性、与载体的相互作用直接影响着催化剂的催化活性与稳定性。通过合理化地引入表面催化活性物种及其对催化剂活性物质和结构状态的研究将可能对催化剂的工业生产与理论研究提供有效的支持。本文通过双溶剂方法成功将氧化钴纳米小颗粒负载进SBA-15的孔道当中,通过系统地表征确定了氧化钴在介孔氧化硅表面的高度分散状态。证明了通过上述的组装过程氧化钴可以与介孔硅酸盐壁之间建立起强相互作用,表面的硅羟基被氧化钴种修饰覆盖,并且在Orange II的降解反应中表现出优异的催化性能。
Synthesis of highly dispersed Co3O4 / SBA-15 catalyst and its application in Orange II Degradation
Abstract
Mesoporous silica-based nanomaterials (MSNs) have attracted wide attention in various applied fields including catalysis, drug delivery, biomedical, adsorption, separation, sensors, and optical devices applications, because of their large specific surface and pore volume, narrow pore size distribution, flexible mesoscopic structure and surface functionality, and biocompatibility. However, the surface inert characteristics of mesoporous silica limit its direct utilizability in most applications. Accordingly, the characteristics of surface-active species(Distribution, Redox, Acidity, Wettability, and etc.) on the modified mesoporous silica will directly affect their functionality. In particular, in the heterogeneous catalysis, the state of the active components on the carrier is closely related to the synthetic method of catalyst, therefore, the surface modification technology of mesoporous silica undoubtedly become the key factors for determining their catalytic performance.
Transition metals are the major contributors to the catalytic activity in industrial catalytic systems, whose state, including concentration, distribution, activity and interaction with carriers, on the catalytic support directly influence the catalytic activity and stability of the catalyst. The rational introduction of catalysts’ surface active species in heterogeneous catalysis, and the study on the active species state and the structure of the catalyst will provide good support for the industrial production and theoretical research of the catalyst. In this paper, the cobalt oxide nano-small particles were successfully loaded into the pores of SBA-15 by the two-solvent method, and the highly dispersed state of cobalt oxide on the mesoporous silica surface was determined by systematic characterization. It is proved that the cobalt oxide can establish a strong interaction with the mesoporous silicate wall through the above assembly process, the surface silicon hydroxy group is covered by the cobalt oxide species, and exhibits excellent catalytic performance in the degradation reaction of Orange II.
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
第一章 文献综述 1
1.1 前沿 1
1.2 PS / PMS活化 3
1.2.1 能量,碱性,氧化剂和过渡金属活化 3
1.2.2 纳米材料活化 4
1.3 论文选题思路 10
第二章 实验内容 11
2.1 前沿 11
2.2 实验部分 12
2.2.1 原料 12
2.2.2 SBA-15样品的制备 12
2.2.3 Co2 /SBA-15的合成 13
2.2.4 表征 13
2.2.5 催化评估 14
2.3 实验结果与分析 14
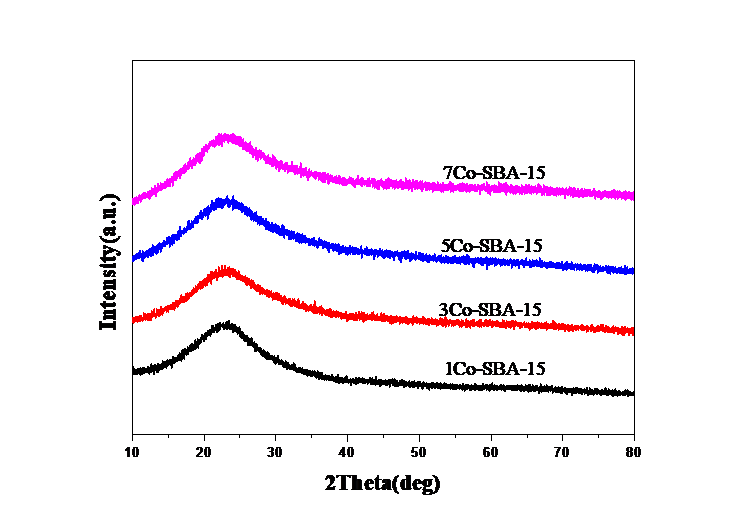
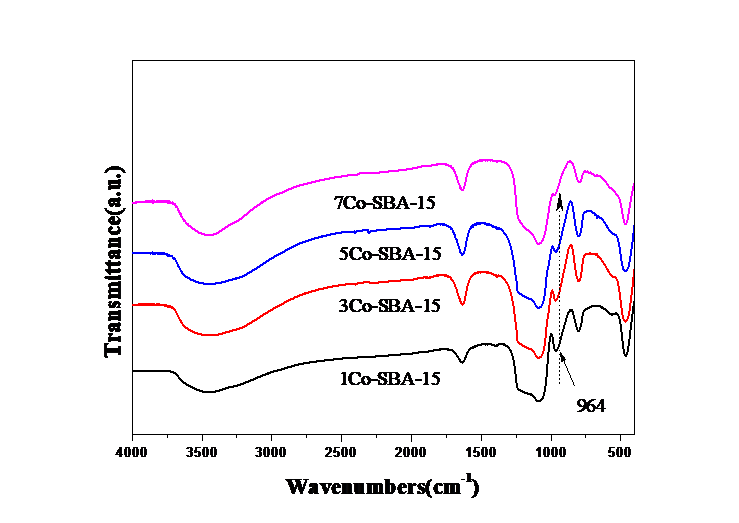
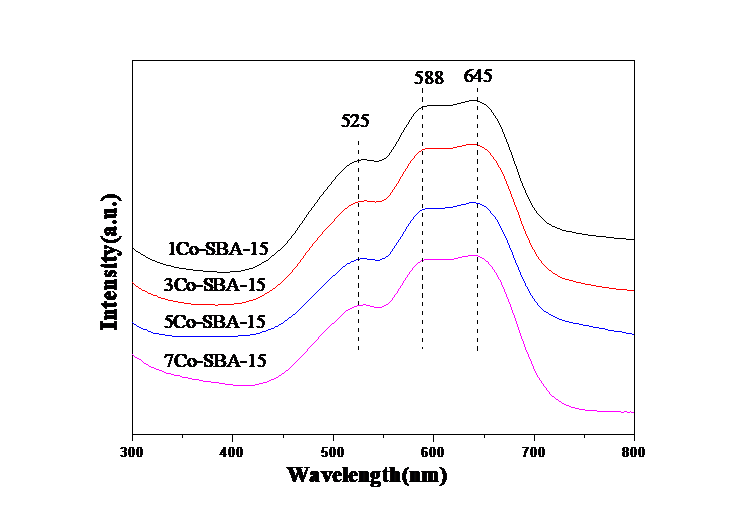
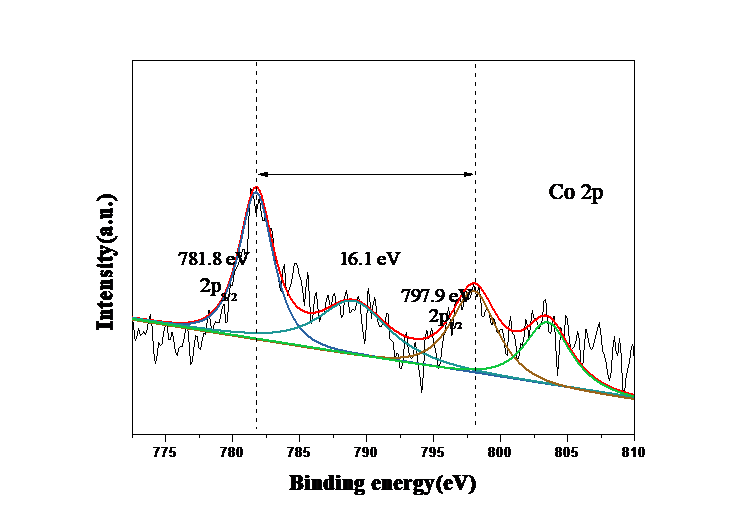
2.3.1 钴物种的状态 14
2.3.2 催化性能分析 17
2.2.1 降解Orange II的不同反应条件 19
2.2.3 催化剂的可重复使用性 22
2.2.4 结论 23
参考文献 24
致谢 26
第一章 文献综述
1.1 前沿
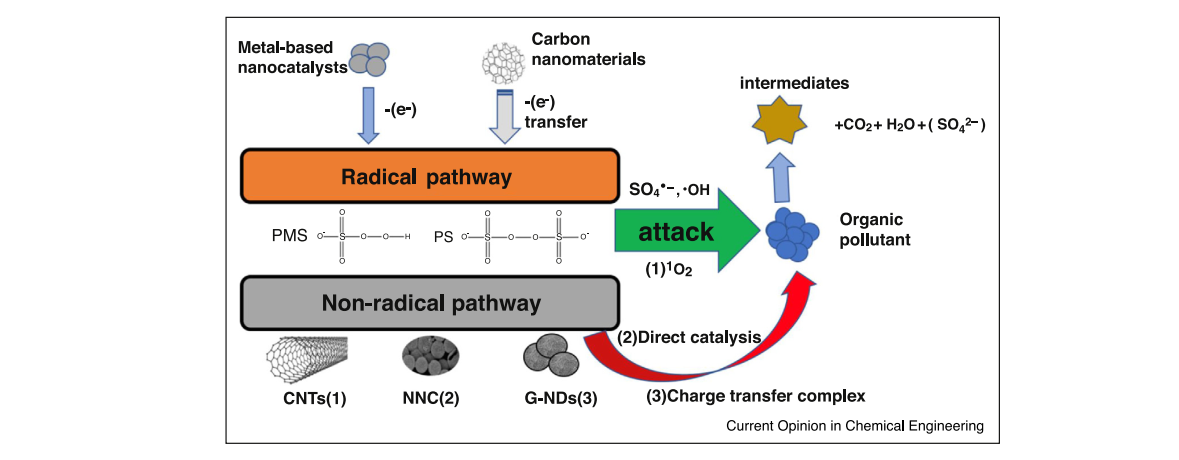
水中的有机污染物仍然是环境的一大问题,特别是那些难以用传统方法处理的难降解和或微生物降解的污染物。近年来,以硫酸根为基础的高级氧化工艺(SR-AOPs)因其良好的去污能力以及使用条件较温和而受到越来越多的关注。以钴为活性中心活化过氧硫酸盐(PMS),使其产生降解所需要的硫酸盐自由基,这是一种有效方法。本段内容综述了近年来用于PMS活化的各种非均相钴基催化剂的研究进展,包括钴氧化物、钴铁氧体和不同基质负载氧化钴。
近几十年来,高级氧化过程(AOPs)由于具有清除顽固有机污染物的潜在能力而受到越来越多的关注。在这种强氧化剂的作用下,有机污染物能够被分解成无害低毒的小分子化合物,甚至完全矿化成二氧化碳和水[1-2]。Fenton反应及其衍生反应,如光电芬顿、电芬顿、超声芬顿和超声-光电芬顿等,作为典型的产生•OH的AOPs过程,由于产生了强氧化剂•OH(氧化电位为1.8-2.7 V,相对于普通氢电极(NHE)),引起了人们的广泛研究[3]。然而,这些方法仍然面临着铁盐和Co2 的大量利用、氧化剂的化学不稳定性和储存运输困难、最优反应pH值(2-4)较低、以及后续大量污泥的分离和后处理等缺点[4-6]。
基于硫酸根(Co2 •-)(SR-AOPs)的高级氧化工艺已成为一种很有前途的替代方法,因为它具有一系列与生成氢氧化物方法不同的优点:(a) Co2 •-具有氧化电位(2.5-3.1 V vs. NHE),可与•OH相比较[7],甚至更高;(b) Co2 •-通过电子转移与含有不饱和键或芳香族电子的有机化合物发生更有选择性和更有效的反应,而•OH也可能与由氢抽提或亲电加成的不同背景以高反应速率发生反应[7-9];(c) Co2 •-作为一种主要的氧化物质,在2-8的pH范围内与有机化合物发生有效反应[10-12];(d) Co2 •-的半衰期一般为30-40秒,这使得Co2 •-比•OH(小于1秒)具有更稳定的传质和更好地与目标化合物接触[13-15]。
相关图片展示: