改性沸石对水中氨氮的模拟吸附研究毕业论文
2020-04-21 16:58:53
摘 要
为获得吸附水样中氨氮的经济高效吸附材料及吸附性能,本文拟以氨氮污染废水为对象,通过改性剂种类、改性剂浓度、改性时间和改性方式等因素研究了沸石改性的方法,通过吸附动力学和等温吸附实验初步探索了改性沸石的吸附机制。
结果表明,天然沸石对模拟水样中氨氮的去除率较低,不超过30%。微波改性沸石的效果不明显。盐酸改性后的沸石对水中氨氮的吸附能力降低,浓度越高酸改性效果越差,沸石负载氢离子可能减弱了对氨氮的静电吸附能力。0.4mol/L氢氧化钠改性的沸石吸附氨氮废水2h后,废水中氨氮含量的去除率提高45%。乙酸钠改性的沸石去除氨氮的效果更好,浓度为0.49mol/L乙酸钠改性沸石吸附氨氮废水1h,对氨氮的吸附量从未改性的20.25mg/kg增加到56.92mg/kg,提高64%,去除率达到63.97%。氢氧化钠和乙酸钠改性沸石均可能使天然沸石表面负载钠盐,增大沸石阳离子交换能力。相比氢氧化钠改性,乙酸钠改性沸石表现处快速吸附和缓慢平衡的特点。乙酸钠改性沸石对氨氮浓度为20mg N/L的吸附过程符合准一级反应动力学方程,当氨氮浓度为50mg/L时,准一级模型和准二级模型均能较好地拟合改性沸石的氨氮吸附数据。乙酸钠改性沸石的氨氮等温结果采用Langmuir与弗伦德利希模型拟合,R2分别为0.832和0.874,乙酸钠改性沸石对氨氮的去除可能由吸附和离子交换共同影响。
研究结果为湖库富营养化及低浓度氨氮废水治理提供氨氮吸附材料筛选的基础数据。
关键词:改性沸石,乙酸钠,氨氮,吸附特性
Simulated Adsorption of Ammonia Nitrogen in Water by Modified Zeolite
Abstract
In order to obtain an economical and efficient material for ammonia nitrogen adsorption in water samples and its adsorption performance, the modification methods of zeolite were studied by the types of modifiers, concentration of modifiers, modification time and modification methods. The adsorption mechanism of modified zeolite was preliminarily explored by adsorption kinetics and isothermal adsorption experiments.
The results showed that the removal rate of ammonia nitrogen from simulated water samples by natural zeolite was lower than 30%. The effect of microwave modification of zeolite is not obvious. The adsorption capacity of hydrochloric acid modified zeolite to ammonia nitrogen in water decreases, and the higher the concentration, the worse the effect of acid modified zeolite. Hydrogen ions loaded on zeolite may weaken the electrostatic adsorption capacity of ammonia nitrogen. The removal rate of ammonia nitrogen in water increased by 45% after natural zeolite was modified by 0.4 mol/L sodium hydroxide for 2 hours. The ammonia nitrogen removal efficiency of natural zeolite modified by sodium acetate was better. The ammonia nitrogen wastewater was adsorbed by zeolite modified by sodium acetate at 0.49 mol/l for 1 h. The amount of ammonia nitrogen adsorbed by natural zeolite increased from 20.25 mg/kg to 56.92 mg/kg, increased by 64%, and the removal rate reached 63.97%.Sodium hydroxide and sodium acetate modified zeolite may make the surface of natural zeolite loaded with sodium salt and increase the cation exchange capacity of zeolite. Compared with sodium hydroxide modification, sodium acetate modified zeolite exhibits fast adsorption and slow equilibrium. The adsorption process of sodium acetate modified zeolite for ammonia nitrogen concentration of 20 mg N/L conforms to the Quasi-First-Order reaction kinetics equation. When the concentration of ammonia nitrogen is 50 mg/L, the Quasi-First-Order model and quasi-second-order model can well fit the ammonia nitrogen adsorption data of modified zeolite. The results of ammonia nitrogen isotherm of sodium acetate modified zeolite were fitted by Langmuir and Freundlich models, R2 were 0.832 and 0.874, respectively. The removal of ammonia nitrogen by sodium acetate modified zeolite may be influenced by both adsorption and ion exchange.
The results provide basic data for screening ammonia-nitrogen adsorption materials for eutrophication of lakes and reservoirs and treatment of low concentration ammonia-nitrogen wastewater.
Key words: modified zeolite, sodium acetate, ammonia nitrogen,adsorption characteristics
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
目录 IV
第一章 绪论 1
1.1引言 1
1.2水体氮素污染现状及防治 1
1.3氨氮处理研究现状 1
1.3.1氨氮转形处理法 2
1.3.2氨氮解体处理法 3
1.4天然沸石的结构特性 4
1.5改性沸石的方法及研究现状 4
1.5.1物理改性法 4
1.5.2酸性改性法 4
1.5.3碱性改性法 4
1.5.4无机盐改性法 5
1.6本论文的目的、内容与意义 5
第二章 材料与方法 6
2.1材料 6
2.1.1供试吸附材料 6
2.1.2药剂与耗材 6
2.2仪器设备 6
2.3实验方法 6
2.3.1氨态氮的测定 6
2.3.2材料的参数及表征 6
2.3.3沸石吸附因素实验 7
2.3.4沸石单因素改性实验 7
2.3.5微波-盐联合改性实验 10
2.3.6改性沸石吸附动力学 10
2.3.7改性沸石吸附等温线 10
2.4 数据处理 10
第三章 结果与分析 12
3.1吸附材料参数 12
3.2吸附材料的形貌结构 12
3.3氨氮标准曲线 13
3.4沸石吸附因素实验结果 13
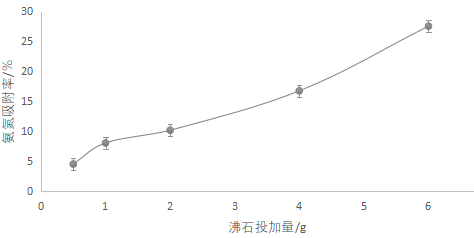
3.4.1投加量对吸附的影响 13
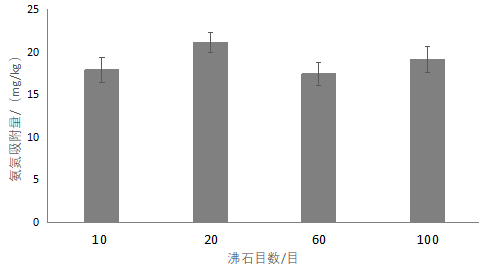
3.4.2目数对吸附的影响 14
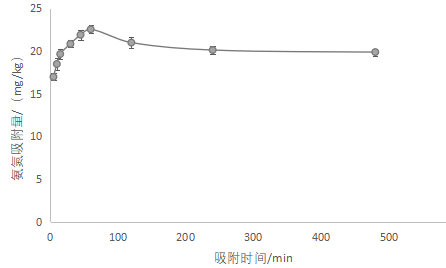
3.4.3吸附时间对吸附的影响 14
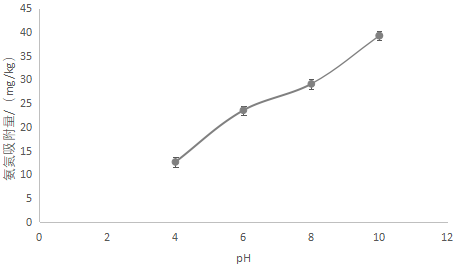
3.4.4 pH对吸附的影响 15
3.5沸石单因素改性实验结果 15
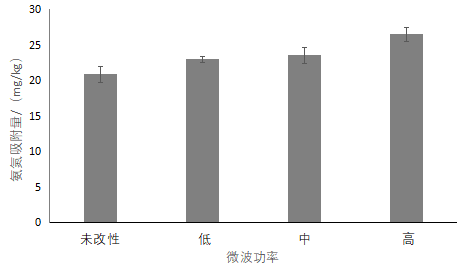
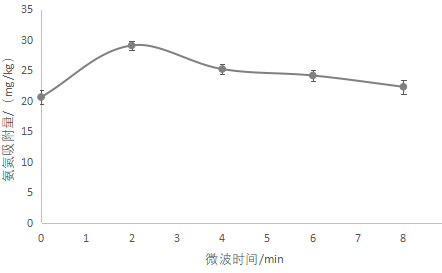
3.5.1沸石微波改性结果 15
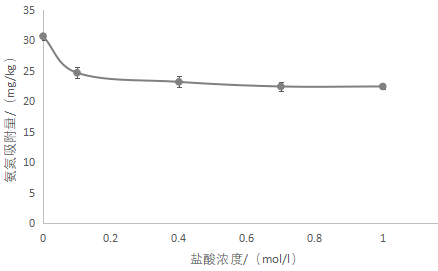
3.5.2沸石酸改性结果 16
3.5.3沸石碱改性结果 17
3.5.4沸石盐改性结果 18
3.6沸石联合改性结果 19
3.7吸附动力学实验结果 20
3.8吸附等温线实验结果 21
第四章 总结与展望 23
4.1主要结论 23
4.2研究展望 23
参考文献 24
致谢 26
第一章 绪论
1.1引言
湖库富营养化对人类的健康和流域的生态平衡造成了危害。经过整治,我国湖库富营养化情况虽然有一点改善,但情况依然没有想象中那么乐观。氨氮是水体富营养化的重要控制因子之一 。一般处理污染废水中含有的氨氮的方法主要有氨 吹脱法、折点 氯化法、生物 脱氮法等。但是这些方法有较多的缺点,比如成本高、某些工 艺的处理过程复杂等。沸石是一种便宜的材料,其结构是硅(铝)氧四面体,非常的稳定。沸石还具有许多特性,比如比表 面积较高、多 孔、阳离 子交 换特性等,使得其有很大的潜力,应用价值很广泛。近年来,在污水处理方面,天 然沸石逐渐受到人们的关注,而国内外科学家也重点研究了如何对沸石进行改性,这一现象已经成为一个研究热点。
1.2水体氮素污染现状及防治
氨氮是指水中以游离氨 (NH3) 和氨离子 (NH4 ) 形式存在的氮,一般以NH3-N表示。污染的废水中主要是氨氮,其会进行氧化分解,同时消耗大量氧, 而导致水中溶解氧含量降低,对水生动物的正常生长构成了威胁,甚至导致鱼类死亡[1]。氨氮废水来源非常广泛,人类生产生活的诸多方面都会导致氨氮废水的产生,如人类本身的吃喝拉撒、垃圾渗滤液等;农业方面的畜禽养殖和农田尾水;工业方面的冶金、化工、化肥、煤气、炼焦、柔革、味精、肉类加工等作业,都涉及到氨氮废水[2]。近几十年来随着社会经济的迅速发展,环境污 染问题使我国淡 水资源日益短缺,大量氨氮废水被人们排入自然水中,造成水源的 质量逐渐下降,水体富营 养化和环境污染越来越严重;较高的氨氮 浓度也使得常规生物处理工 艺受到抑制,出水氨氮指标偏高。因此必须要从 现状出发,进一步对含氨氮废 水处理技术和手 段进行研究,确保能够更有 效的治理污水,降低其对各方 面带来的不良影 响。
1.3氨氮处理研究现状
相关图片展示: