省家电拆解业多溴阻燃剂及二噁英污染物排放研究毕业论文
2021-11-26 23:33:45
论文总字数:38572字
摘 要
持久性有毒污染物(PTS)和持久性有机污染物(POPs)具有很强的毒性,不仅难降解、可远距离迁移,还会随食物链在动物和人体中累积、放大,具有内分泌干扰特性,可对人类健康和环境产生严重危害。家电拆解过程中主要代表性PTS和POPs有多溴联苯(PBBs)、多溴二苯醚(PBDEs)、二噁英及含有重金属的颗粒物。这些污染物具有环境和职业卫生危害。
本论文以某省五家典型家电拆解企业为例,分析了五家企业拆解下来的塑封料、含铅玻璃 、废线路板(WPB)、填充物和废塑料五类拆解件以及家电拆解四类车间的降尘、飞灰、废气及环境空气中的PBBs和PBDEs的含量和组分,了解拆解零部件中该类污染物是否符合2006.7.1开始正式实施的RoHS标准;通过对Ausmelt furnace炉协同处置废印刷电路板(WPCB)排放的二噁英浓度和组成研究,以分析Ausmelt furnace炉协同处置(WPCB)
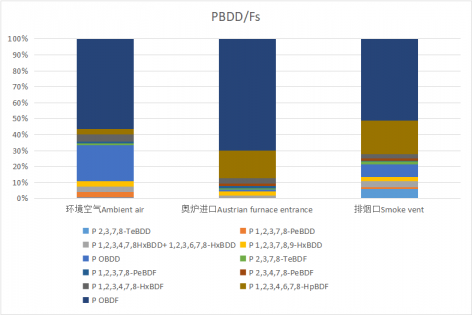
与国内外同类企业的污染特征及差异,在此基础上评估作业场所的环境状况及作业工人的职业暴露风险。对五家企业的PM2.5、PM10和TSP及其中的重金属含量分析。通过以上研究分析以期为WPB资源化过程中的污染控制与职业卫生防护提供相关参考。研究结果表明,拆解件中无PBBs检出,WPB部分含有PBDEs以十溴二苯醚为主,超过了RoHS标准。PBDEs浓度最高的是洗衣机和电视机/电脑拆解车间,以PBDE-209为主,环境空气中PBDEs暴露量最高的是洗衣机拆解车间。气相取样点∑11 PCDD/Fs最高的是排烟口,最低的是环境空气;气相取样点∑11PBDD/Fs最高的是排烟口,最低的是环境空气。对环境空气中二噁英类物质进行暴露风险评估,其对工人的暴露量为0.364 pgTEQ•Kg-1•d-1,符合世界卫生组织(WHO)规定的PCDD/Fs日允许摄入量(TDI)1~4 pgTEQ•Kg-1•d-1标准。
关键词:家电拆解;多溴联苯;多溴二苯醚;二噁英;重金属颗粒物
Abstract
Persistent Toxic Pollutants (PTS) and Persistent Organic Pollutants (POPs) are highly toxic. Not only are they difficult to degrade and can migrate over long distances, they also accumulate and amplify in animals and humans with the food chain. Can cause serious harm to human health and the environment. The main representative PTS and POPs in the dismantling process of household appliances are polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs), polybrominated diphenyl ethers (PBDEs), dioxins and particulates containing heavy metals. These pollutants have environmental and occupational health hazards.
This paper takes five typical household appliance dismantling enterprises in a province as an example, and analyzes five types of dismantling parts of plastic packaging materials, leaded glass, waste circuit boards (WPB), fillers and waste plastics and household appliances dismantled by the five enterprises. Dismantle the content and composition of PBBs and PBDEs in the dust, fly ash, exhaust gas and ambient air of the four types of workshops, and understand whether the pollutants in the dismantled parts meet the RoHS standards officially implemented since July 7, 2006 Ausmelt furnace co-processing of waste printed circuit board (WPCB) emissions of dioxin concentration and composition study to analyze Ausmelt furnace co-processing (WPCB)
Based on the pollution characteristics and differences of similar enterprises at home and abroad, the environmental conditions of the workplace and the occupational exposure risks of the workers are evaluated on this basis. Analysis of PM2.5, PM10, TSP and heavy metal content in five companies. Through the above research and analysis, it is expected to provide relevant references for pollution control and occupational health protection in the process of WPB recycling. The results of the study showed that no PBBs were detected in the dismantled parts, and the PBDEs contained in the WPB were mainly decabromodiphenyl ether, which exceeded RoHS standards. The highest concentration of PBDEs is in the washing machine and TV / computer disassembly workshop, mainly PBDE-209, and the highest exposure to PBDEs in the ambient air is in the washing machine disassembly workshop. The highest gas sampling point ∑11 PCDD / Fs is the smoke vent and the lowest is ambient air; the highest gas sampling point ∑11PBDD / Fs is the smoke vent and the lowest is ambient air. The exposure risk assessment of dioxins in the ambient air, the exposure to workers is 0.364 pgTEQ • Kg-1 • d-1, which is in accordance with the daily allowable intake of PCDD / Fs specified by the World Health Organization (WHO) ( TDI) 1 ~ 4 pgTEQ • Kg-1 • d-1 standard.
Keywords: dismantling of home appliances;PBBs;PBDEs;dioxin;heavy metal particles
目 录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1研究背景 1
1.2国内外研究现状 1
1.3研究目的意义及内容 2
第2章 溴系阻燃剂在不同介质分布 4
2.1.材料与方法 4
2.1.1样品的来源 4
2.1.2样品的采集 4
2.1.3样品提纯、净化和分析 5
2.1.4质量控制与质量保证 6
2.1.5职业暴露评估 6
2.2.结果与讨论 7
2.2.1拆解件中PBBs、PBDEs分析 7
2.2.2拆解车间中的PBBs分析 7
2.2.3拆解车间中的PBDEs分析 9
2.2.4职业暴露评估 10
2.2.5不同地区PBDEs浓度对比 11
2.3.结论 12
第3章 奥炉协同处置废印刷电路板排放的二噁英浓度和组成研究 14
3.1.材料与方法 14
3.1.1样品采集 14
3.1.2仪器与试剂 15
3.1.3实验前处理 15
3.1.4HRGC HRMS分析条件 16
3.1.5定量方法 16
3.1.6质量控制与质量保证QA/QC 17
3.1.7检出限 17
3.2结果与讨论 18
3.2.1不同单元气相中PCDD / Fs和PBDD / Fs浓度水平 18
3.2.2 PCDD / Fs 和 PBDD / Fs 气相中同族物分布分析 20
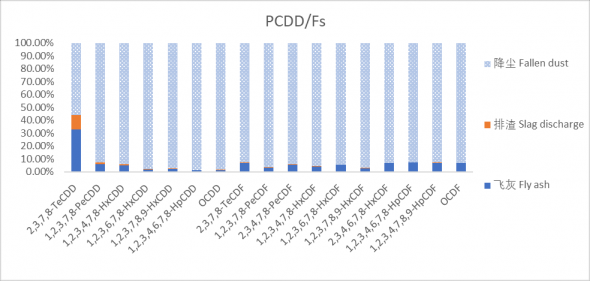
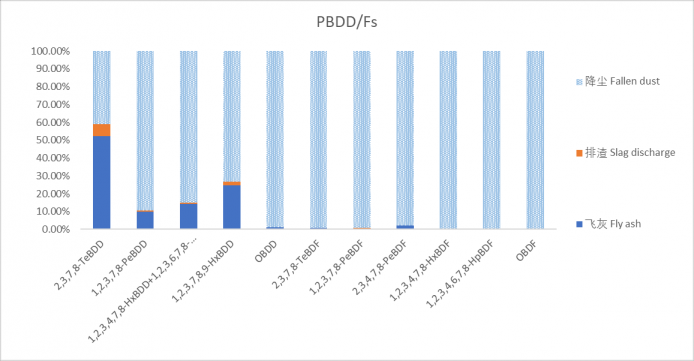
3.2.3 PCDD/Fs和PBDD/Fs的固相分配特征 23
3.2.4呼吸暴露风险评估 24
3.2.5结论 25
第4章 拆解车间含重金属颗粒物分析 26
4.1材料与方法 26
4.1.1.样品及采集 26
4.1.2检测方法与仪器 26
4.1.3样品处理 26
4.2结果与讨论 26
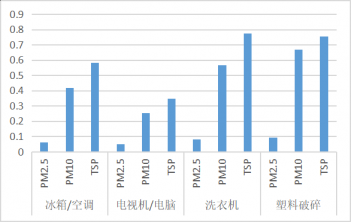
4.2.1TSP、PM10、PM2.5浓度分析 26
4.2.2拆解车间中的样品介质重金属分析 27
4.2.3其他地区电子垃圾拆解重金属的对比与影响 28
4.3结论 29
第5章 展望 30
参考文献 31
第1章 绪论
1.1研究背景
由于电子废物成分复杂,加上不规范的拆解、非法倾倒、露天焚烧及随意处置等,会产生大量的POPs和PTS,多溴联苯(PBBs)、多溴二苯醚(PBDEs)和二噁英属于国际公约禁用的POPs,多溴联苯、多溴二苯醚包括一溴到十溴的的聚合物及其异构体,主要用于家电高分子材料中作阻燃剂[1-3],对人的毒害主要体现在破坏内分泌系统及胎儿的生长[4,5]。含该类物质阻燃剂的材料在循环利用过程中的高温下会产生溴化二苯二噁英或呋喃,这两类物质属于致癌物质,并可造成包括土、水以及空气在内的环境广泛的污染[6-8]。目前国际上对该类物质生产进行了限制,但在回收再利用的家电等物质中该类物质依然存在,且燃烧后造成二次污染[9,10]。多氯代二苯并二噁英/呋喃(PCDD/Fs)是目前发现的无意识合成的副产品中毒性最强的化合物,曾引发多起国际重大环境公害事件,其高风险地区主要集中在电子垃圾拆解地区、有机氯代化工厂周边和垃圾焚烧炉附近地区。溴代二噁英(PBDD/Fs)与PCDD/Fs具有相似的结构和毒性,来源有含溴物质的高温反应及含溴代阻燃剂的高温燃烧。
还有电子废物如废旧电路板WPB属于危险废物(代900-045-49)[1],主要由玻纤、金属、高聚物和电子元件等构成,为满足电器阻燃要求,WPB的绝缘基底中常添加有含溴的阻燃剂。当采用露天焚烧、酸蚀等不适当的操作容易产生严重的二次污染[8, 9]。高效洁净实现WPB资源化无害化利用成为电子废弃物利用的关键[10, 11]。目前我国WPB资源化利用主要有酸法、破碎重力分选法、裂解法及等,普遍存在着环境风险大、资源利用率不高、投资大等问题[12-14]。
请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:38572字
相关图片展示: