基于GIS的南京养老设施空间布局优化研究毕业论文
2020-04-15 20:23:27
摘 要
21世纪,我国的人口老龄化水平不断提高,老龄化问题日益严重。养老问题逐渐成了社会热点问题、也是学者关注的焦点,而养老设施布局合理与否对于解决养老这一社会问题而言意义重大。南京作为中国东部地区重要的中心城市,是继上海、北京、天津之后,第四个最早进入老龄化社会的城市。本文以南京市为例,应用APH层次分析法和熵值权重法构建养老设施布局指标体系,基于GIS空间分析,对南京的201家养老设施进行空间分布格局评价,得出适宜性评价结果。结果表明:(1)选址中医院诊所与工厂对适宜性影响较大,而交通因素对其影响较小。(2)中心城区的养老设施布局整体适宜性高,郊区的适宜性低,且分布数量较少,只占1/8。并对南京市未来养老设施布局进行了优化设计,以期为之后的养老设施布局设计提供支撑。
关键词:南京 老龄化 养老设施布局 GIS空间分析
Research on the layout optimization of Nanjing pension facilities based on GIS
Abstract
In the 21st century, the level of population aging in China has been continuously improving, and the problem of population aging has become increasingly serious. Old-age pension has gradually become a hot social issue, but also the focus of scholars. Whether the layout of pension facilities is reasonable or not is of great significance to solve the problem of pension. As an important central city in eastern China, Nanjing is the fourth city to enter an aging society after Shanghai, Beijing and Tianjin. Taking Nanjing as an example, this paper uses APH analytic hierarchy process (AHP) and entropy weight method to construct the index system of the layout of old-age facilities. Based on GIS spatial analysis, 201 old-age facilities in Nanjing are evaluated for their spatial distribution pattern, and the results of suitability evaluation are obtained. The results show that: (1) hospitals and factories have great influence on suitability, while traffic factors have little influence on suitability. (2) The overall suitability of the old-age facilities layout in the central urban area is high, while the suitability of the suburbs is low, and the number of distribution is small, accounting for only 1/8.The future layout of pension facilities in Nanjing was optimized in order to provide support for the future layout design of pension facilities.
Key Words: Nanjing; Aging; Layout of pension facilities; Spatial Analysis of GIS
目录
摘要 Ⅰ
ABSTRACT Ⅱ
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 选题背景目的与意义 1
1.2 研究思路与技术路线 3
1.2.1 研究思路 3
1.2.2 技术路线 3
第二章 理论基础和技术方法 5
2.1 相关概念 5
2.2 国内外研究现状 5
2.2.1 国内研究现状 5
2.2.2 国外研究现状 6
2.2.3 结论 6
2.3 技术方法 6
第三章 研究设计 9
3.1 研究区域 9
3.2 数据来源与预处理 9
第四章 南京养老设施空间分布现状和存在的问题 11
4.1 南京市现阶段养老设施分布 11
4.2 南京市养老设施分布存在的主要问题 12
第五章 南京养老设施空间分布适宜性评价与优化 13
5.1 评价指标体系的构建 13
5.1.1 影响因素调查分析 13
5.1.2 指标确定 14
5.2 评价指标权重的确定 16
5.2.1 数据预处理 16
5.2.2 确定评价指标的权重 17
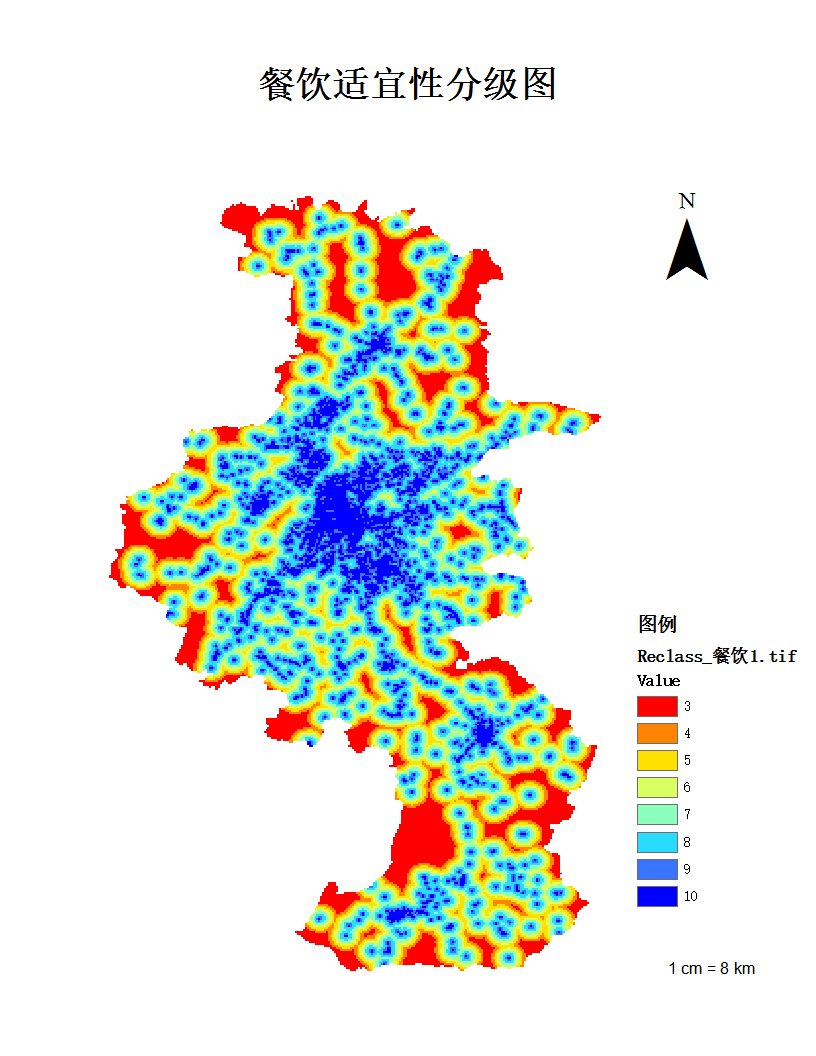
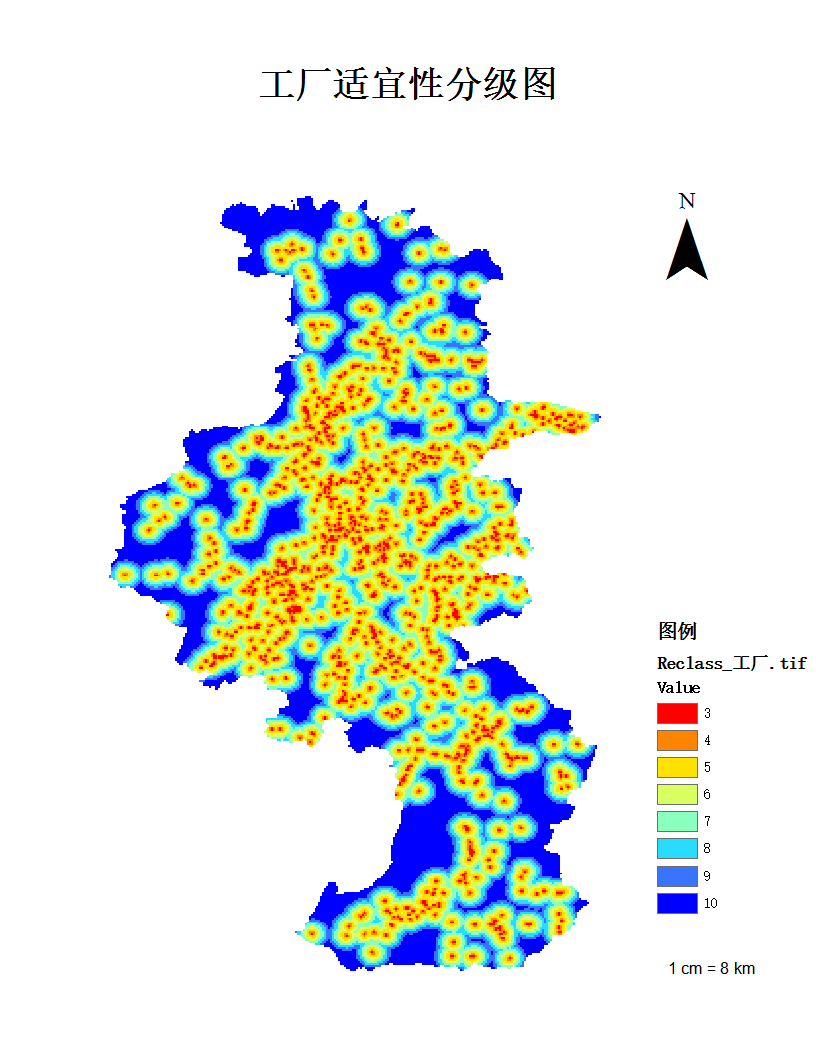
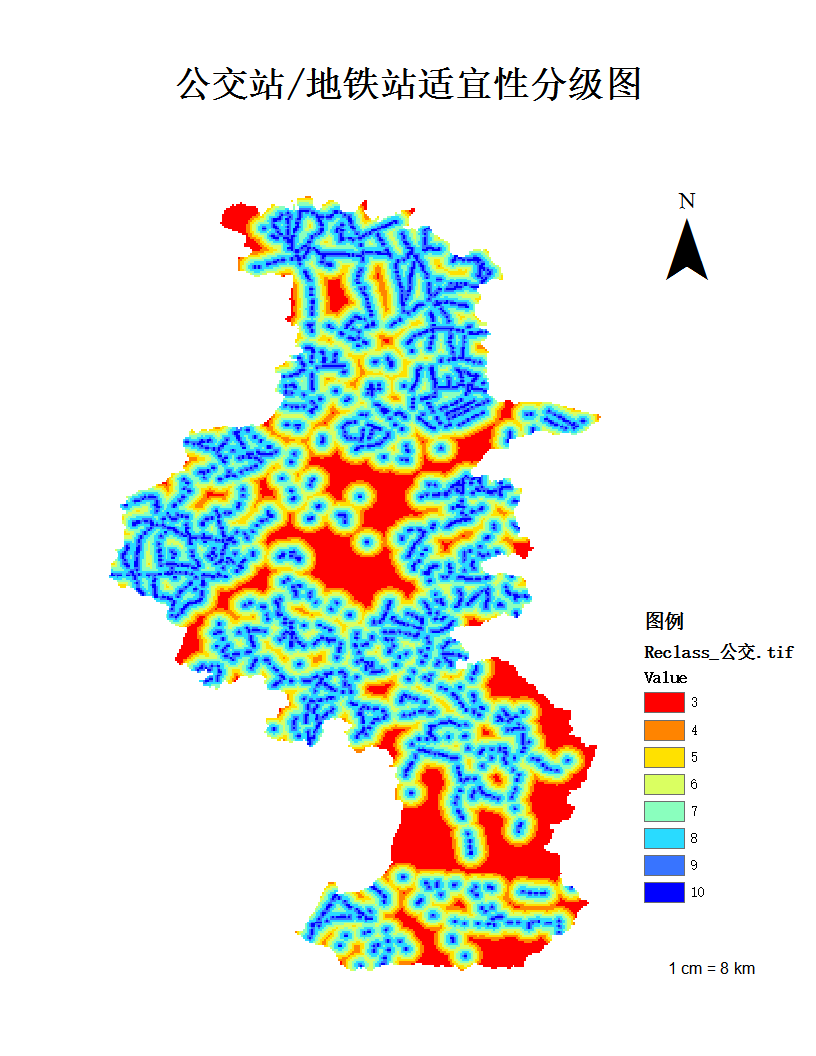
5.3 南京养老设施空间分布适宜性评价实例 18
5.3.1 评分方法与等级划分 18
5.3.2 评价结果 21
5.4 南京养老设施布局优化方案 23
5.4.1 考虑因素 23
5.4.2 优化结果 23
第六章 结论与展望 29
6.1 研究结论 29
6.2 问题展望 30
参考文献 31
致谢 33
第一章 绪论
1.1 选题背景目的与意义
1.1.1 选题背景
由国家统计局统计数据可得,截止2018年年底,我国60周岁及以上人口为24949万,占总人口比重的17.9%,其中65周岁及以上人口16658万人,占总人口的11.9%[1]。按照联合国定义,当一个国家或地区 65 岁及以上老年人口数量占总人口比例超过 7% 时,就意味着这个国家或地区进入了老龄化;比例达到 14%即进入深度老龄化[2]。
可见中国已步入老龄化阶段,且正向深度老龄化阶段迈进。南京作为中国东部地区重要的中心城市[3],是继上海、北京、天津之后,第四个最早进入老龄化社会的城市。在南京市民政局于2018年4月召开新闻发布会上,南京市老龄委副主任、市民政局副局长赵军在会上发布一个重要信息,那就是南京去年已经进入深度老龄化社会[2]。
数据显示,2017 年 60 岁及以上南京户籍人口为1418878 人,具体构成如下表 1-1 所示。65岁及以上人数比上一年增加了69319 ,达到 957373人,占户籍总人口比例由 13.40% 增至 14.07%。这是南京市老年人口比例第一次超过 14%,意味着南京进入深度老龄化。而未来十五年,南京市老年人口增长趋势依然强劲。
表1-1 2017年南京市户籍老年人口构成(单位:人,%) | |||
年份 | 人数 | 占总人口的比例 | 占60岁及以上比例 |
60岁及以上 | 1418878 | 20.85 | 100.00 |
65岁及以上 | 957373 | 14.07 | 67.47 |
80岁及以上 | 216607 | 3.18 | 15.27 |
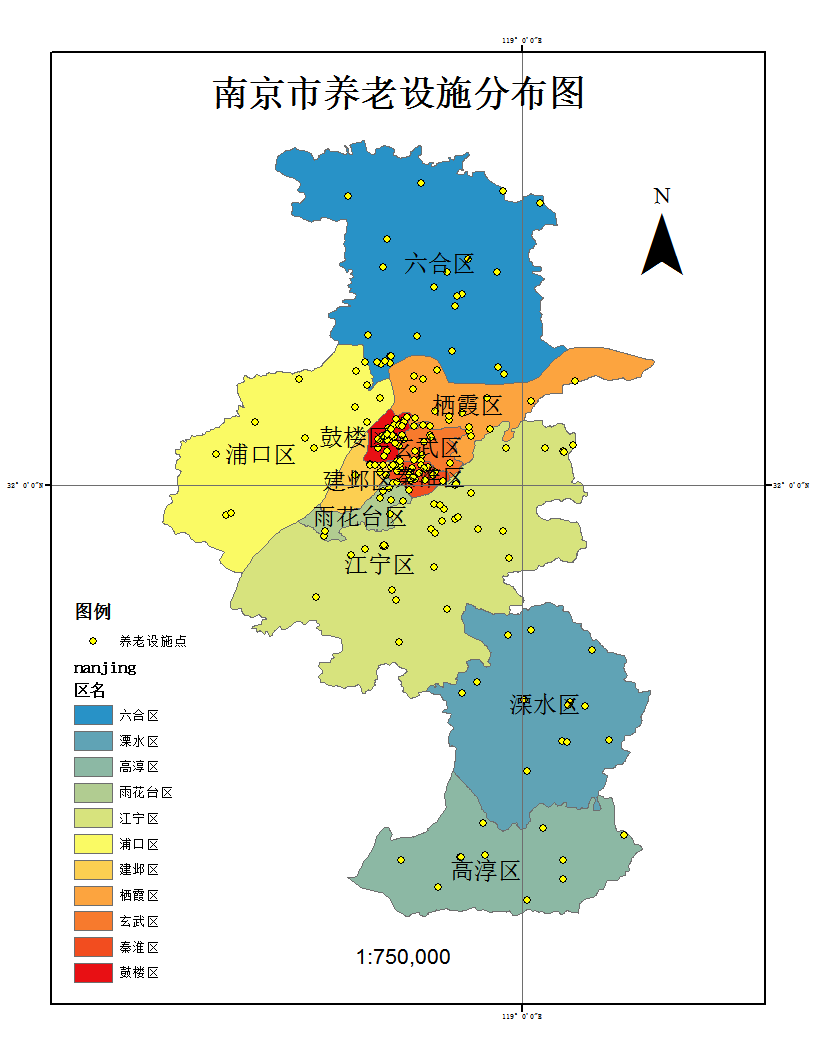
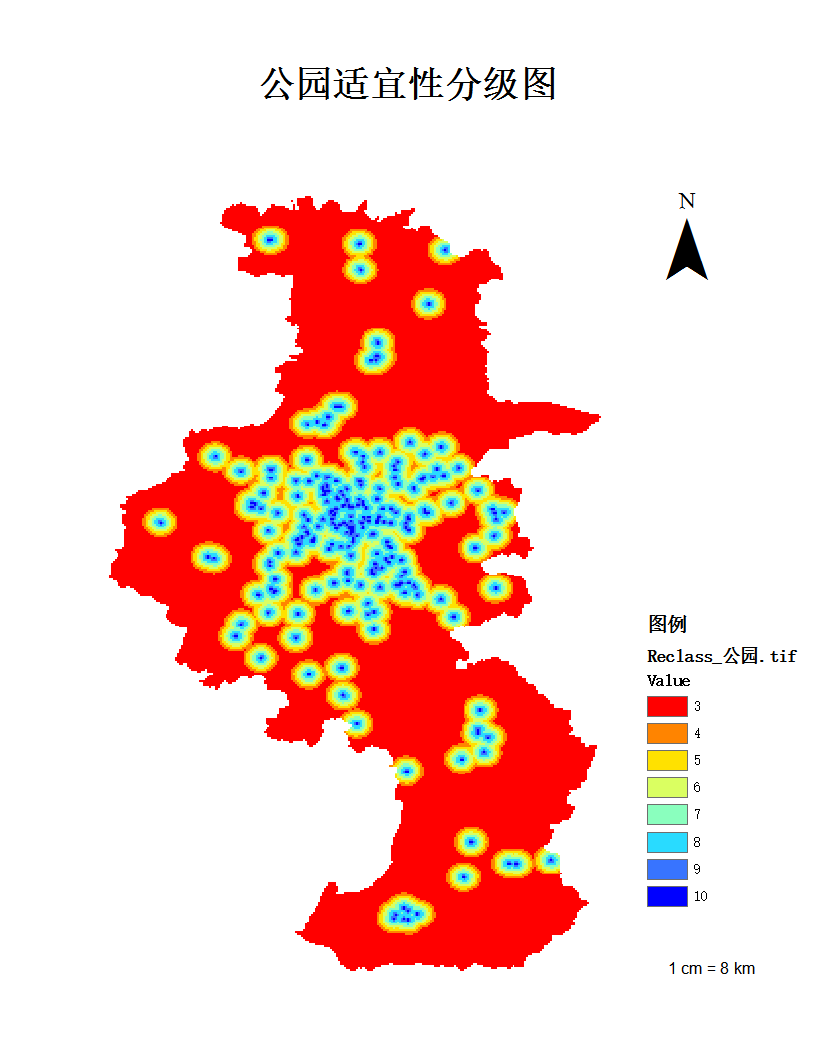
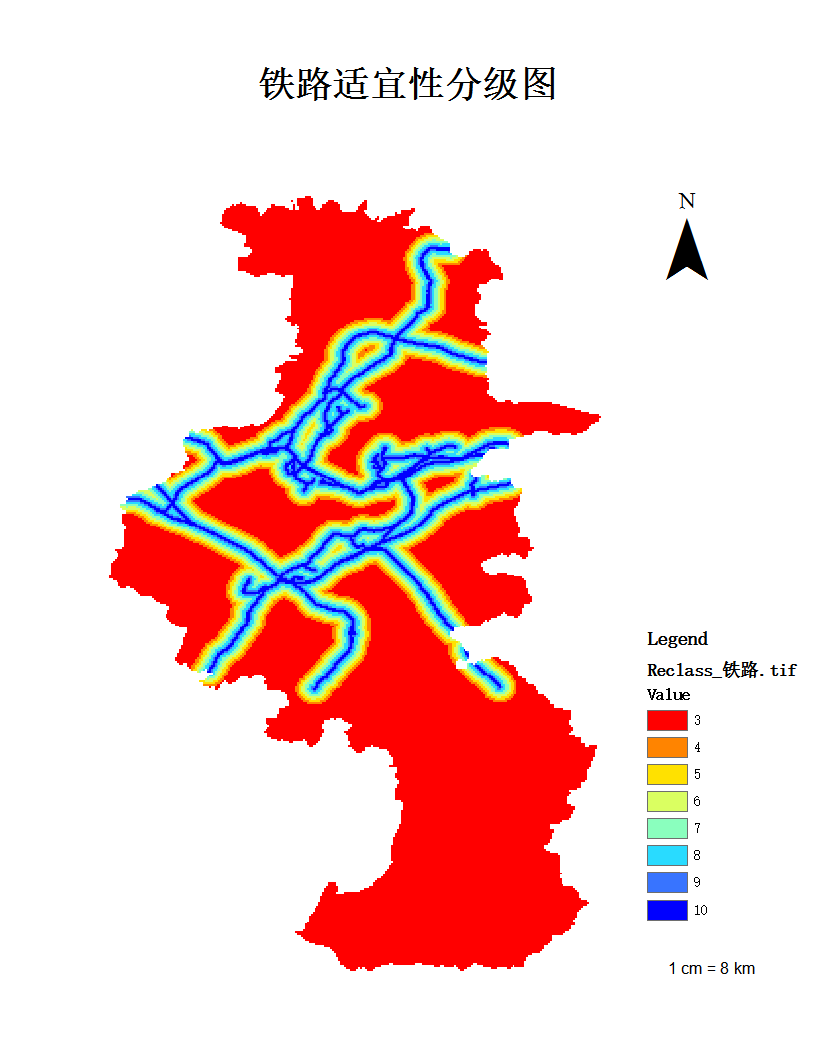
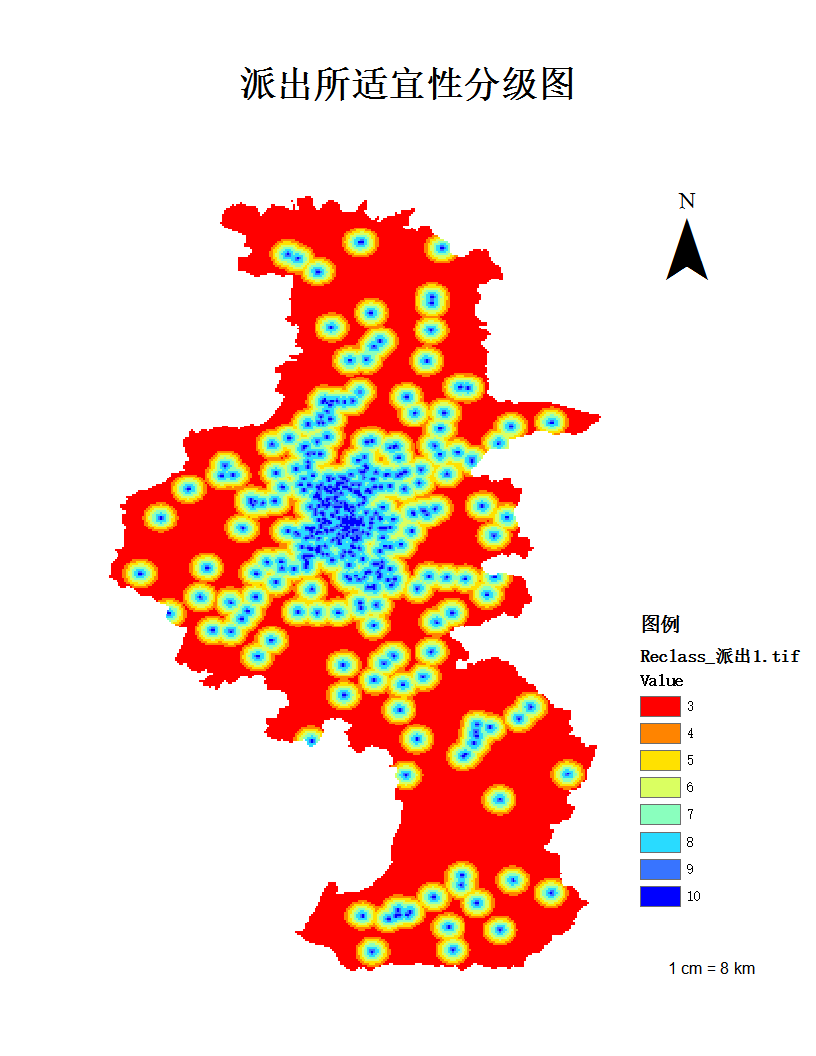
但全市老年人口的分布,因地区定位、交通、家庭等因素呈现不均分布形态,其中大致分为三个梯队,分布人口最多的,以鼓楼区为首的第一梯队:鼓楼区、秦淮区、江宁区、六合区;分布分口在10000名左右的第二梯队:江北新区、玄武区、溧水区、栖霞区、高淳区;分布人口最少的第三梯队:浦口区、建邺区、雨花台区。具体的分布状况如下图1-1所示:
以上是毕业论文大纲或资料介绍,该课题完整毕业论文、开题报告、任务书、程序设计、图纸设计等资料请添加微信获取,微信号:bysjorg。
相关图片展示: