Tb:CaF2纳米粉体的合成与表征毕业论文
2021-11-25 23:11:04
论文总字数:24640字
摘 要
光隔离器是光纤通信中的重要部件,其核心是基于法拉第效应的磁光材料。评价磁光材料性能高低的主要参数是维尔德常数,它反映的是磁光材料对偏振光的旋转能力,而维尔德常数的大小与材料的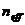 (有效波尔磁子数)的值密切相关。在稀土离子中,Tb3 离子的
(有效波尔磁子数)的值密切相关。在稀土离子中,Tb3 离子的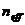 (有效波尔磁子数)比较大,其4f-5d的跃迁属于短波长范围,能够有效提高法拉第旋转效率。CaF2属于具有高度对称结构的立方晶系,能制成透明陶瓷,且其透光范围广、声子能量低,是目前综合性能最优的光学材料之一。目前关于Tb:CaF2磁光透明陶瓷的研究还较少,本论文采用共沉淀法合成Tb:CaF2磁光透明陶瓷的原料烧结所用的Tb:CaF2纳米粉体,研究Tb3 离子掺杂对粉体物相、形貌以及烧结性能的影响,同时研究Tb:CaF2透明陶瓷的发光性能。主要内容和结论如下:
(有效波尔磁子数)比较大,其4f-5d的跃迁属于短波长范围,能够有效提高法拉第旋转效率。CaF2属于具有高度对称结构的立方晶系,能制成透明陶瓷,且其透光范围广、声子能量低,是目前综合性能最优的光学材料之一。目前关于Tb:CaF2磁光透明陶瓷的研究还较少,本论文采用共沉淀法合成Tb:CaF2磁光透明陶瓷的原料烧结所用的Tb:CaF2纳米粉体,研究Tb3 离子掺杂对粉体物相、形貌以及烧结性能的影响,同时研究Tb:CaF2透明陶瓷的发光性能。主要内容和结论如下:
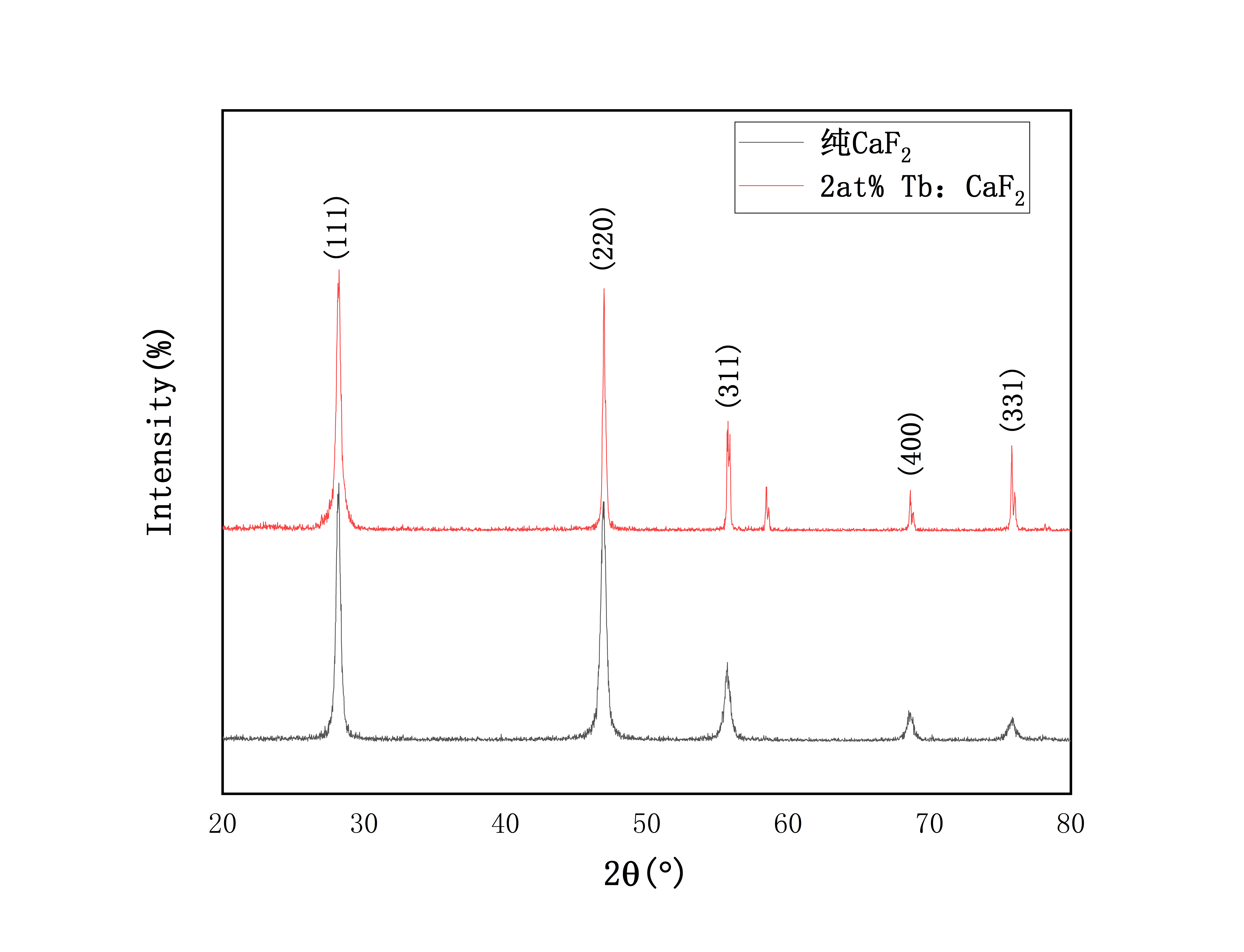
- 通过共沉淀法合成了掺杂浓度为2at%的Tb:CaF2纳米粉体,利用XRD、SEM、激光粒度仪等测试手段对试样粉体进行了表征。结果表明,掺杂Tb3 离子后CaF2基质的晶格结构仍保持完整而没被破坏,并且所合成的纳米粉体为纯的氟化钙结构,粉体粒径约为40nm。
- 通过真空热压烧结法制备了2at%Tb:CaF2透明陶瓷,样品在1200nm处的光学透过率为91.29%,透明陶瓷的断面形貌显示其内部结构致密,未发现存在气孔,说明通过共沉淀法合成的Tb:CaF2纳米粉体烧结活性比较高。
- 对2at%Tb:CaF2透明陶瓷进行发光特性的研究,在562nm处的特征发射峰强,呈现绿色荧光,同时测试了Tb3 离子在562nm波长处的的荧光寿命为5.9ms,显示出其在荧光照明方面具有一定的应用潜力。
关键词:铽;氟化钙;纳米粉体;透明陶瓷;发光特性
Abstract
Optical isolator is an important component in optical fiber communication. Its core is magneto-optical material based on Faraday effect. The Verdet constant is the main parameter to evaluate the performance of magneto-optic material, which reflects the rotation ability of magneto-optic material to polarized light and the Verdet constant is closely related to the value of the 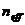 ( (effective Bohr magneton number). Among rare-earth ions, the value of the
( (effective Bohr magneton number). Among rare-earth ions, the value of the 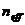 of Tb3 ion is relatively large (effective Bohr magneton number), and its 4f-5d transition belongs to the short-wavelength range, which can effectively improve Faraday rotation efficiency. CaF2 is a highly symmetrical cubic crystal system, which can be made into transparent ceramics with a wide light transmission range and low phonon energy. At present, there are few studies on Tb:CaF2 magneto-optic transparent ceramics. In this paper, the co-precipitation method was used to prepare Tb:CaF2 nanometer powders which were the raw materials of Tb:CaF2 magneto-optic transparent ceramics. The influence of Tb3 ions doping on the phases, morphologies and sintering properties of the powders was studied, and the luminescence characteristics of Tb:CaF2 transparent ceramics were also explored.The main contents and conclusions are as follows:
of Tb3 ion is relatively large (effective Bohr magneton number), and its 4f-5d transition belongs to the short-wavelength range, which can effectively improve Faraday rotation efficiency. CaF2 is a highly symmetrical cubic crystal system, which can be made into transparent ceramics with a wide light transmission range and low phonon energy. At present, there are few studies on Tb:CaF2 magneto-optic transparent ceramics. In this paper, the co-precipitation method was used to prepare Tb:CaF2 nanometer powders which were the raw materials of Tb:CaF2 magneto-optic transparent ceramics. The influence of Tb3 ions doping on the phases, morphologies and sintering properties of the powders was studied, and the luminescence characteristics of Tb:CaF2 transparent ceramics were also explored.The main contents and conclusions are as follows:
- Tb:CaF2 nanometer powders with doping concentration of 2at% were synthesized by coprecipitation method, and the sample powders were characterized by means of XRD, SEM and laser particle size analyzer. The results showed that the lattice structure of CaF2 matrix remained intact after doping Tb3 ions, and the synthesized nanometer powders were of high chemical purity and agglomerated to a certain extent.
- The 2at%Tb:CaF2 transparent ceramics were prepared by vacuum hot-pressing sintering method. The optical transmittance of the samples at 1200nm was 91.29%. The cross-section morphology of the transparent ceramics showed that the internal structure was dense and no pores were found, indicating that the sintering activity of Tb:CaF2 nanometer powders synthesized by coprecipitation method was relatively high.
- The luminescent characteristics of 2at%Tb:CaF2 transparent ceramics were studied. The characteristic emission peak was strong at 562nm, showing green fluorescence. Meanwhile, the fluorescence lifetime of Tb3 ions at 562nm was 5.990ms, indicating that it has certain application potential in fluorescent lighting.
Key Words:Terbium;Calcium fluoride;nanopowders;Transparent ceramics;Luminescence properties
目录
第一章 绪 论 3
1.1 法拉第效应 3
1.2 磁光材料 4
1.2.1 磁光玻璃 4
1.2.2 磁光晶体 5
1.2.3 磁光透明陶瓷 5
1.3 影响透明陶瓷光学性能的因素 5
1.4 纳米粉体制备技术 6
1.5 研究课题的提出和研究内容 7
1.5.1 CaF2基质材料的性质 7
1.5.2 Tb3 离子的磁光性能 7
1.5.3 研究内容 8
第二章 实验原料、设备及表征方法 9
2.1实验原料 9
2.2实验设备 9
2.3测试与表征方法 10
2.3.1 X射线衍射分析(XRD) 10
2.3.2 扫描电子显微镜(SEM) 10
2.3.3 紫外-可见-近红外分光光度计 11
2.3.4荧光光谱及荧光寿命分析 11
2.3.5 激光粒度分析仪 11
第三章 Tb:CaF2纳米粉体的制备与结果分析 12
3.1实验过程 12
3.2结果与讨论 13
3.2.1 Tb3 离子掺杂对CaF2纳米粉体的影响 13
3.2.1.1 物相与晶体结构分析 13
3.2.1.2 形貌观察与团聚现象分析 14
3.2.2 Tb:CaF2透明陶瓷烧结性能与光学质量 16
3.2.2.1透明陶瓷透光率分析 16
3.2.2.2陶瓷断面形貌分析 18
3.2.3 Tb:CaF2透明陶瓷中的光谱性能 18
3.2.3.1 Tb:CaF2透明陶瓷激发光谱分析 18
3.2.3.2 Tb:CaF2透明陶瓷发射光谱分析 19
3.2.3.3 Tb3 离子在透明陶瓷中的荧光寿命 20
第四章 结 论 22
参考文献 23
致 谢 25
第一章 绪 论
激光(Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation,LASER)是指光通过受激辐射放大,自从1960年美国人梅曼在实验室中获得人类的第一束激光以来,激光由于具有高亮度、高方向性、高单色性以及高相干性的优点,因而被广泛应用于工业、医学、军事以及通信行业。在光纤通信和高功率激光系统中,反射光会干扰光源并产生噪音,限制了光波的长距离传输,为了提高整个系统工作时的稳定性,必须对系统中的反向光进行有效隔离。光隔离器是一种只允许单向光通过的光非互易性器件,即沿正向传输的光损耗很低,而沿反向传输的光会有很大损耗,能够有效减少系统中的反向光,因此是上述系统中不可或缺的一部分。光隔离器是基于法拉第效应工作的,故也被称为法拉第磁光隔离器。光隔离器的关键是器件中的磁光材料,近年来其研究与应用越来越受到人们的重视。本章主要介绍法拉第效应的原理,磁光材料的种类,影响透明陶瓷光学性能的因素,纳米粉体制备技术,最后介绍研究课题的提出与研究内容。
1.1 法拉第效应
磁光效应是指在外加磁场的作用下,具有固有磁矩的物质其电磁特性(如磁导率、磁化方向、磁化强度、磁畴结构等)发生变化,使得光在该物质内部的传输特性(如偏振状态、光强、相位、传输方向等)也发生变化的现象[1]。目前人们熟知的磁光效应有四种,包括法拉第效应、克尔效应、塞曼效应和科顿-穆顿效应。这里主要介绍法拉第效应。
线偏振光沿磁场方向通过介质时,其偏振面旋转一个角度,这种由透射引起的偏振面旋转叫做法拉第效应[2]。图1是法拉第效应的示意图,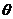 为偏振光的旋转角,
为偏振光的旋转角,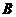 为磁场强度,
为磁场强度,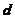 为样品长度,它们之间的关系如下:
为样品长度,它们之间的关系如下:
请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:24640字
相关图片展示:



您可能感兴趣的文章
- 激光作用下ZrNiSn合金热电材料组成、结构和性能的演化规律开题报告
- 原位生长于碳纤维表面的钒氧化物柔性电极制备开题报告
- 锂硫电池用TixOy-S/HGs复合材料的制备与性能开题报告
- MnO2纳米片修饰ZnO纳米棒阵列的气敏性能研究开题报告
- 基于三维碳基孔结构和电解质协同优化的微型超级电容器文献综述
- 基于C-MEMS工艺的微型混合锂离子电容器构筑及性能开题报告
- 多孔碳负载钼基纳米材料作为高性能析氢电催化剂文献综述
- Cu掺杂ZnxCd1-xS纳米晶的制备与性能研究开题报告
- 用于光伏的III-V族半导体低成本生长外文翻译资料
- 太阳能电池中的GaSb / InGaAs 量子点阱混合结构有源区外文翻译资料




