富Sn对p型掺杂Cu2SnS3热电性能的影响毕业论文
2020-04-23 20:15:05
摘 要
高性能的环境友好型热电材料在当下的能源环境下拥有重要的研究意义和应用前景。三元硫化物CTS (Cu2SnS3) 为p型热电材料。而CTS中,Co的掺入则显著的提高了其热电性能。但是,Co的加入之所以可以提升CTS的ZT值,是建立在高电导率、热导率和低塞贝克系数的基础之上的。为此本实验希望通过在掺杂Co10%和15%的CTS中加入熔点较低的锡 (熔点为231.89℃) ,以期在高温烧结过程中,使得其熔化并CTS的晶界或基相中形成了富锡相,形成“势垒”,阻碍低能量载流子的通过而获得一个高的塞贝克系数和更低的热导率。虽然,这会在一定程度上降低电导率,但是由于具有其耦合关系,这一工作也颇具挑战。
结果表明:
- 在不同含量Co掺杂的CTS中进行富锡,都对样品的塞贝克系数的提升起到积极的作用,且富锡量越大,塞贝克系数也越高,高温下(约450°C),Co掺杂15% CTS富锡7%的样品的塞贝克系数,就由未富锡样品的约100 V/K上升至富锡5%样品的489.7 V/K的高值。
- 样品的电导率却因为富锡量的上升而快速下降,Co掺杂10%CTS样品,相较于未富锡样品,富锡样品的电导率明显下降。50°C时,电导率由未富锡的样品的1049.8 Scm-1下降到富锡1%时的447.7 Scm-1。
- 由于电子热导的减小和较为合理的塞贝克系数、电导率,最终,富锡1%的样品均得到了最高的ZT值,使用Co掺杂量10%基体样品达到了0.66。
为此,虽然样品在富锡后,其塞贝克系数的确得到了较大的提升,但是,由于未能保持合理的高电导率,最终得到的PF值并没有得到预期的提升。但是,因为富锡导致的热导率的下降,最终,富锡1%的样品仍表现出了最的性能。
关键词:Cu2SnS3 富锡 塞贝克系数 电导率 功率因子 ZT值
Abstract
Environmental friendly high-performance thermoelectric materials have important research significance and application prospects in the current energy environment. The ternary sulfide CTS (Cu2SnS3) is a p-type thermoelectric material. In CTS, the incorporation of Co significantly improves the thermoelectric performance. However, the addition of Co can increase the ZT value of CTS based on high conductivity, thermal conductivity and low Seebeck coefficient. For this reason, this experiment hopes to add a lower melting point of tin (melting point of 231.89°C) in the doped Co10% and 15% CTS, in order to melt it and form in the grain boundary or base phase of CTS during high temperature sintering. The tin-rich phase forms a "barrier" that hinders the passage of low-energy carriers to obtain a high Seebeck coefficient and lower thermal conductivity. Although this will reduce the conductivity to some extent, this work is also challenging due to its coupling relationship.
The results show:
1. The tin-rich in different content of Co-doped CTS plays a positive role in the increase of the Seebeck coefficient of the sample, and the larger the tin-rich amount, the higher the Seebeck coefficient, at high temperature (about 450°C), the Seebeck coefficient of a Co-doped 15% CTS tin-rich 7% sample increased from about 100 V/K for the non-rich tin sample to a high value of 489.7 V/K for the 5% tin-rich sample.
2. The conductivity of the sample decreases rapidly due to the increase in the amount of tin. Co-doped 10% CTS sample, the conductivity of the tin-rich sample is significantly lower than that of the non-rich tin sample. At 50°C, the conductivity decreased from 1049.8 Scm-1 for the non-rich tin sample to 447.7 Scm-1 for the tin rich 1%.
3. Due to the reduction of the electronic thermal conductivity and the reasonable Seebeck coefficient and conductivity, in the end, the highest ZT value was obtained for 1% of the tin-rich samples, and 0.66 was used for the 10% matrix sample with Co doping.
For this reason, although the Seebeck coefficient of the sample has been greatly improved after the tin-rich tin, the final PF value has not been expected to increase due to the failure to maintain a reasonable high conductivity. However, because of the decrease in thermal conductivity caused by tin-rich, in the end, 1% of tin-rich samples still showed the best performance.
Key words: Cu2SnS3; Sn-rich CTS; Seebeck coefficient; Power factor; ZT
目 录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 课题研究背景 1
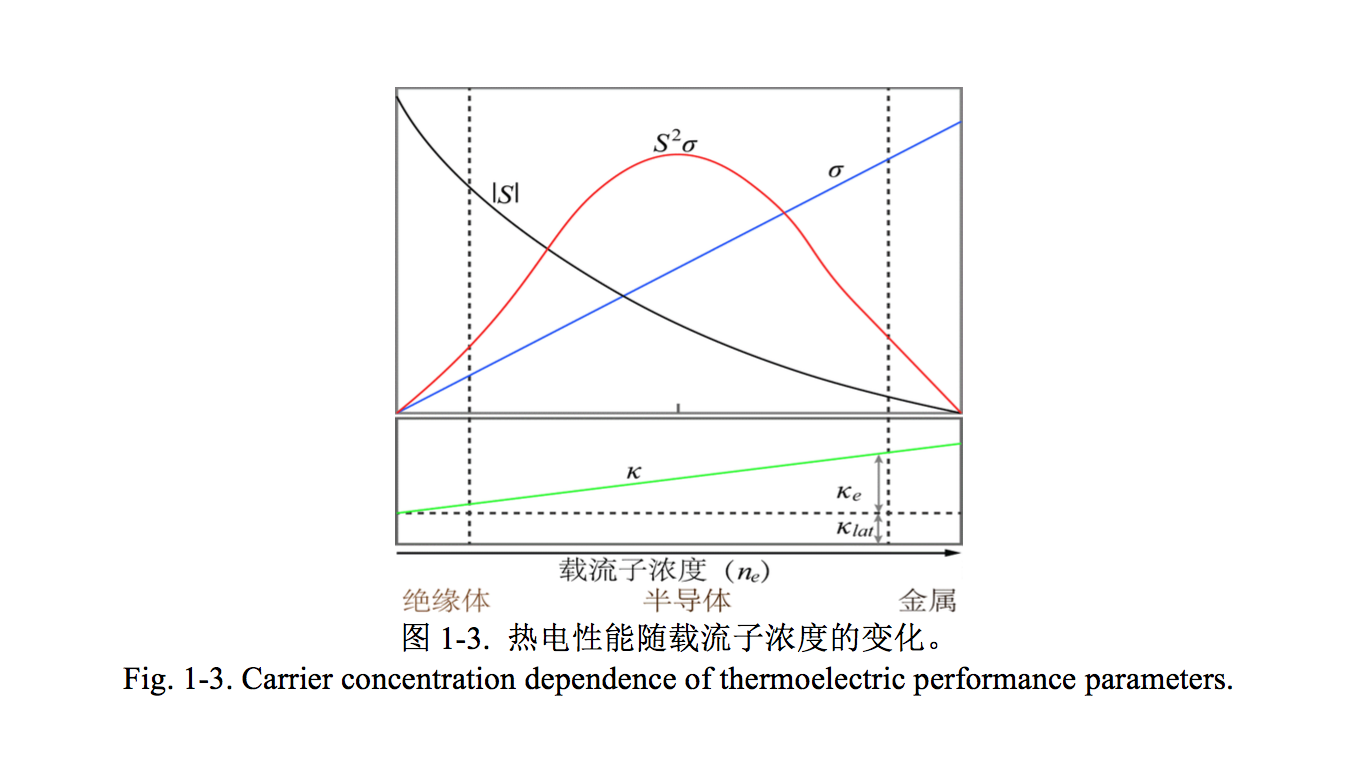
1.2 热电材料简介 2
1.2.1 热电材料理论 2
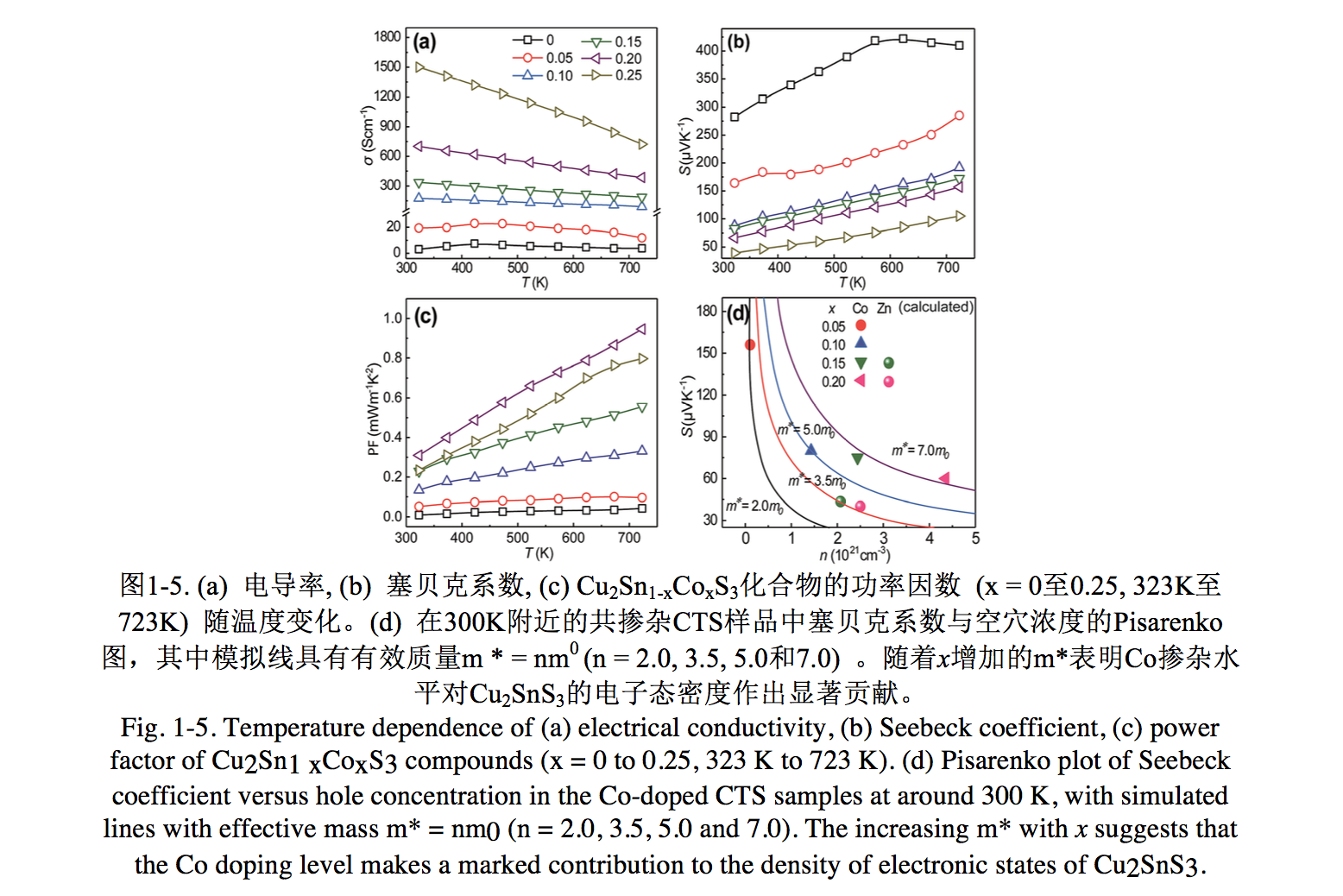
1.2.2 三元硫化物Cu2SnS3 6
1.3 本课题的研究目的和内容 7
第二章 实验方法 9
2.1 样品制备及原料仪器 9
2.2 样品制备方法 9
2.2.1 高温合成反应 9
2.2.2 对CTS基体富锡 10
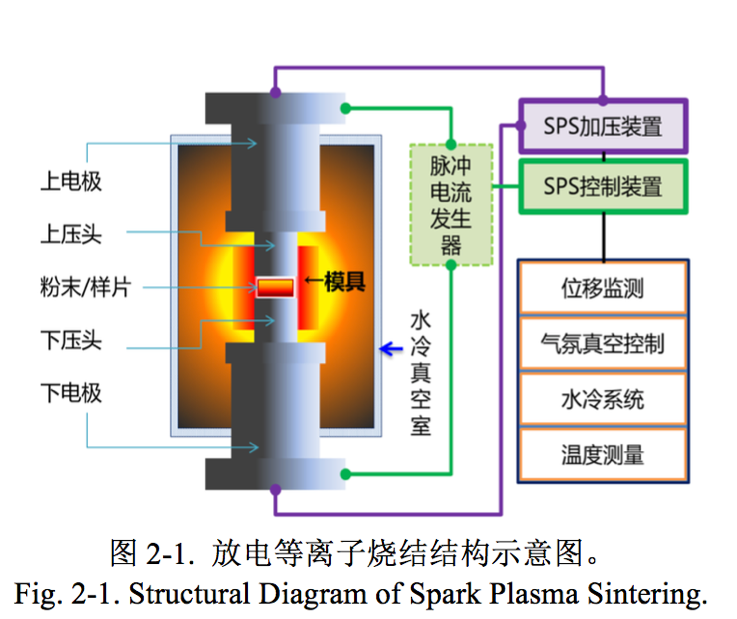
2.2.3 放电等离子烧结 10
2.3 样品分析与表征 10
2.3.1 相组成分析 10
2.3.2 显微结构分析 11
2.3.3 密度测试 11
2.3.4 电输运性能测试 11
第三章 富锡对10%Co掺杂CTS热电性能的影响 12
3.1 引言 12
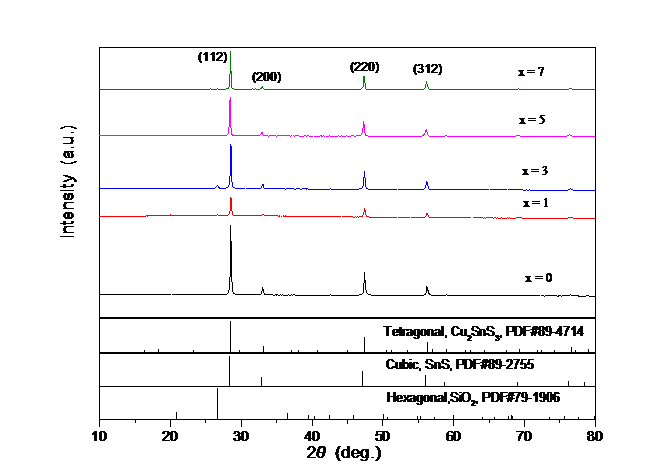
3.2 物相分析 12
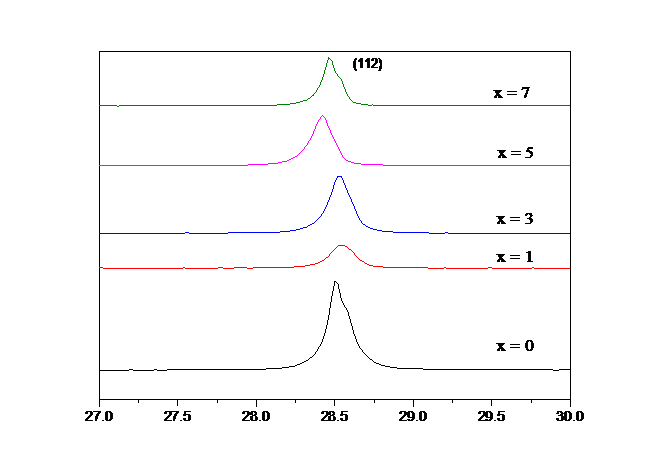
3.2.1 XRD分析 12
3.2.3 密度测试 14
3.3 电输运特性 15
3.3.1 电导率 15
3.3.2 塞贝克系数 15
3.3.3 功率因子 16
3.4 热传导特性 17
3.4.1 电子热导 17
3.4.2 ZT值 18
3.5 本章结论 19
第四章 富锡对15%Co掺杂CTS热电性能的影响 20
4.1 引言 20
4.2 物相分析 20
4.2.1 XRD分析 20
4.2.2 SEM分析 22
4.2.3 密度测试 22
4.3 电气输运性能 23
4.3.1 电导率 23
4.3.2 塞贝克系数 24
4.3.3 功率因子 25
4.4 热传导特性 26
4.4.1 电子热导 26
4.4.2 ZT值 26
4.5 本章结论 27
第五章 结论 28
参考文献 30
致 谢 33
第一章 绪论
1.1 课题研究背景
目前,在全世界范围内,对能源的需求依然旺盛,对能源的消耗也在不断的增长。但是,化石能源(以煤炭等为主)的产量却在下降。就长期的发展来看,目前的以不可再生能源为主的能源结构是无法满足社会发展的需求的。于是,在全世界对清洁能源的共同需求的背景下,热电材料也受到了更多的关注[1]。
仅以我国来看,我国2018年GDP超过13.6万亿,经济增量达到1.4万亿美元,全球经济新增量的30%来自中国。而能源则是经济和工业发展的重要基础。随着我国的工业(尤其是新兴工业)和经济的快速发展,我国对能源的需求也在不断的提高。但是,随着能源消耗上升而来的是严重的环境污染问题。2018年仅中国就占全球二氧化碳排放量的27%,相较2017年增长4.7%,化石燃料排放量创下新高。同时,严重的雾霾、全球变暖所带来的反常气候和大气、水体、土壤的污染也愈发严重。但是,化石能源燃烧所释放的能量利用率仅仅在30%左右,有大约70%的能量都以热能、光能等形式被浪费。为此,寻找某种可以低损耗、高效率、无毒害、制备工艺简单的技术以做到有效的利用这部分能量,将会成为一个对解决能源浪费、污染问题和可持续发展问题的行之有效的解决方案和未来新能源的一个重要发展方向[2]。
相关图片展示:

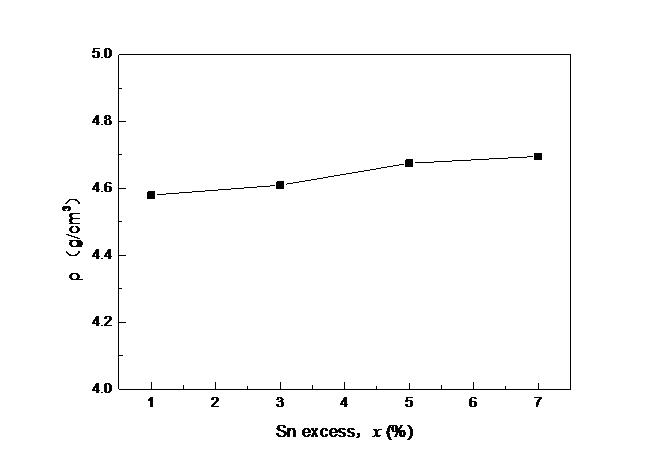
您可能感兴趣的文章
- 蒸养纤维掺杂高铁低钙水泥混凝土的抗海水冲磨性能研究文献综述
- TIPA对水泥-锂渣体系力学性能和水化性能的影响外文翻译资料
- TEA对锂渣-水泥复合粘结剂流变性能及水化性能的影响外文翻译资料
- 硫酸铝无碱液体促进剂的效果研究烷醇胺对硅酸盐水泥水化过程的影响外文翻译资料
- 新型C-A-S-H/PCE纳米复合材料:设计表征和对水泥水化的影响外文翻译资料
- 工业中碳捕获技术以及以水泥回转窑作为核心的吸附再生器外文翻译资料
- Ca/Al层状双氢氧化物的制备及其结构对水泥早期强度的影响外文翻译资料
- 蒸汽养护后混凝土养护方法对混凝土机械强度和透气性的影响外文翻译资料
- 含白云石或石灰石的偏高岭土水泥在相组成与抗压强度的异同外文翻译资料
- 与硅质铁尾矿结合的混凝土的耐久性外文翻译资料




