玻璃表面微结构制备方法比较与性能预测毕业论文
2021-12-09 17:18:11
论文总字数:25013字
摘 要
玻璃及玻璃制品因其良好的光学性能,高化学稳定性,原料来源广泛等优点,而作为建筑、装饰材料被广泛应用,随着信息技术和光伏技术的发展,玻璃的应用领域进一步扩展。但玻璃应用的日渐广泛,也带来了光污染,清洁成本大等问题亟待解决,这就需要玻璃这一材料能具有易清洁,防眩光等性能。通过对自然生物表面的研究,这些性能均与表面微结构密切相关。玻璃表面制备微结构的工艺与方法众多,包括机械加工法,化学蚀刻法,丝网印刷技术,镀膜技术等,本文对这些工艺与方法进行对比分析,以化学蚀刻法为研究对象,分析氟化物蚀刻法的反应机理;通过文献类比,从蚀刻液化学组成、反应时间、温度、酸处理三个方面对蚀刻工艺进行优化;观察微结构的表面形貌,结合形貌特点探究微结构对玻璃光学性能的影响;依据表面润湿性理论与模型分析微结构对玻璃表面润湿性能影响。
通过文献类比和分析预测,得到以下结果:
(1)氟化物蚀刻玻璃的表面微结构形成原理在于生成难溶性氟硅酸盐覆盖在玻璃表面,防止玻璃进一步受到蚀刻,而玻璃未被覆盖处继续发生蚀刻反应,造成玻璃表面不均匀蚀刻,形成蜂窝状微结构。
(2)蚀刻形成的蜂窝状微结构的好坏取决于难溶性氟硅酸盐形成晶粒尺寸、分布是否均匀。蚀刻液中加入铵盐、氟化钙以及硫酸钡等分散剂可使生成的晶粒尺寸适当减小,均匀分布在玻璃表面,利于蜂窝状微结构的形成。此外,通过控制蚀刻反应的时间和温度、蚀刻液选用硫酸处理也可达到优化蚀刻工艺的目的。
(3)表面微结构诱导玻璃发生性能转变,使玻璃保证高透光率的同时具有显著防眩光性能;表面微结构使玻璃表面亲水性增强,在低表面能物质修饰后,可实现超亲水性向超疏水性转变。
关键词:玻璃表面微结构;化学蚀刻工艺;光学性能;润湿性
Abstract
Glass and glass products are widely used as construction and decoration materials due to their good optical properties, high chemical stability, and a wide range of raw material sources. With the development of information technology and photovoltaic technology, the application field of glass has been further expanded. However, the increasing application of glass has also brought about problems such as light pollution and high cleaning costs. This requires glass to be easy-cleaning and with other excellent properties such as anti-glare. Through the study of natural biological surfaces, these properties are closely related to the surface microstructure. There are many processes and methods for preparing microstructures on the glass surface, including mechanical processing, chemical etching, screen printing technology, coating technology,etc.This paper makes a comparative analysis of these processes and methods, and takes chemical etching method as the research object to analyze the reaction mechanism of fluoride etching method.By analogizing literatures , the etching process can be optimized from three aspects: composition of etching solution, reaction time, temperature and acid treatment. The influence of the microstructure on the optical properties of glass was investigated combined with observation of the surface morphology of the microstructure.According to the surface wettability theory and model, the influence of microstructure on the surface wettability of glass was analyzed.
Through analogizing and analysing literatures, the following results are obtained:
(1) The surface microstructure formation principle of fluoride etched glass lies in the forming of insoluble fluorosilicate covering the glass surface,which prevents the glass from being further etched, while the etching reaction continues to occur where the glass is not covered, resulting in uneven etching of the glass surface and the formation of honeycomb microstructure.
(2) The quality of honeycomb microstructure formed by etching depends on the size of crystalline grains and uniform distribution of insoluble fluorosilicate.By adding ammonium salt,calcium fluoride and dispersants such as barium sulfate into the etching solution, the size of crystalline grains can be reduced appropriately and crystalline grains were evenly distributed on the glass surface, which is benefit to the forming of honeycomb microstructure.In addition, the etching process can be optimized by controlling the time and temperature of etching reaction and selecting sulfuric acid to treat the etching solution.
(3) The surface microstructure induces the transformation of the glass’s properties , so that the glass has high light transmittance and significant performance of anti-glare;The surface microstructure enhanced the hydrophilicity of the glass surface, and the transformation from superhydrophilicity to superhydrophobicity could happen after the modification of low surface energy materials.
Key Words:microstructure on glass surface;chemical etching process;optical properties;wettability
目 录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 固体表面润湿性 1
1.2 生物表面微结构与特殊湿润性 1
1.3 固体表面润湿性理论与模型 2
1.3.1 接触角与Young方程 2
1.3.2 Wenzel模型 2
1.3.3 Cassie-Baxter模型 3
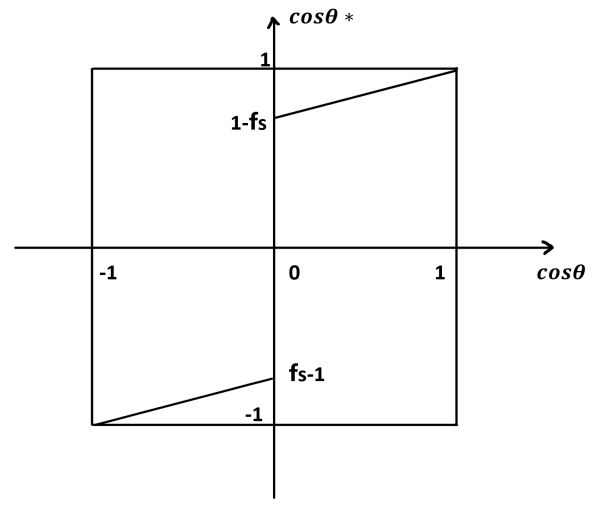
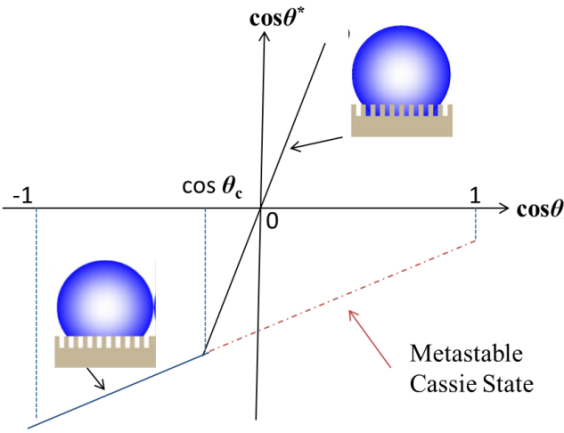
1.3.4 Wenzel状态与Cassie状态之间的关系 4
1.3.5 滚动角理论 5
1.4 玻璃表面微结构制备工艺 6
1.4.1 机械加工法 6
1.4.2 化学蚀刻法 6
1.4.3 玻璃的丝网印刷工艺 9
1.5 研究意义与内容 10
第2章 氟化物蚀刻玻璃机理及工艺优化 12
2.1 引言 12
2.2 氟化物蚀刻工艺流程与分析方法 12
2.2.1 蚀刻流程 12
2.2.2 蚀刻后样品的测试与表征 12
2.3 氟化物蚀刻玻璃反应机理 13
2.4 蚀刻工艺的优化 15
2.4.1 蚀刻液组成的优化 15
2.4.2 蚀刻温度和时间的优化 16
2.4.3 酸处理的优化 18
2.5 本章小结 19
第3章 表面微结构对玻璃光学性能的影响 20
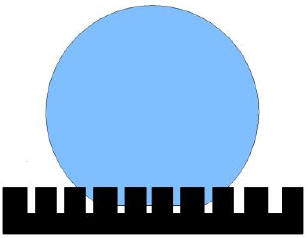
3.1 表面微结构形貌研究 20
3.2 表面微结构对玻璃透光率的影响 20
3.3 表面微结构对玻璃反射率和雾度的影响 21
3.4 本章小结 23
第4章 表面微结构对玻璃表面润湿性的影响 24
4.1 表面微结构对玻璃表面亲水性的影响 24
4.2 表面微结构对玻璃表面疏水性的影响 25
4.3 本章小结 26
第5章 结论与展望 27
5.1 结论 27
5.2 展望 27
参考文献 28
致谢 30
第1章 绪论
1.1 固体表面润湿性
润湿是一种流体从固体表面置换另一种流体的过程,是固体表面最为常见的现象之一,广泛存在于自然界和人类生产生活中。固体表面润湿性不仅是基础理论研究的重要领域,而且还在涂层、印刷、防水等工业领域具有重要应用前景。玻璃作为日常生活最常见的固体表面之一,其表面清洁便与润湿过程息息相关,众多研究人员以表面润湿性为理论基础,对玻璃表面进行超亲水或超疏水改性,研制出易清洁玻璃。可见,研究固体表面润湿行为,掌握润湿规律对于理论研究和指导实际生产有着重要意义。
1.2 生物表面微结构与特殊湿润性
自然界中有许多生物为适应生存环境而进化出了特殊的润湿性能,经过大量研究发现,这些特殊的润湿性能与表面微纳结构有密切关系。
1997年W.Barthlott与C.Neinhuis发现发现并报道了荷叶表面水滴滚落带走灰尘等污染物的自清洁特性,并将其命名为荷叶效应[1]。他们将荷叶这一特殊润湿性能归结于荷叶表面的微米级乳突和覆盖在乳突表面的低表面能的蜡晶状物质(如图1.1所示)。之后大量研究人员投入到植物叶片表面研究,研究发现水稻叶、芋头叶、玫瑰花瓣等表面均存在微纳复合结构,因而具有疏水性或其他优异性能。
请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:25013字
相关图片展示:


您可能感兴趣的文章
- 蒸养纤维掺杂高铁低钙水泥混凝土的抗海水冲磨性能研究文献综述
- TIPA对水泥-锂渣体系力学性能和水化性能的影响外文翻译资料
- TEA对锂渣-水泥复合粘结剂流变性能及水化性能的影响外文翻译资料
- 硫酸铝无碱液体促进剂的效果研究烷醇胺对硅酸盐水泥水化过程的影响外文翻译资料
- 新型C-A-S-H/PCE纳米复合材料:设计表征和对水泥水化的影响外文翻译资料
- 工业中碳捕获技术以及以水泥回转窑作为核心的吸附再生器外文翻译资料
- Ca/Al层状双氢氧化物的制备及其结构对水泥早期强度的影响外文翻译资料
- 蒸汽养护后混凝土养护方法对混凝土机械强度和透气性的影响外文翻译资料
- 含白云石或石灰石的偏高岭土水泥在相组成与抗压强度的异同外文翻译资料
- 与硅质铁尾矿结合的混凝土的耐久性外文翻译资料




