表面粗糙度对求解薄膜光学常数的影响毕业论文
2021-12-09 17:29:48
论文总字数:20039字
摘 要
光学常数包括折射率和消光系数,是决定薄膜光学性能的基本物理量,其准确求解意义重大。传输矩阵法是求解薄膜光学常数的常用方法。传输矩阵是一种反映光通过多个界面与介质后电场矢量变化的矩阵,包含着薄膜各层的光学常数、膜厚信息。根据传输矩阵,可以推导薄膜系统的反射率、透射率;反过来,通过求解隐函数方程,也可以得到薄膜的光学常数。
表面粗糙的薄膜厚度不均匀,这会导致光的散射和非相干效应,此时使用传输矩阵法求解的光学常数不再准确。已知对于表面粗糙度较小的薄膜,可以引入Fresnel矫正因子来表示此时的菲涅尔反射、透射系数。据此,本文提出了修正的传输矩阵法,用于优化粗糙薄膜光学常数的求解。
在实验过程中,本文首先根据Fresnel矫正因子计算了不同粗糙度薄膜的反射率、透射率。随后,通过计算探讨了在使用修正的传输矩阵法求解光学常数时,表面粗糙度估计误差对结果的影响。最后,在实际薄膜中使用修正的传输矩阵法求解光学常数,并与传输矩阵法的求解结果对比,验证修正的传输矩阵法的有效性。
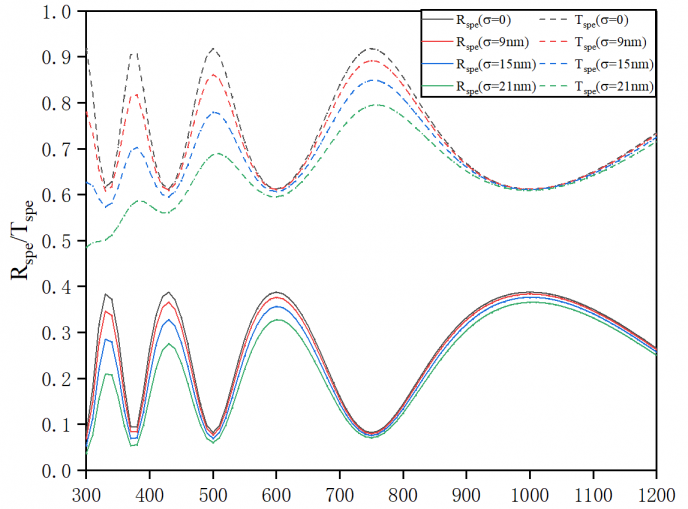
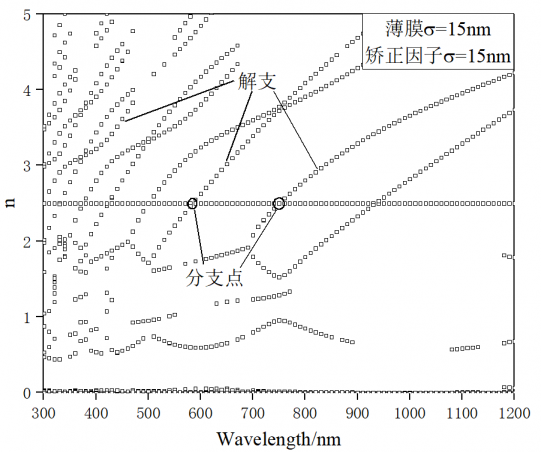
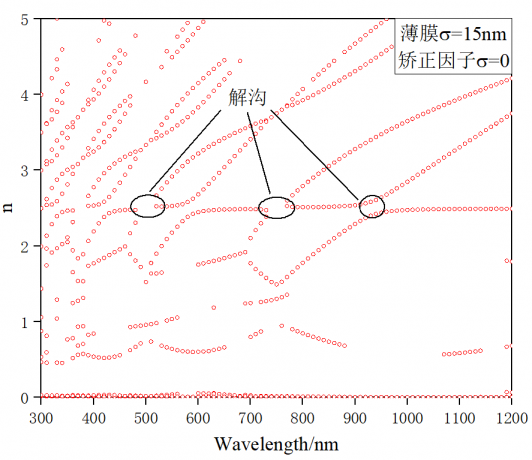
研究结果表明:在使用传输矩阵法求解薄膜的光学常数时,由于表面粗糙度的影响,解曲线不连续,以解沟为间隔交替偏大、偏小。而在使用修正的传输矩阵法时,随着表面粗糙度估计值接近实际值,解曲线向真实的光学常数逼近,解沟逐渐消失。在实际薄膜中的验证也表明,使用修正的传输矩阵法的解曲线连续性更好,在短波区结果的准确度有较大提升。
关键词:传输矩阵法;表面粗糙度;光学常数;Fresnel矫正因子
Abstract
Optical constants, including refractive index and extinction coefficient, are the basic physical quantities that determine the optical properties of thin films, and their accurate solution is of great significance. Transfer-Matrix method is a common method for determining the optical constants of thin films. Transfer-Matrix is a matrix reflecting the change of the electric field vector after the light propagates in multiple interfaces and media. It contains the optical constants and film thickness information of each layer. Using the Transfer-Matrix, the reflectance and transmittance of the film system can be derived; conversely, by solving the implicit function equation, the optical constant of the film can also be obtained.
The uneven thickness of the rough surface will result in light scattering and incoherent effects, lead to a deviation of the optical constants solved by the Transfer-Matrix method in the actual thin film. It is known that for thin films with small surface roughness, Fresnel correction factors can be introduced to represent the Fresnel reflection and transmission coefficients. Therefore, this paper proposes a Modified Transfer-Matrix method for optimizing the solution of the optical constants of rough films.
During the experiment, the paper first calculated the reflectance and transmittance of the films with different roughness according to the Fresnel correction factor. Then, through calculation, the influence of surface roughness estimation error on the results when using the Modified Transfer-Matrix method to solve the optical constants is discussed. Finally, the Modified Transfer-matrix method is used to solve the optical constant in the actual film, and compared with the results of the Transfer-Matrix method to verify the effectiveness of the Modified Transfer-Matrix method.
The research results show that: when using the Transfer-Matrix method to solve the optical constant of the film, the solution curve is discontinuous due to the effect of surface roughness, and the solution grooves are alternately larger and smaller at intervals. When the Modified Transfer-Matrix method is used, as the estimated value of surface roughness approaches the actual value, the solution curve approaches the true optical constant, and the solution groove gradually disappears. The verification in the actual film also shows that the solution curve using the Modified Transfer-Matrix method is better in continuity, and the accuracy of the results in short wavelength region is greatly improved
Key Words:Transfer-Matrix method;Surface roughness;Optical constants;modified Fresnel coefficients
目录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 光学薄膜简介 1
1.2 薄膜光学的基本理论简介 1
1.2.1 薄膜介质的光学常数 1
1.2.2 平面光波透过膜系时的反射率与透射率 3
第2章 光学薄膜特性的理论计算 5
2.1 传输矩阵法求解薄膜的反射率、透射率 5
2.2 传输矩阵法求解薄膜的光学常数 7
2.3 表面粗糙度矫正因子 8
2.4 RefDex软件介绍 9
第3章 引入矫正因子的理想薄膜中表面粗糙度的影响 12
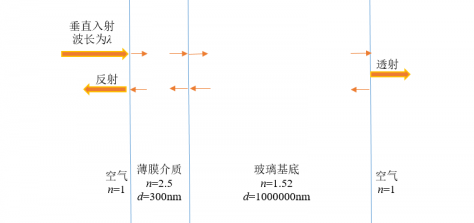
3.1 表面粗糙度对反射率与透射率的影响 12
3.3 表面粗糙度对光学常数求解的影响 14
3.2.1 具有表面粗糙度的理想薄膜的光学常数求解 14
3.2.1 解集的过滤与分析 14
第4章 矫正因子对实际薄膜光学常数求解的优化 21
4.1 CuGaSe2光学薄膜 21
4.2 光学常数的求解 21
4.3 结果对比 23
第5章 小结 25
参考文献 26
致谢 28
第1章 绪论
1.1 光学薄膜简介
光学薄膜是由薄的分层介质构成的,通过界面传播光束的一类光学介质材料。光学薄膜在各个领域的应用和普及,始于20世纪30年代物理气相沉积制备法的出现。如今,几乎所有的光学系统、光电系统或光电仪器都离不开光学薄膜,也找不到别的技术可以取代光学薄膜。
基于光学薄膜良好的空间周期结构,我们根据光学薄膜理论对薄膜的结构、组分和性能进行复杂的人工剪裁和设计,从而得到想要的优良性能。按实际应用可以把光学薄膜分类为反射膜、增透膜、滤光膜、光学保护膜、偏振膜、分光膜和位相膜等。光学反射膜可以增加反射率,常用来制造反光、折光和共振腔器件。光学增透膜沉积在光学元件表面,可以减少表面反射,增加光学系统透射。光学滤光膜是指衰减光强度或改变光谱成分的膜层,常用来增减色温、改变波长,遮住不需要的光、改变颜色等[1]。
在新兴的科技领域,光学薄膜同样有着广泛的发展前景。各种新型微结构薄膜相继出现,如高强度激光膜、金刚石及类金刚石膜、软X射线多层膜、太阳能选择性吸收膜和光通信用光学膜等[2],给光学薄膜技术注入新的生命力。薄膜技术的研究方兴未艾,从薄膜的制备、微结构研究,到物理机制、性能的表征,以及各种应用开发研究,都有新领域值得我们探索。
1.2 薄膜光学的基本理论简介
光学薄膜的理论基础是电磁场理论和麦克斯韦方程,涉及光在传播过程中,通过分层介质时的反射、透射和偏振特性等。
最简单的光学薄膜模型是表面光滑、各向同性的均匀介质薄层。在这种情况下,可以用光的干涉理论来研究光学薄膜的光学性质。当一束单色平面波入射到光学薄膜上时,在它的两个表面上发生多次反射和折射,反射光和折射光的方向由反射定律和折射定律给出,反射光和折射光的振幅大小则由菲涅耳公式确定。
1.2.1 薄膜介质的光学常数
物质光学常数是决定物质光学性能的核心基本参数,由介质的折射率n与消光系数k两部分组成。其物理意义以及推导如下。
对于各向同性介质中的电磁场,有麦克斯韦方程组:
其中,D是电位移矢量,E是电场强度矢量,H是磁场强度矢量,B是磁感应强度矢量,j和jD分别是传导电流密度矢量和位移电流密度矢量( ),而ρ是电荷体密度。
),而ρ是电荷体密度。
以及联系电磁场基本矢量与介质特性的物质方程:
请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:20039字
相关图片展示: