亚铜离子激活玻璃荧光太阳能聚集器的仿真分析毕业论文
2021-12-09 17:25:42
论文总字数:25704字
摘 要
亚铜离子(Cu )具有的紫外-可见发光效率高、荧光寿命短、地壳丰度高和价格低廉等特点,因而能用于开发新型的荧光玻璃。Cu 激活荧光玻璃因在可见光区无明显吸收带,能特别适合用于要求高可见光透过的领域。与有机聚合物基质材料相比,荧光玻璃具折射率可调节幅度大,及热稳定性、化学稳定性和力学性能良好等特点,在白光LED和荧光太阳聚集器(LSC)等成本敏感领域具有重要的潜在应用。虽然,最近Cu 激活荧光玻璃在发光效率、大斯托克斯位移和热稳定性等方面取得了不小的进展。但是,Cu 激活玻璃在LSC器件领域的应用研究,目前仍罕见报道。因此,本实验希望借助试验数据结合理论分析的方法,对基于Cu 激活玻璃的LSC器件进行性能分析,揭示影响效率的关键光谱性质参数,以便指导Cu 激活荧光玻璃进一步的实用化开发。
本文首先综述了Cu 荧光玻璃的研究进展,然后选择钙铝硅酸盐玻璃体系,采用熔融淬冷法,成功地制得了具有大斯托克斯位移的橙黄色Cu 激活荧光玻璃,并对比分析不同氧化锗含量的样品的光谱性质。通过分析LSC的结构及能量转换过程,构筑数学模型对光子的吸收过程进行仿真研究,主要研究了Cu 激活玻璃作为夹层的基于平面玻璃光波导的LSC的光电转换效率,实验主要通过改变荧光量子效率及模型尺寸来探讨光电转换效率及收益比的变化趋势。
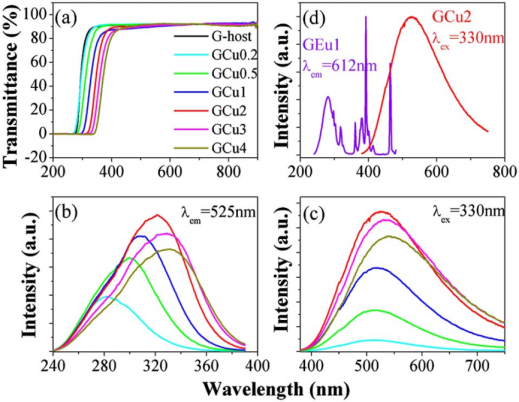
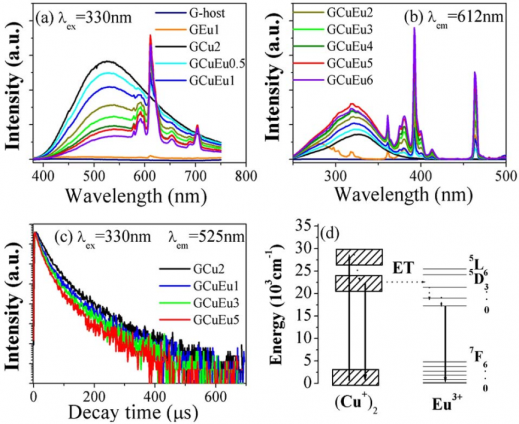
研究结果表明:含有氧化锗的铝硅酸盐玻璃存在两种适合Cu 的格位,分别对应350nm/525nm和400nm/700nm的激发带/发射带,且前者具备更高的荧光量子效率(PLQY);Cu 激活玻璃的PLQY越高,LSC的光电转换效率也越大,随着尺寸的增加,光电转换效率呈现出先增大而后减小的趋势。
关键词:Cu 离子;荧光玻璃;荧光太阳聚集器
Abstract
Copper ion (Cu ) has the characteristics of high ultraviolet-visible luminous efficiency, short fluorescent life, high crustal abundance and low price, which can be used to develop new fluorescent glass. Cu activated fluorescent glass has no obvious absorption band in the visible light region, which is particularly suitable for applications that require high visible light transmission. Compared with organic polymer matrix materials, fluorescent glass has a large adjustable refractive index, good thermal stability, chemical stability and mechanical properties, which has important potential applications in cost-sensitive areas such as white LEDs and fluorescent solar concentrators (LSC). Although, recently, great progress has been made in Cu activated fluorescent glass in luminous efficiency, large Stokes shift and thermal stability. The application research of Cu activated glass in the field of LSC devices is still rarely reported. Therefore, this experiment hopes to use the experimental data combined with theoretical analysis to perform performance analysis on LSC devices which based on Cu activated glass to reveal the key spectral properties parameters that affect efficiency, so as to guide the further practical development of Cu activated fluorescent glass.
In this paper, the research progress of Cu fluorescent glass was reviewed at first, and then the calcium aluminum silicate glass system was selected as the study object. By using the melt quenching method, orange-yellow emitting Cu activated fluorescent glasses with large Stokes shift were successfully prepared, and comparative analysis on the spectral properties of glass samples with different germanium oxide content was carried out. By analyzing the structure and energy conversion process of LSC, the photon absorption process was simulated by building a mathematical model, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency of LSC based on planar optical waveguide in a laminated glass with Cu activated glass as the interlayer was studied. In the experiment, the dependence of the photoelectric conversion efficiency and the ratio of revenue of LSC was explored as factors of the fluorescence quantum efficiency of Cu activated glass and the size of LSC.
The results show that there are two sites suitable for Cu in aluminosilicate glass containing germanium oxide, in which their corresponding excitation/emission bands were found to be at 350nm/525nm and 400nm/700nm, respectively. And the first one shows a higher photoluminescence quantum efficiency (PLQY). If there is a higher the PLQY of Cu activated glass, the greater the photoelectric conversion efficiency of LSC could be observed. As the size increasing, the photoelectric conversion efficiency increased first and then decreased.
Key Words: Cu ions; Fluorescent glass; Fluorescent solar concentrator
目录
第1章 绪论
1.1 亚铜离子激活发光材料
1.1.1 亚铜离子在晶体中的发光
1.1.2 亚铜离子配合物的发光
1.1.3 亚铜离子负载沸石材料的发光
1.1.4 亚铜离子在玻璃中的发光
1.2 亚铜离子激活荧光玻璃
1.2.1 亚铜离子在玻璃中的发光性质特点
1.2.2 基于平面光波导的太阳能荧光聚集器
1.2.3 “三明治”结构的玻璃太阳能荧光聚集器
1.3 课题的主要研究内容、目的和意义
第2章 亚铜离子荧光玻璃的制备和光学性质表征
2.1 实验的原料和采用的设备
2.2 玻璃的制备和表征的流程
2.3 玻璃的透过和吸收
2.4 玻璃的发光性能
第3章 太阳能荧光聚集器的仿真研究
3.1 太阳能荧光聚集器的工作原理
3.2 太阳能荧光聚集器的蒙特卡洛理论
3.3 太阳能荧光聚集器的数学模型
3.3.1太阳能荧光聚集器的自吸收现象
3.4 太阳能荧光聚集器的荧光收集效率
3.5 太阳能荧光聚集器的荧光传输效率
3.6 参数设定
3.6.1 太阳能电池及外层玻璃参数设定
3.6.2 亚铜离子荧光玻璃参数
3.7 仿真结果分析
3.7.1 收益参数分析及参数设定
3.8不同荧光量子效率及尺寸对光电转换效率的影响
第4章 结果与展望
4.1 研究总结
4.2 不足与展望
参考文献
致谢
附录1
第1章 绪论
发光是自然界中一种很常见的物理现象。它指的是物质将能量以光的形式发射出来的过程。为了将发光应用到生产生活中,人们开发了各式发光材料,制造了各种人工光源,并广泛应用于照明、显示、通信、激光和生物等领域。发光材料主要由基质和激活剂组成。其中,激活剂是能够产生发光的物质,它们能在不同基质环境中呈现出不同发光性质。因而,它们在发光材料中扮演发光中心的角色,并根据发光机制主要可分为复合发光中心、分立发光中心和复合离子型发光中心三类。在日程生活的实际应用中,发光材料最常见的激发方式为光致发光和电致发光。其中,光致发光的过程如图1.1所示。A表示发光中心,它的光致发光可分为光激发,受激吸收、光辐射返回基态或非辐射返回基态三个阶段。
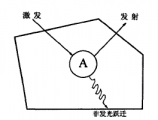
图1.1 光致发光的过程示意图[[1]]
请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:25704字
相关图片展示: