Ag属硫族化合物薄膜热电材料的MBE制备及输运性质研究毕业论文
2021-12-10 17:49:02
论文总字数:35411字
摘 要
在众多新能源材料中,热电材料是一种可以实现热能和电能直接可逆转换的新能源材料。在过去的几十年,热电材料已经获得了广泛研究,其主要内容包括材料热电性能及其优化机制研究、高性能新型热电材料的开发以及高效温差发电器件和高效制冷器件的研发。在热电应用领域,热电转换技术已经在室温附近的制冷和精确温控领域获得了较为成熟的商业应用。但目前热电材料的能源转换效率大多低于10%,因此研究者们一直致力于探索更加高效的热电材料。Ag属硫族化合物是一种具有热电潜力的新型材料,理论计算表明Ag2Te、Ag2Se分别是拓扑绝缘体和外尔半金属,根据多带传输模型,有望在室温附近获得较高的功率因子。
本论文以Ag属硫族化合物为研究对象,采用分子束外延生长(Molecular Beam Epitaxy,简称MBE)在原子尺度上控制薄膜的生长。研究MBE不同工艺参数对Ag属硫族化合物热电薄膜材料的物相、微观结构和输运性能的影响。本论文研究的主要内容和结果如下:
- 采用分子束外延生长可以得到致密度高、结晶性良好的Ag属硫族化合物热电薄膜材料,且通过原位观测表明符合化学计量比。
- 元素束流比、薄膜生长温度是MBE生长的主要调控参数;提高生长温度将促进生长薄膜的结晶性,且薄膜产物的组成,主要依赖于元素束流比。
- Ag属硫族化合物热电薄膜材料在高于相变温度生长时,其晶粒尺寸较大,结晶性较好,但若生长温度过高,Se、Te的反蒸发效应变得显著,不利于产物组分的调控。
- 通过外延生长的Ag2Te薄膜,获得目前文献报道的室温最佳功率因子1.1 mWm-1K-2,为目前该体系最好结果。
关键词:Ag属硫族化合物;MBE外延生长;热电薄膜材料
Abstract
Among many new energy materials, thermoelectric material is a new energy material that can directly and reversibly convert thermal energy and electrical energy. In the past few decades, thermoelectric materials have obtained extensive research, and their main contents include research on the thermoelectric properties of materials and their optimization mechanisms, the development of high performance new thermoelectric materials, and the development of high-efficiency thermoelectric power generation devices and high-efficiency refrigeration devices. Thermoelectric conversion technology has obtained relatively mature commercial applications in the fields of refrigeration and precise temperature control near room temperature. However, the energy conversion efficiency of thermoelectric materials is currently below 10%, so researchers have been working to explore more efficient thermoelectric materials. Ag-chalcogen compound is a new material with thermoelectric potential. Theoretical calculations show that Ag2Te and Ag2Se are topological insulators and Weir semimetals respectively. According to the multi-band transmission model, it is expected to obtain a higher power factor near room temperature.
In this thesis, Ag2X(X=S、Se、Te)is used as the research object. And MBE (Molecular Beam Epitaxy) is used to control the growth of the film on the atomic scale. The effects of different process parameters of MBE on the phase, microstructure and transport properties of Ag-chalcogen compound thermoelectric thin film materials were studied. The main contents and results of this paper are as follows:
(1) Ag-chalcogen compound thermoelectric thin film material with high density and good crystallinity can be obtained by MBE, and in-situ observation shows that it meets the stoichiometric ratio.
(2) Element flux ratio and film growth temperature are the main control parameters of MBE. Increasing the growth temperature will promote the crystallinity of the growth film, and the composition of the film product mainly depends on the element beam flux ratio.
(3) When the Ag chalcogenide thermoelectric thin film material grows above the phase transition temperature, its grain size is larger and its crystallinity is better, but if the growth temperature is too high, the anti-evaporation effect of Se and Te becomes significant. This is not conducive to the regulation of product components.
(4) Through MBE grown Ag2Te thin film, the best room-temperature power factor 1.1 mWm-1K-2 reported in the literature is obtained, which is the best result of this system at present.
Key Words: Ag chalcogenide; MBE; Thermoelectric thin film material
目录
摘 要 I
Abstract II
第一章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景及意义 1
1.2 热电理论简介 1
1.2.1 热电效应 1
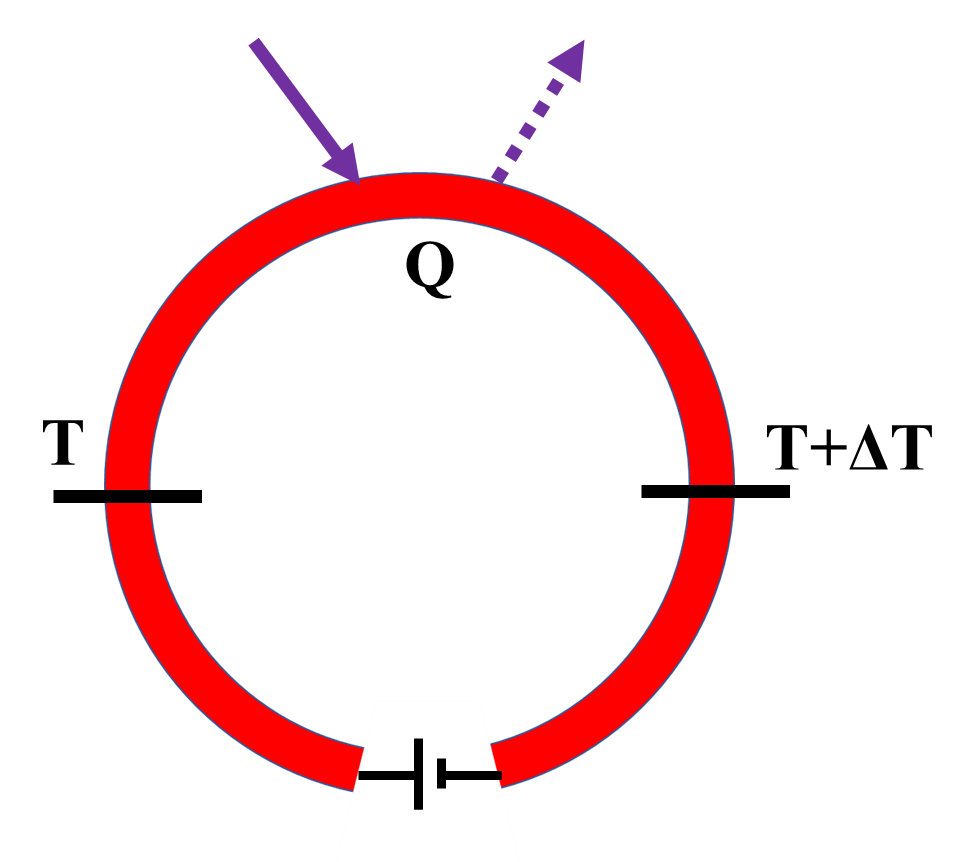
1.2.1.1塞贝克效应 1
1.2.1.2帕尔贴效应 2
1.2.1.3汤姆逊效应 3
1.2.1.4 Kelvin关系 3
1.2.2 热电材料的性能参数 4
1.2.3 热电材料的输运性质 4
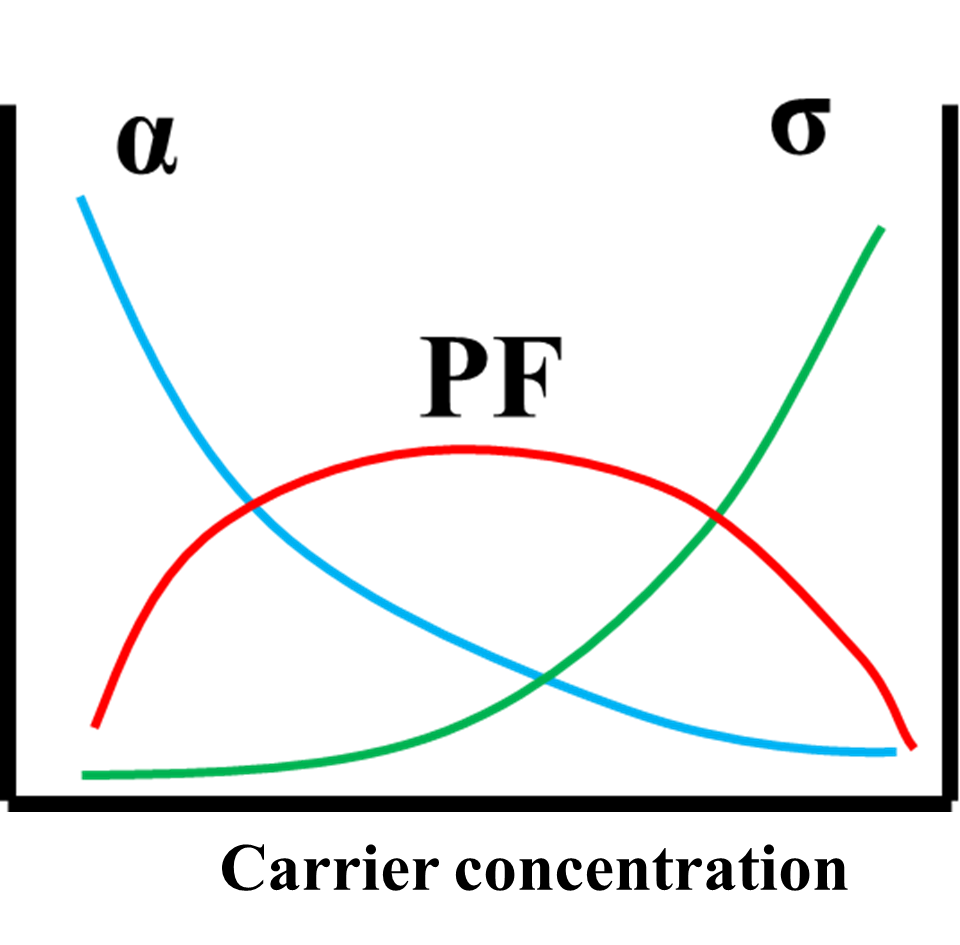
1.2.3.1 热电参数间的基本关系 4
1.2.3.2 载流子及其输运特性 5
1.3 热电材料 7
1.3.1 块体热电材料 7
1.3.2 薄膜热电材料 8
1.4 Ag属硫族化合物薄膜 9
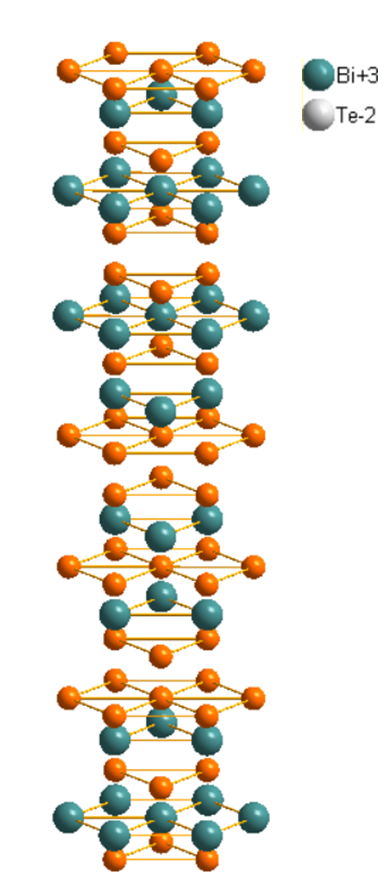
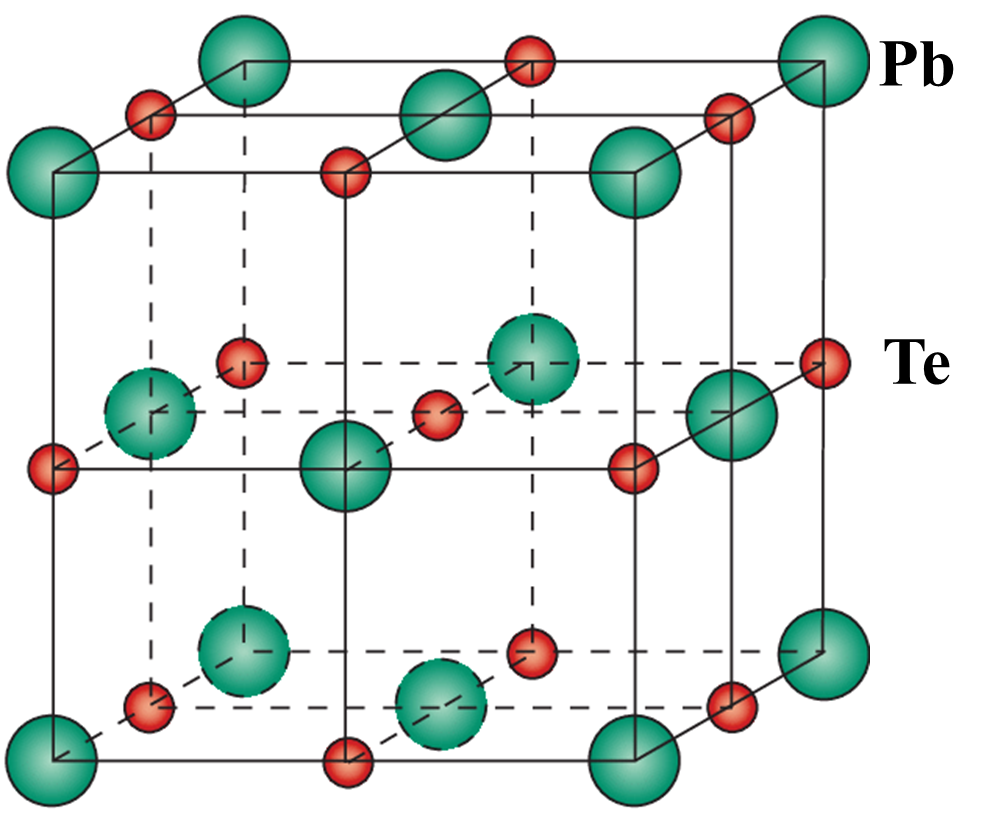
1.4.1 Ag属硫族化合物结构及特点 9
1.4.2 Ag属硫族化合物的制备方法 10
1.4.3 Ag属硫族化合物热电薄膜材料研究进展 10
1.5 本文主要研究内容 11
第二章 实验方法和实验设备 13
2.1 超高真空技术(UHV) 15
2.2 分子束外延技术(MBE) 17
2.3 结构表征 18
2.3.1 掠射角X射线衍射分析(GIXRD) 18
2.3.2 场发扫描电子显微镜(FESEM) 19
2.3.3 电子探针显微分析(EPMA) 19
2.3.4 光电子能谱测试分析(XPS) 19
2.3.5 原子力显微镜分析(AFM) 20
2.4 输运性能测试及设备 20
2.4.1 CTA电导率和塞贝克系数的测试 20
2.4.2 PPMS载流子浓度、迁移率测试 21
第三章 Ag2Te薄膜的可控生长工艺探索及其输运性能的研究 22
3.1 实验方案 22
3.2 不同Ag/Te束流比对Ag2Te薄膜物相、微结构和电性能的影响 22
3.2.1 不同束流比对Ag2Te薄膜物相的影响 22
3.2.2 不同束流比对Ag2Te薄膜微结构的影响 25
3.2.3 不同束流比对Ag2Te输运性能的影响 29
3.2 不同生长温度对Ag2Te物相、微观结构和电性能的影响 33
3.2.1 不同生长温度对Ag2Te物相的影响 33
3.2.2 不同生长温度对Ag2Te微结构的影响 34
3.3.3 不同生长温度对Ag2Te输运性能的影响 35
3.4 本章小结 36
第四章 Ag2Se的初步探索 37
第五章 总结和展望 39
5.1 论文研究总结 39
5.2 后续工作展望 39
参考文献 40
致谢 43
第一章 绪论
1.1 研究背景及意义
随着全球工业化的快速发展和人民生活水平的不断提高,不可再生的化石燃料资源的消耗大幅增加,带来的环境问题日益突出,全球面临能源需求持续增加、碳排放减少的双重挑战,因而保证能源供给和能源安全是各国政府要解决的重要问题。[1]因而,新能源材料以及新能源技术的开发和利用成为能源问题的主要解决途径。在众多新能源材料中,热电材料是一种可以实现热能和电能直接可逆转换的新能源材料。在过去的几十年,热电材料已经获得了广泛研究,其主要内容包括材料热电性能及其优化机制研究、开发高性能新型热电材料以及研发高效温差发电器件和高效制冷器件。并且热电材料在并在室温附近的制冷和精确温控领域获得了较为成熟的商业应用。虽然热电材料优势突出并已经实现商业应用,但是其大规模应用仍然有诸多的限制,其根源在于热电材料的热电转化效率较低、热电性能优化物理机制仍不够明确,因此,仍需要进一步深入研究热电材料的微观本质和内部机理。
1.2 热电理论简介
热电材料的相关物理理论可以追溯到19世纪早期。热电理论主要包括:三大热电效应及其关联、热电材料性能参数和热电材料的输运性质。
1.2.1 热电效应
请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:35411字
相关图片展示: