聚合物纳米复合材料中陶瓷纤维取向调控及性能研究毕业论文
2021-12-10 17:47:43
论文总字数:28232字
摘 要
有机聚合物电介质材料由于其具有高击穿场强、低介电损耗、柔性易加工等性能而被制成薄膜电容器,但是有机薄膜电容器的介电常数较低,不利于电容器的储能性能。在之前的研究中已经提出将具有高介电常数的陶瓷填料加入有机聚合物基体中,在有机聚合物基体具有高击穿场强的基础上,提升复合薄膜电容器的介电常数。值得注意的是,在薄膜电容器工作时,电场方向总是垂直于薄膜的面外方向,所以可以设计一种各向异性的结构来提高复合薄膜电容器在面外方向的介电性能。
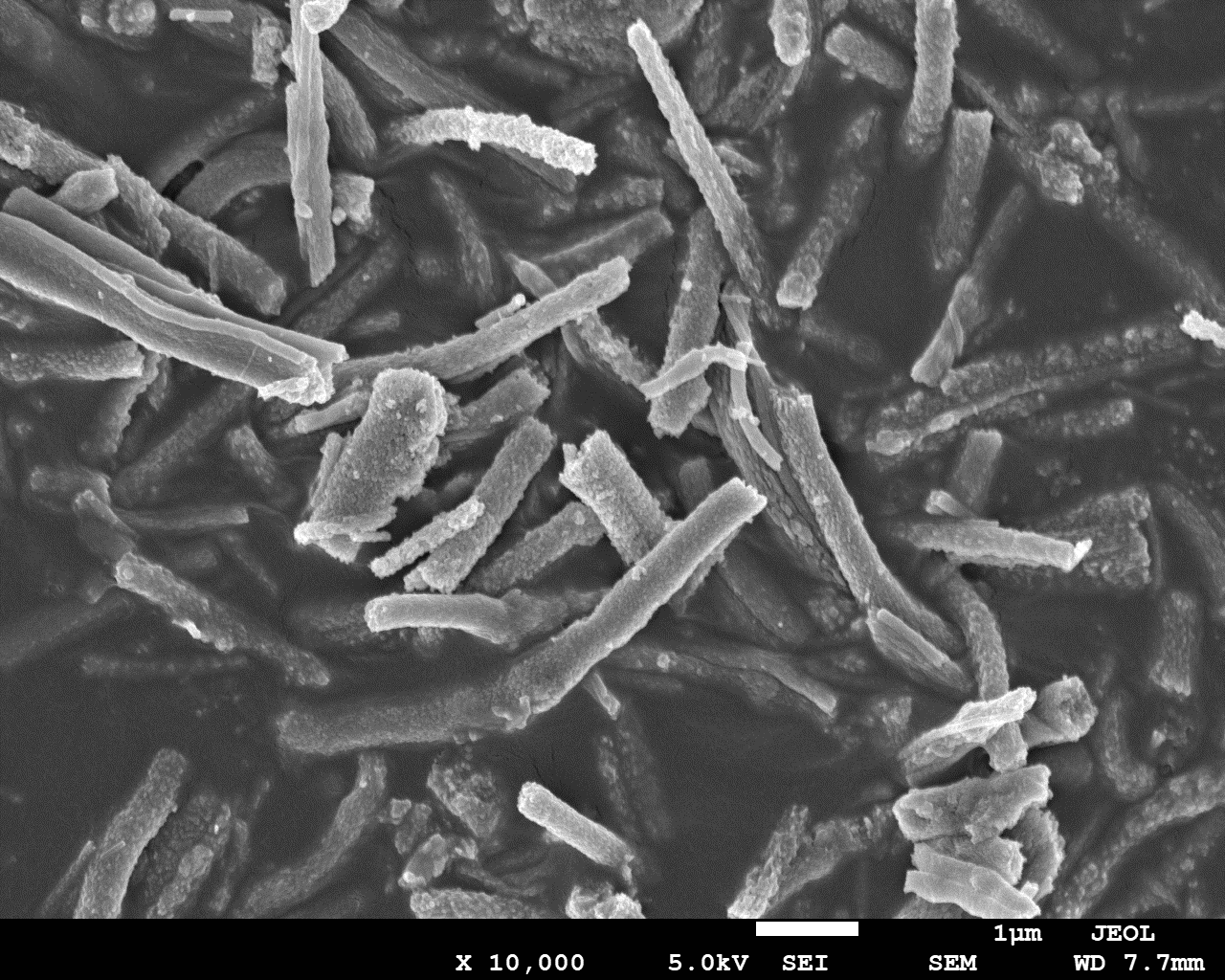
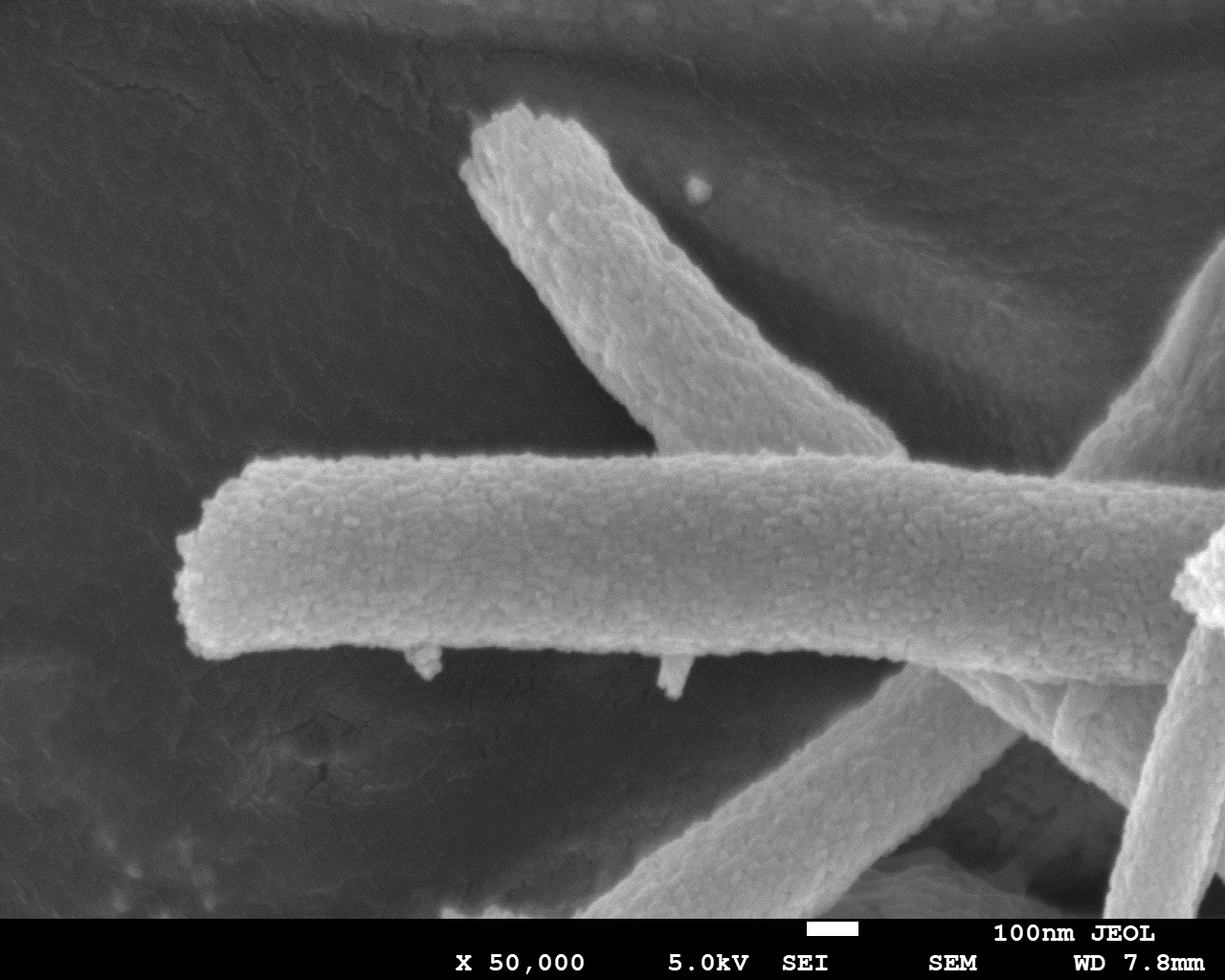
根据这一思路,本论文设计了一种具有高介电常数和磁性的无机陶瓷纤维作为填料,加入有机聚合物基体中,通过外加磁场辅助的溶液流延法制备具有纤维垂直取向的复合薄膜电容器,以望提升有机基复合薄膜电容器的介电常数。通过改进的静电纺丝工艺在无机陶瓷TiO2(TO)纤维中嵌入具有磁性的Fe3O4(FO)纳米颗粒(20 nm),制备的纳米复合纤维在具有高介电性能的同时具有一定的磁性,并通过XRD、SEM、红外等测试手段对制备的无机陶瓷复合纤维进行结构表征,研究结果表明:在使用改进的静电纺丝工艺所制备的TO纳米纤维的表面结晶行为良好,FO@TO纳米复合纤维表面结晶情况没有受到FO纳米颗粒的掺入而受到影响。
随后将FO@TO纳米复合纤维和有机聚合物PVDF基体进行复合,然后通过外加磁场辅助的溶液流延法来制备具有取向调控结构的复合薄膜,并对得到的复合薄膜进行了介电、铁电等性能研究。FO@TO复合纤维在PVDF中的添加量在1.0 vol.%~5 vol.%之间时,复合薄膜的介电常数与纤维添加量之间线性增加,在体积分数为5 vol.%时,具有纤维垂直取向的复合薄膜的介电常数为20.5,纤维随机取向的复合薄膜的介电常数为14.5,纯PVDF的介电常数为10.4,结果表明:无机陶瓷纤维在有机物基体中具有垂直取向的复合薄膜的介电常数提升明显,相较纯PVDF提升了近100%。在100 MV/m时,纯PVDF的电位移为1.2 μC/cm2,无机复合纤维的含量为5 vol.%时,无机复合纤维在复合薄膜中随机取向的的电位移为1.5 μC/cm2,无机复合纤维在复合薄膜中垂直取向的电位移 2.33 μC/cm2,结果表明:无机复合纤维的加入能明显提升复合薄膜电容器的电位移,其中具有纤维垂直取向的复合薄膜的电位移相比于纯PVDF提升了接近100%。通过对复合薄膜中无机纤维进行取向调控,使纤维垂直于薄膜的面外方向,可以使复合薄膜具有更佳的介电性能。
关键词:纳米纤维;介电性能;取向调控;复合薄膜
Abstract
Organic polymer dielectric materials are made into thin film capacitors because of their high breakdown field strength, low dielectric loss, and flexibility and ease of processing. However, the dielectric constant of organic thin film capacitors is low, which is not conducive to the energy storage performance of capacitors. In previous studies, it has been proposed to add a ceramic filler with a high dielectric constant to an organic polymer matrix, to increase the dielectric constant of the composite film capacitor based on its high breakdown field strength. It is worth noting that when the film capacitor works, the direction of the electric field is always perpendicular to the out-of-plane direction of the film, so an anisotropic structure can be designed to improve the dielectric properties of the composite film capacitor in the out-of-plane direction.
Based on this idea, this paper designs an inorganic ceramic fiber with high dielectric constant and magnetic properties as a filler, adds it to the organic polymer matrix, and uses a magnetic field-assisted solution casting method to prepare a composite film capacitor with vertical fiber orientation. In order to improve the dielectric constant of organic-based composite film capacitors. The Fe3O4 (FO) nanoparticles (20 nm) with magnetic properties are embedded in the inorganic ceramic TiO2 (TO) fibers through an improved electrospinning process. The prepared nanocomposite fibers have a certain magnetic property while having high dielectric properties. XRD, SEM, infrared and other testing methods were used to characterize the structure of the prepared inorganic ceramic composite fibers. The research results show that the surface of the TO nanofibers prepared using the improved electrostatic spinning process has good crystallization behavior, and the surface of the FO@TO nanocomposite fibers crystallizes The situation was not affected by the incorporation of FO nanoparticles.
Subsequently, the FO@TO nanocomposite fiber and the organic polymer PVDF matrix were compounded, and then a composite film with an orientation control structure was prepared by a solution casting method assisted by a magnetic field, and the obtained composite film was subjected to dielectric, ferroelectric and other performanc. When the amount of FO@TO nanocomposite fibers in PVDF is between 1.0 vol.% and 5.0 vol%, The dielectric constant of the composite film increases linearly with the amount of fiber added. When the volume fraction is 5 vol.%, the dielectric constant of the inorganic ceramic fibers have a vertically oriented composite film is 20.5, the dielectric constant of the randomly oriented composite film is 14.5, and the dielectric constant of pure PVDF is 10.4. The results show that the inorganic ceramic fibers have a vertically oriented composite film in the organic matrix. The dielectric constant increase is obvious, which is nearly 100% higher than that of pure PVDF. At 100 MV/m, the electrical displacement of pure PVDF is 1.2 μC/cm2, and when the content of inorganic composite fibers is 5 vol.%, The electrical displacement of inorganic composite fibers randomly oriented in the composite film is 1.5 μC/cm2. The vertical displacement of the composite fiber in the composite film is 2.33 μC/cm2. The results show that the addition of inorganic composite fibers can significantly increase the electrical displacement of the composite film capacitor. The electrical displacement of the composite film with the vertical orientation of the fiber is compared with that of pure PVDF, improved by nearly 100%. By controlling the orientation of the inorganic fibers in the composite film so that the fibers are perpendicular to the out-of-plane direction of the film, the composite film can have better dielectric properties.
Key Words: Nanofibers; Dielectric properties; Orientation control; Composite film
目 录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 研究背景 1
1.2 电介质材料物理基础 1
1.2.1 电介质材料的极化与介电常数 1
1.2.2 电介质材料的介电损耗 3
1.2.3 电介质材料的击穿特性 4
1.2.4 电介质材料的储能特性 4
1.3 国内外研究现状 5
1.4 研究思路及内容 6
第2章 实验试剂及测试手段 8
2.1 实验主要试剂 8
2.1.1 静电纺丝实验所需要的实验试剂原材料 8
2.1.2 制备复合薄膜所需要的实验原材料与仪器设备 8
2.2 实验主要表征及测试方法 9
2.2.1 X射线衍射 9
2.2.2 扫描电子显微镜 9
2.2.3 蒸渡电极 9
2.2.4 傅里叶变换红外光谱分析 9
2.2.5 介电铁电性能测试 10
第3章 具有高介电常数与磁性的纳米复合纤维的制备与表征 11
3.1 静电纺丝技术理论基础 11
3.2 FO@TO纳米复合纤维的制备 11
3.3 FO@TO纳米复合纤维的表征 12
3.3.1 形貌表征 12
3.2.2 结构表征 13
3.3 FO@TO纳米复合纤维的表面改性与表征 14
3.3.1 FO@TO纳米复合纤维的表面改性 14
3.3.2 FO@TO纳米复合纤维表面改性的表征 15
第4章 具有纳米纤维取向的PVDF基复合介电薄膜的制备与结构表征 16
4.1 PVDF基复合介电薄膜的制备 16
4.2 PVDF基复合介电薄膜的形貌表征 16
4.3 PVDF基复合介电薄膜的结构表征 19
4.4 PVDF基复合介电薄膜的红外光谱分析 20
第5章 具有纳米纤维取向的PVDF复合介电薄膜的性能分析 21
5.1 PVDF基复合介电薄膜的介电性能分析 21
5.2 PVDF基复合介电薄膜的电极化性能 23
第6章 结论 26
参考文献 27
致谢 29
附录1 30
附录2 31
第1章 绪论
1.1 研究背景
能源利用问题在近年来无论是在工业领域还是在社会的发展方面都是困扰我们的焦点所在。而在所有能源紧缺的问题中,电能的有效循环利用也一直是人们研究的重点之一。而电能的存储是能够合理的利用可再生能源发电的有效途径。而在目前主要发展的储能和能源转换的装置中,蓄电池、超级电容器和介电电容器这三种储能装置受到了人们的重点关注[1-3]而在这三种储能装置中,介电电容器表现出了更高的储能密度、更高的工作电压、更低的损耗等特点,在智能电网电源调节、高频逆变器、绝缘栅双极晶体管缓冲器(IDBT)等方面有着广泛的应用[4],由此受到了广泛的关注研究。但是对于传统的电介质电容器,主要分为无机陶瓷电介质材料以及有机聚合物电介质材料。但是这两者均不能满足人们日益增长的对于电子设备的要求。无机陶瓷电介质材料如BaTiO3,BaSrO3,TiO2等,因其具有高的介电常数而被广泛研究,但是同时也存在击穿场强低和制备过程复杂的缺点,而这也是限制陶瓷电介质材料被广泛应用的原因[5]。而对于传统有机聚合物电介质材料如PVDF,BOPP,PEI等,大多数有机聚合物电介质材料可以在较高的电场下正常工作,并具有一定的柔性和可加工性能,但是通常其介电常数都较低,使其在使用过程中必须要求增加体积来达到使用需求的储能密度的目的,也不能满足对于日益增长的对紧凑、微型化又高效的电力系统的需求[6]。因此为了能提升电介质电容器的击穿场强和介电常数,研究者通过复合的方式,将陶瓷与有机物的特性结合,得到具有高击穿场强、高介电常数的复合材料[7]。目的是在能够保证有机聚合物本身特性(如柔性)的同时,能够提升材料的介电常数以及击穿场强,最终能够提升复合材料的储能密度[8]。
1.2 电介质材料物理基础
1.2.1 电介质材料的极化与介电常数
通常条件下,在电介质材料在不受到电场的作用时,电介质材料的内部电荷呈现无规则的排布,而正、负束缚电荷之间的偶极矩相互抵消,所以整体宏观上对外并不表现电性。但是当对电介质材料加上外加电场时,由于材料内部束缚的电荷在受到外加电场的作用时,正、负电荷会在受到电场作用下发生移动,造成电介质材料产生局部电荷。我们称电介质材料的这一行为叫做电介质极化[9]。
电介质极化又根据其极化的方式和机理的不同,可以分为:电子位移极化、离子位移极化、偶极子转向极化(固有电矩转向极化)和界面极化(空间电荷极化)[10]四种。
请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:28232字
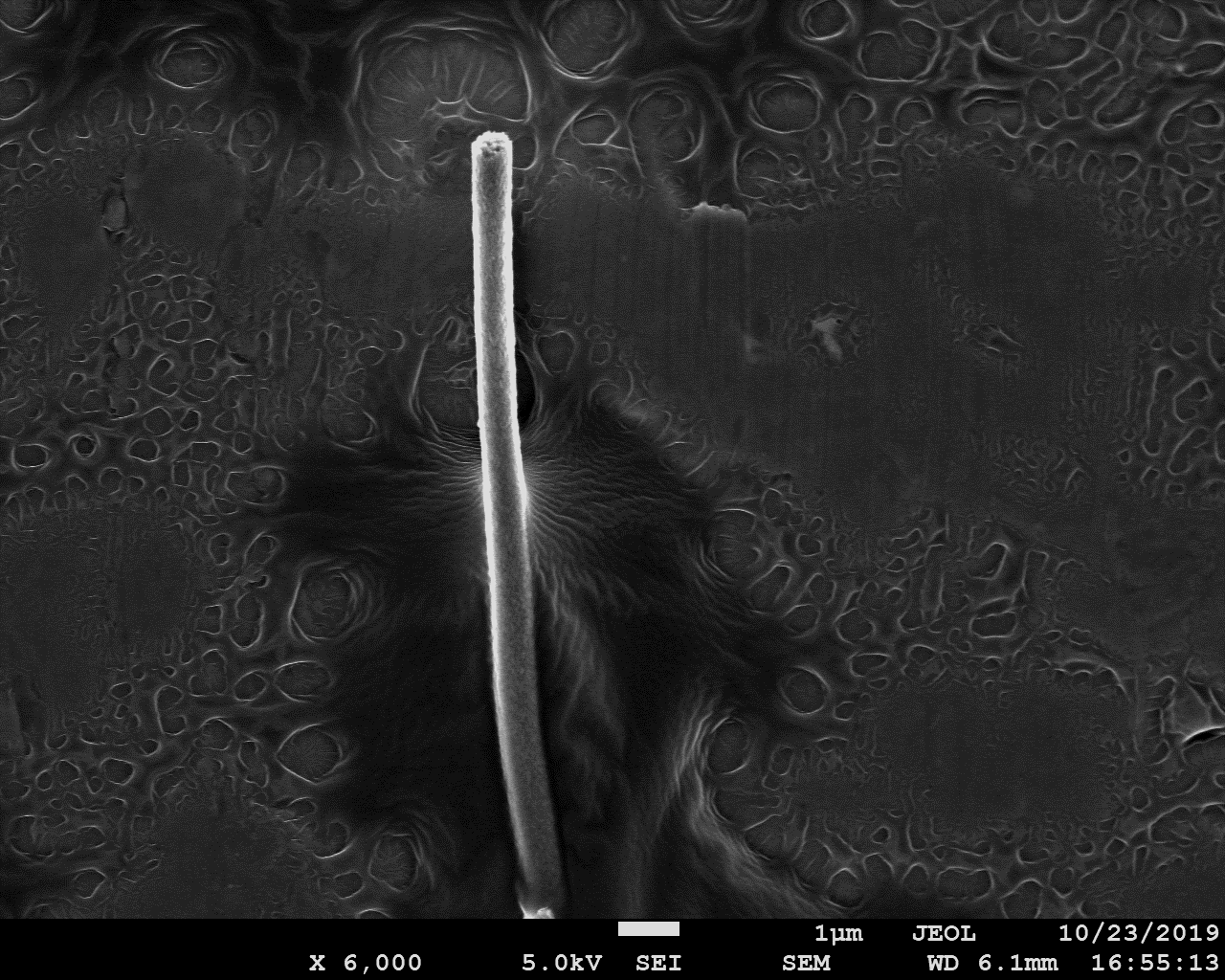
相关图片展示: