Cu基电子-离子混合导体中界面调控与输运性能毕业论文
2021-12-09 17:36:29
论文总字数:23773字
摘 要
Cu2Se化合物具有独特的电学性能,间接禁带宽度接近太阳能电池的最优禁带宽度值,能够提供较高的转化效率,非常适合最为光电转换材料。Cu2Se在高温时会发生结构相变,高温β相中Cu原子变成可自由迁移的类液态Cu离子,通过强烈散射声子来降低材料的晶格热导率,具有良好的发展前景。
但是,高温β相的铜离子高速迁移导致了化合物的不稳定,易在电场或温差下迁移到材料表面,同时高温下Se易挥发,从而造成了化合物初始性能的下降。对于 Cu2Se 热电材料而言,最大挑战就是在进一步提高热电性能的同时,抑制-Cu2Se 相中的离子迁移行为,提高其化学稳定性。
为了解决Cu2Se基热电材料存在的问题,进一步提高Cu2Se基热电材料的性能,尝试Cu2Se化合物复合石墨。设计掺杂的实验梯度为0、0.05、0.1、0.15、0.3、0.45, x为Cu2Se/x%wt 石墨加入量占基体Cu2Se化合物的质量百分数,x=0表示未与石墨复合的样品。采用自蔓延高温合成技术可快速制备得到Cu2Se/石墨复合粉体,结合放电等离子体烧结技术得到致密块体材料。对PAS烧结后得到的块体进行线切割处理后进行热电性能测试。
根据测试得到的结果,Cu2Se/石墨复合材料的XRD图像显示相组成是Cu2Se。石墨复合后对于Cu2Se基热电材料的ZT值没有明显的影响,无碳样品的ZT值在0.1-1.1之间,0.1wt%C的样品ZT值在高温600K时最高可达1.6。复合样品的热导率相对于无碳样品都有不同程度的降低,无碳样品的的热导率最低为0.6Wm-1K-1,最高为1.3Wm-1K-1。热导率降低最明显的是掺杂为0.3wt%C的样品,热导率在0.6Wm-1K-1与1.1Wm-1K-1之间,掺杂量为0.1wt%C的样品热导率最低值为0.5Wm-1K-1。虽然由于电性能的恶化,掺杂后的样品的功率因子都有不同程度的劣化,其中掺杂量为0.1wt%C的样品功率因子没有明显劣化,劣化最明显的是掺杂量为0.3wt%C的样品。由于热导率的降低,功率因子对ZT值的影响被抵消。
关键词:Cu2Se;石墨;热电性能;复合材料
Abstract
Cu2Se compounds have unique electrical properties. The indirect forbidden band width is close to the optimal forbidden band width value of solar cells. It can provide high conversion efficiency and is very suitable for most photoelectric conversion materials. Cu2Se undergoes a structural phase change at high temperatures. Cu atoms in the high-temperature β-phase become free-flowing liquid-like Cu ions. The strong thermal scattering of phonons reduces the lattice thermal conductivity of the material, which has good development prospects.
However, the high-speed β-phase copper ion migration caused the instability of the compound, which easily migrated to the surface of the material under an electric field or temperature difference. At the same time, Se was volatile at high temperature, which caused the degradation of the initial properties of the compound. For Cu2Se thermoelectric materials, the biggest challenge is to further improve the thermoelectric properties while suppressing the ion migration behavior in the europium-Cu2Se phase and improving its chemical stability.
In order to solve the problems of Cu2Se-based thermoelectric materials and further improve the performance of Cu2Se-based thermoelectric materials, Cu2Se compound composite graphite was tried. The designed experimental gradients of doping are 0, 0.05, 0.1, 0.15, 0.3, 0.45, and x is Cu2Se / x% wt. The graphite is added to the mass percentage of Cu2Se compound in the matrix, and x = 0 means the sample not compounded with graphite. Cu2Se / graphite composite powder can be quickly prepared by using self-propagating high-temperature synthesis technology, and compact bulk materials can be obtained by combining with discharge plasma sintering technology. After the PAS sintered block was subjected to wire cutting treatment, the thermoelectric performance test was performed.
According to the test results, the XRD image of the Cu2Se / graphite composite shows that the phase composition is Cu2Se. Graphite compounding has no significant effect on the ZT value of Cu2Se-based thermoelectric materials. The ZT value of carbon-free samples is between 0.1-1.1, and the ZT value of 0.1wt% C samples can reach 1.6 at a high temperature of 600K. The thermal conductivity of composite samples was reduced to different degrees compared to carbon-free samples. The thermal conductivity of carbon-free samples was as low as 0.6 Wm-1K-1 and as high as 1.3 Wm-1K-1. The most obvious decrease in thermal conductivity is the sample with 0.3wt% C doped, the thermal conductivity is between 0.6Wm-1K-1 and 1.1Wm-1K-1, the thermal conductivity of the sample with doped amount of 0.1wt% C The lowest value is 0.5Wm-1K-1. Although the power factor of the doped samples deteriorated to varying degrees due to the deterioration of the electrical properties, the power factor of the samples with a doping amount of 0.1wt% C did not significantly deteriorate, and the most significant degradation was the doping amount of 0.3wt. % C sample. Due to the reduced thermal conductivity, the effect of the power factor on the ZT value is offset.
Keywords: Cu2Se; graphite; thermoelectric properties; composite materials
目 录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 热电效应简介 2
1.1.1 Seebeck效应 2
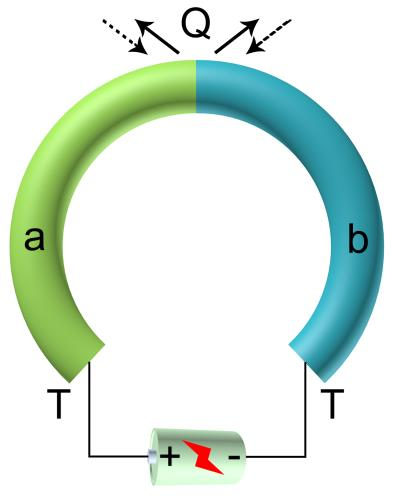
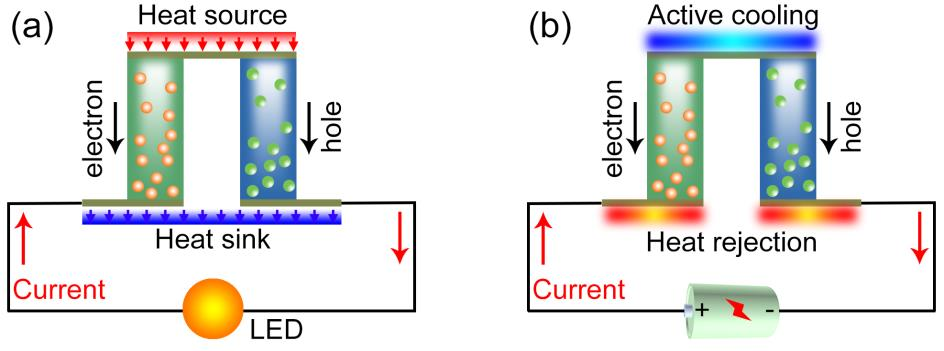
1.1.2 Peltier效应 4
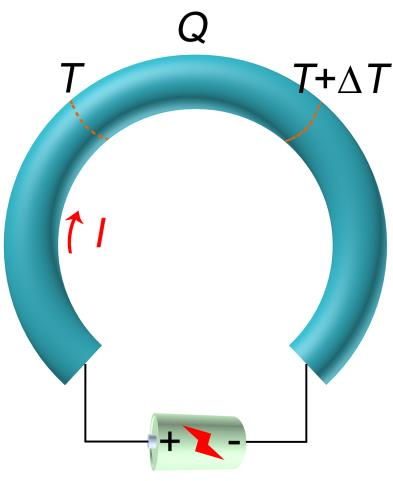
1.1.3 Thomson效应 5
1.14 Kelvin关系 6
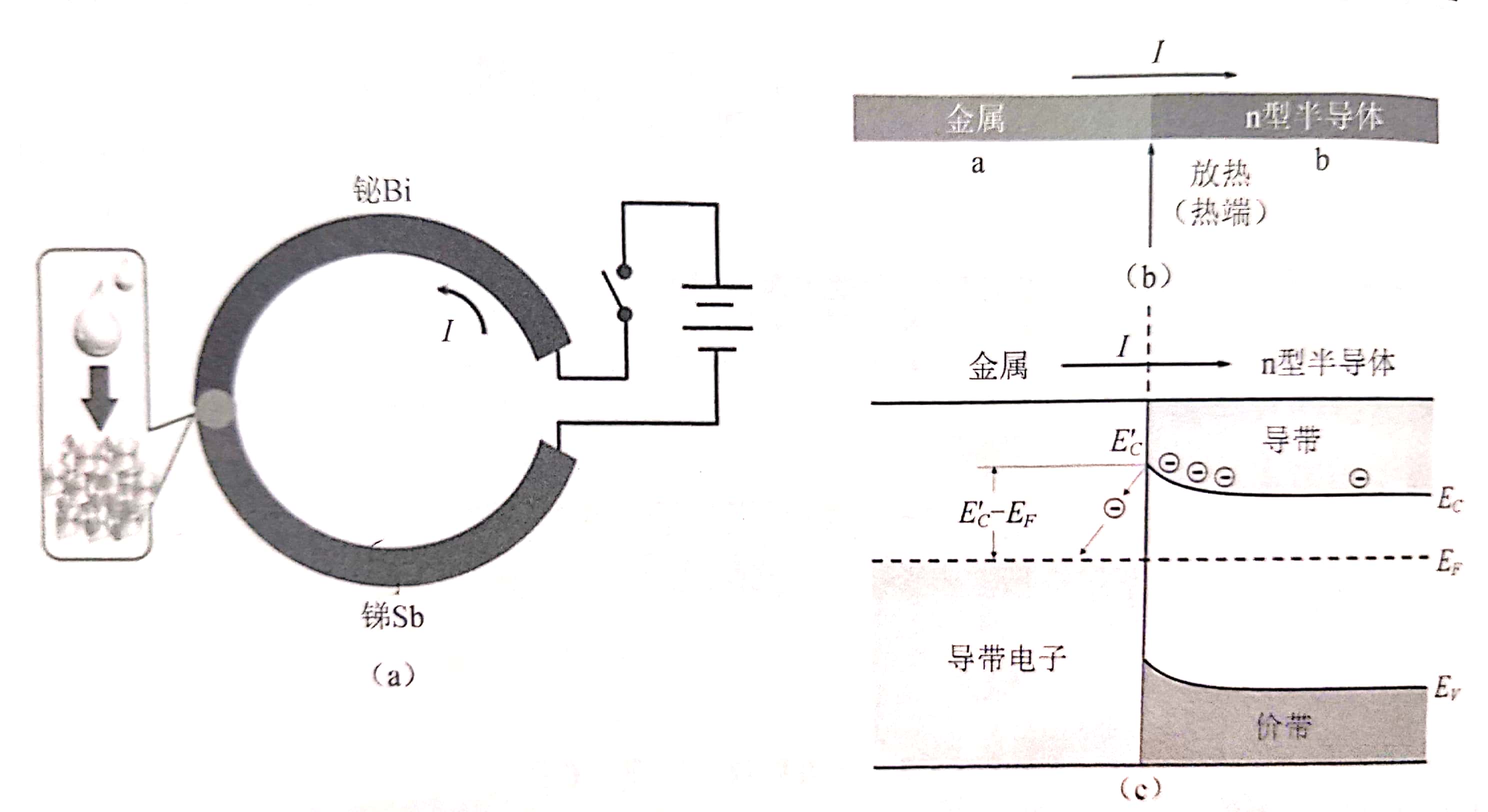
1.2 半导体的热电效应 6
1.3 影响材料热电性能的参数 7
1.4 Cu2Se基热电材料的研究进展 8
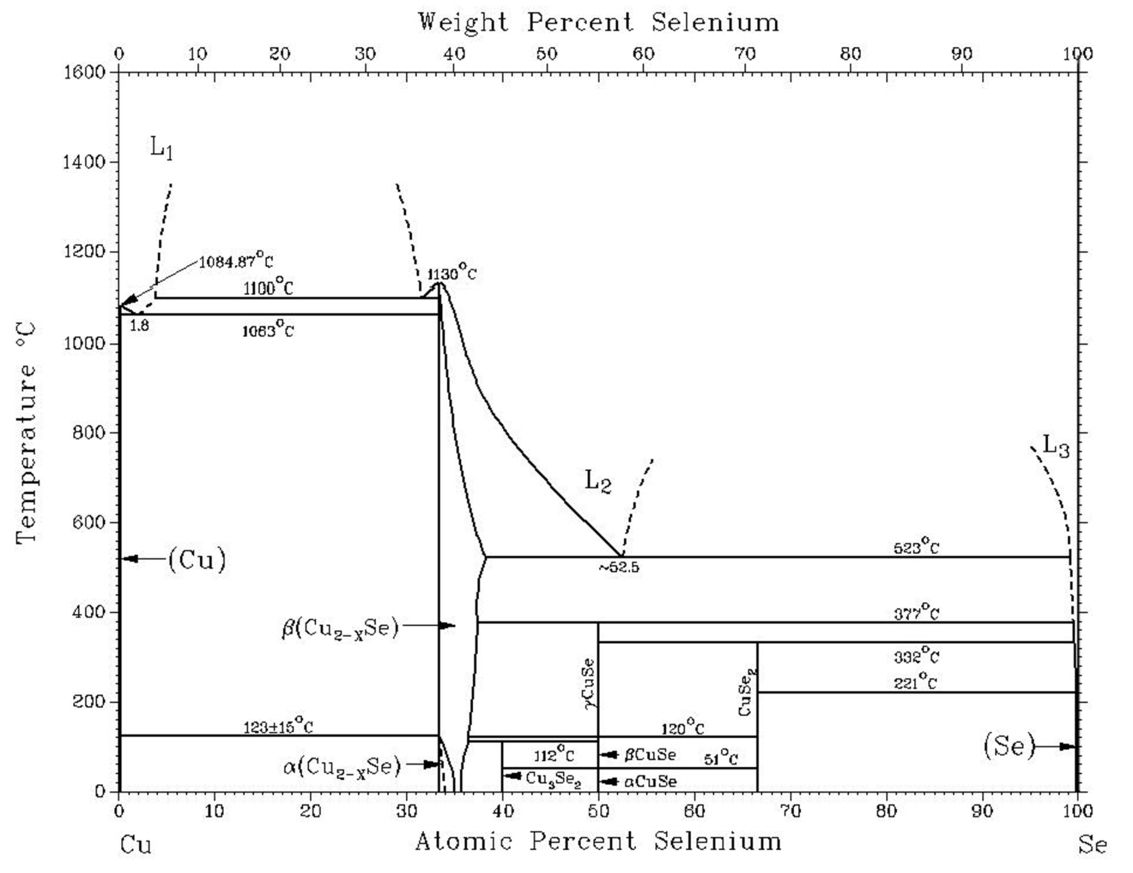
1.4.1 Cu2Se化合物简介 8
1.4.2 Cu2Se化合物的晶体结构研究 10
1.4.3 Cu2Se化合物的相转变研究 11
1.5 石墨简介 11
第2章 材料的制备及表征 12
2.1 材料的制备方法 12
2.2 实验设备 12
2.2.1 压片机 12
2.2.2 自蔓延反应装置 12
2.2.3 等离子体活化烧结设备 13
2.3 材料表征与性能测试 14
2.3.1 材料物相分析 14
2.3.2 块体材料密度的测量 14
2.3.3 Seebeck系数测试及电导率的测试 14
2.3.4 热扩散系数测试 16
第3章 Cu2Se/石墨复合材料热电性能研究 17
3.1 引言 17
3.2 实验内容 17
3.3 实验结果与讨论 18
3.3.1 相组成 18
3.3.2 电性能 19
3.3.3 热性能 22
第4章 总结 24
参考文献 26
致谢 27
第1章 绪论
工业革命以来,我国的经济不断发展,而我国的能源需求,也随着经济发展不断增加。在社会不断发展的当下,人们对能源的需求量不断增大。而日益加快的需求量,与化石能源不断减少的矛盾,是未来全社会未来发展的重要难题。我国能源发展,同样面临不少问题,其中突出的问题,例如,能源短缺,石油储备不足,化石燃烧产生环境污染等,都亟待解决。
中国能源发展形势严峻有多方面原因。首先,中国处于一个不断发展的大环境下,由此,对能源也就有更高的要求。中国的工业化与城市化,都不断督促着能源跟上需求。但是,目前来看,相比于世界人均能源消耗水平来说,中国的人均消水平并不算高。有数据统计,仅为世界水准的45%左右。就我国大部分地区的发展现状来说,现有的能源并不能满足我国未来持续发展的需要。不少因素都影响了中国的能源需求,工业增长,城市人口增长,都是影响因素。其次,石油安全将成为国家安全的重要内容。自从中国成为了石油净进口国每年从国外净进口的石油不断增加,对石油能源的依赖程度不断提高。在将来,随着中国不断地工业化、城市化,中国对石油能源的需求只会更进一步的提高[1]。除此之外,能够影响能源需求的,还包括:大气污染造成的经济损失,未来经济增长等。
正如上文所说,我国化石资源虽然丰富。但储备不够充足,更有开采难度大,人口众多等原因[2]。同时,化石能源的燃烧会对大气环境造成恶劣影响,例如,作为我国主要化石能源的煤炭,在燃烧过程中产生了不少的大气污染。大量的二氧化碳,二氧化硫,颗粒物等均对环境造成恶劣影响。而且,煤炭是一次性能源,不可持续利用,制约发展。
请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:23773字
相关图片展示: