力场调控单片TMDs能带结构及光学性能的研究毕业论文
2021-12-09 17:19:16
论文总字数:24353字
摘 要
过渡金属硫属化合物(TMDs)在目前的研究中拥有良好的理化性质。近年来,围绕纳米级TMDs如MoS2、MoSe2等的许多研究工作因其具有较低的成本、化学稳定性高和优异的电催化性能等优点而备受关注。同时,对于单层TMDs材料,在其原子级厚度的限制下,材料在电化学反应中所产生的电子和空穴将被限制在这些二维材料中,从而产生了独特的物理化学、光电性质。
本课题主要研究了力场调控下TMDs材料的光学性质及电催化析氢性能的变化规律。本课题利用化学气相沉积法合成了单层、单晶TMDs纳米片,并将其转移在柔性可拉伸的聚酰亚胺及钛基记忆合金基底上进行力场调控,探究了力场调控下TMDs材料的能带结构及光学性质的变化规律,同时设计了基于力场调控下的单片TMDs电催化析氢器件,拟通过实验设计探究力场调控下TMDs材料催化活性位点的变化规律,分析其电催化析氢性质变化的原因,为未来制备大面积柔性可拉伸的电催化析氢器件提供理论指导。
本课题的研究结果表明:
(1)MoS2和MoSe2均为正三角形形状的单晶体,在532nm波长、5%功率拉曼激光激发下,MoS2的A1g拉曼峰的位置为403.746cm-1,E2g1拉曼峰的位置为384.096cm-1,MoSe2的A1g拉曼峰的位置为240.856cm-1。
(2)在力场调控的作用下,对二维MoS2晶体施加单轴拉伸应力,其内部晶格结构发生变化,从而使得其层内势能产生非谐性变化,导致其拉曼峰A1g峰的位置基本不变,而E2g1峰的位置出现偏移。
(3)应力可以对二维TMDs材料的电化学析氢性能起到一定的调控作用。
本课题的亮点主要有:
(1)利用化学气相沉积法制备了单层、单晶的TMDs纳米片,并利用自制的应力调控装置对其施加了单轴应力。
(2)利用小型应力调控装置,在对TMDs材料进行应力调控的同时,原位测量了其电化学催化析氢性质,使得对应力调控催化活性及机理的探究得以进行。
关键词:过渡金属硫属化合物;MoS2;力场调控;电催化析氢反应
Abstract
Transition Metal Dichacolgenides (TMDs) in the current study has good physical and chemical properties. In recent years, many researches around nano-scale TMDs(such as MoS2, MoSe2, etc.) have attracted more attention. Because there are many advantages such as lower cost, high chemical stability, and excellent electrocatalytic performance. For single-layer TMDs, under the limitation of their atomic thickness, the electrons and holes generated by the electrochemical reaction will be restricted in these two-dimensional materials, thus they have presented unique physical chemical and photoelectric properties.
This subject mainly studied the changes of optical properties and electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution properties of TMDs materials under the strain regulation. This topic used chemical vapor deposition to synthesize single-layer, single-crystal TMDs nanosheets, and transferred them to flexible and stretchable polyimide and titanium-based memory alloy substrates for the strain regulation. The change law of the band structure and optical properties of the TMDs material was studied. At the same time, a monolithic TMDs electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution device based on the strain regulation was designed. It was planned to explore and analyze the change law of the catalytic active site of the TMDs material under the strain regulation control through experimental design. The reason for the change of electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution properties provides theoretical guidance for the preparation of large-area flexible and stretchable electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution devices in the future.
The research results of this topic show that:
(1) Both MoS2 and MoSe2 are single crystals with regular triangle shape. Under 5% power Raman laser, the A1g Raman peak position of MoS2 is 403.746 cm-1, and the E2g1 Raman peak position is 384.096 cm-1. The position of the A1g Raman peak of MoSe2 is 240.856 cm-1. The Raman wavelength is 532 nm.
(2) Under the action of the strain regulation, uniaxial tensile stress is applied to the two-dimensional MoS2 crystal, and its internal lattice structure changes, resulting in an inharmonic change in the potential energy in its layer, resulting in its Raman peak A1g peak is basically unchanged, and the position of the E2g1 peak is shifted.
(3) Strain regulating can have some influence in the electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction of two-dimensional TMDs.
The highlights of this topic are:
(1) A single layer, single crystal TMDs nanosheet was prepared by chemical vapor deposition method, and a uniaxial stress was applied to it using a self-made stress control device.
(2) Using a small stress control device, while performing stress control on the TMDs, the electrochemical catalytic hydrogen evolution properties were measured in situ, enabling the investigation of the catalytic activity and mechanism of strain controlling.
Key Words:Transition Metal Dichacolgenides (TMDs); MoS2; Strain Engineering; Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
目录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1引言 1
1.2 二维TMDs材料的结构、性质及其制备方法 1
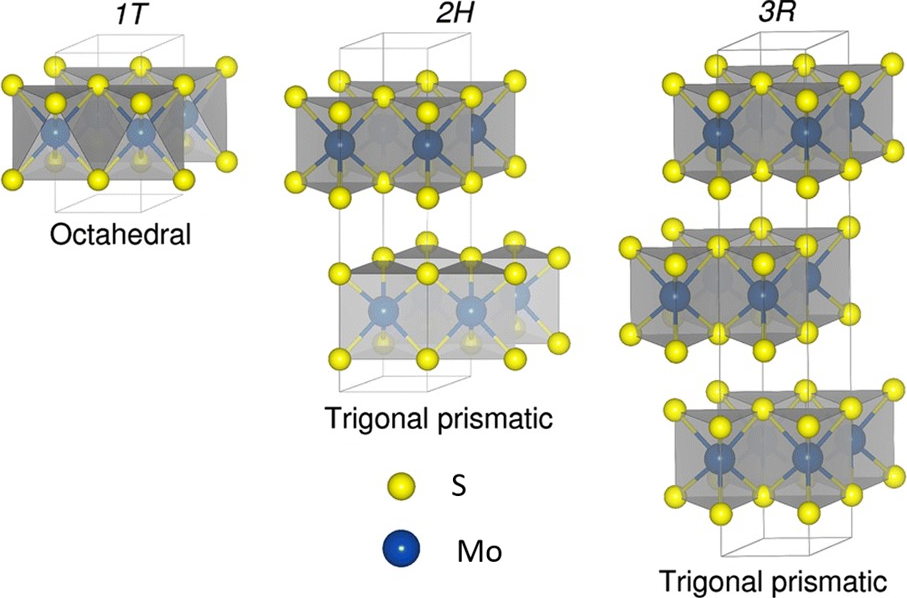
1.2.1 MoS2的结构与性质 1
1.2.2二维MoS2的制备方法 2
1.2.3化学气相沉积法 3
1.2.4 MoSe2的结构与性质 3
1.2.5二维MoSe2的制备方法 3
1.3应力与二维TMDs材料 4
1.3.1应力与二维TMDs材料的关系 4
1.3.2二维TMDs引入应力的方式 4
1.3.3拉伸柔性基底调控应力 4
1.4二维MoS2电催化析氢性能 4
1.4.1电催化析氢反应(HER) 4
1.4.2 MoS2的电催化析氢性能 5
1.5本课题的研究意义及研究内容 5
1.5.1本课题的研究目的及意义 5
1.5.2本课题的研究内容 5
第2章 二维MoS2和MoSe2的制备及分析表征 7
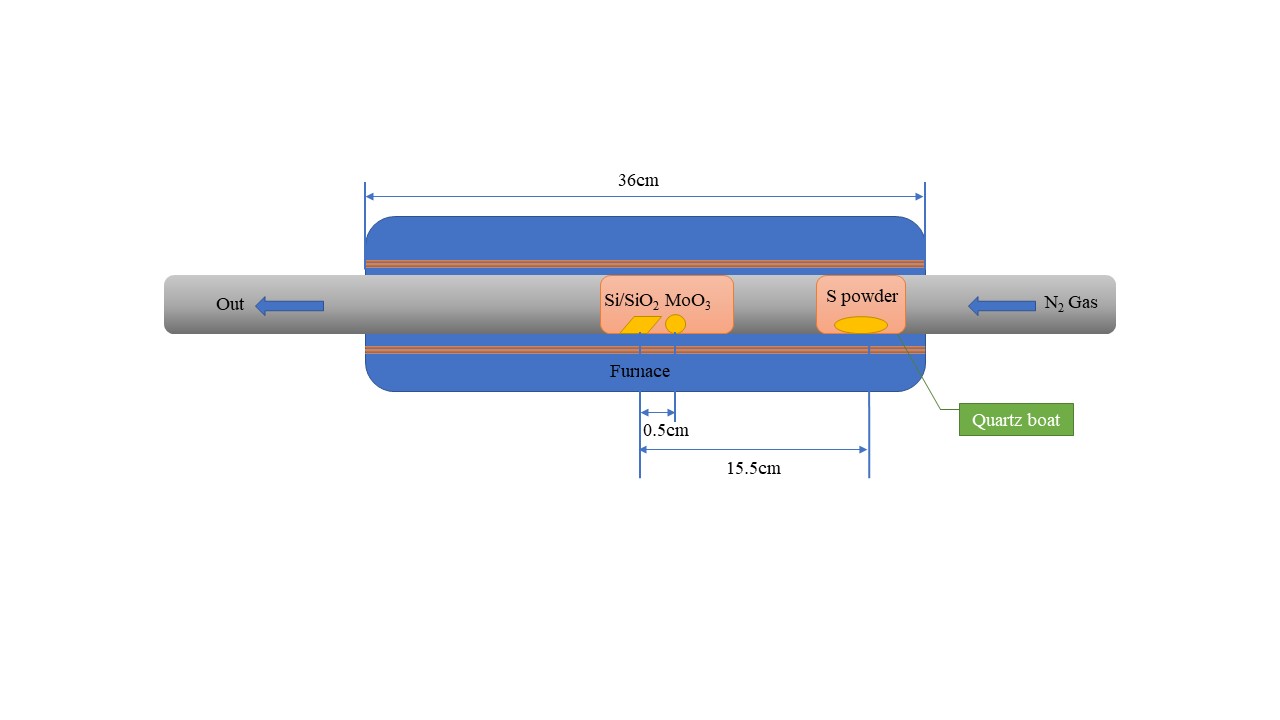
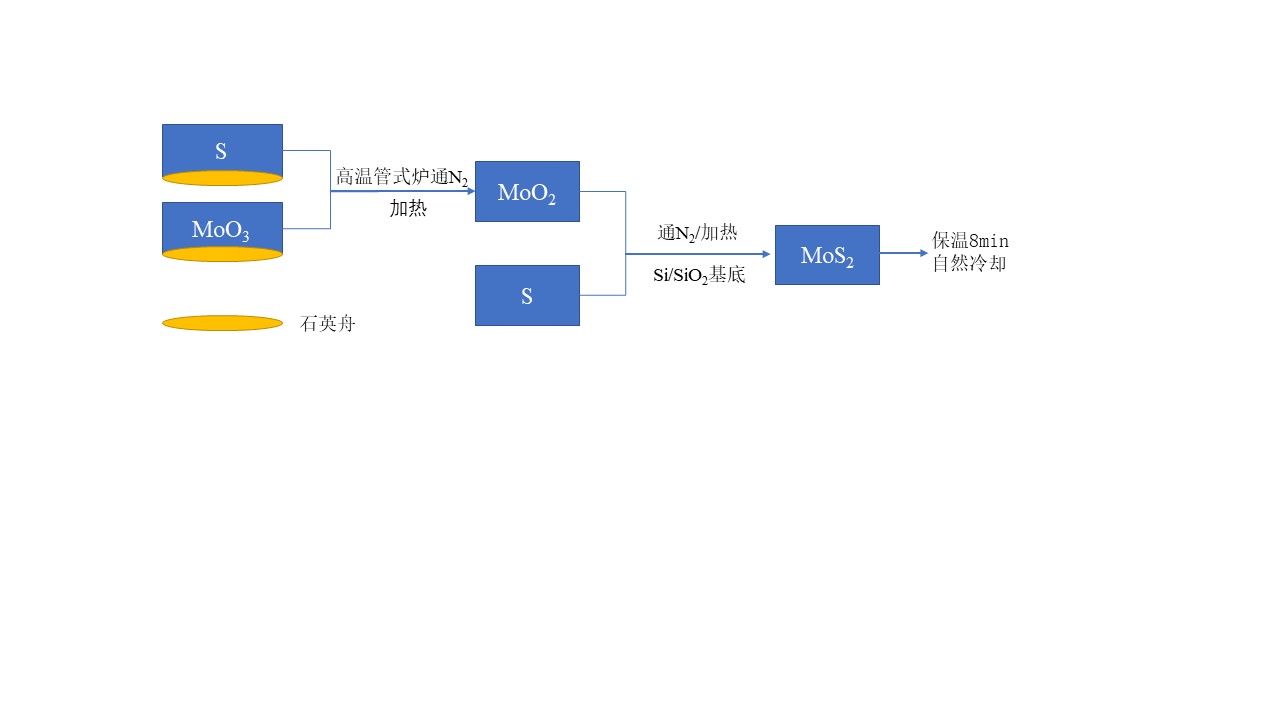
2.1化学气相沉积法制备MoS2实验流程 7
2.2化学气相沉积法制备MoSe2实验流程 8
2.3 MoS2和MoSe2的物性表征 10
2.3.1光学显微镜(OM) 10
2.3.2拉曼光谱(Raman) 12
2.3.3透射电子显微镜(TEM) 13
2.4 MoS2的湿法转移 15
2.5实验试剂及仪器 18
2.5.1实验试剂 18
2.5.2实验仪器 19
第3章 二维MoS2的应力调控 20
3.1 应力调控设备的研究 20
3.2 应力对MoS2光学性质的调控 20
3.3实验试剂及仪器 21
3.3.1实验试剂 21
3.3.2实验仪器 22
第4章 应力调控下二维MoS2的电催化析氢性能 23
4.1 应力调控对二维MoS2的电催化析氢性能的影响 23
4.2 拟设计应力调控MoS2电催化析氢性能的技术路线 23
4.2.1 MoS2向聚酰亚胺基底的转移 24
4.2.2转移后材料的表征 24
4.2.3用电子束蚀刻技术(EBL)对MoS2/聚酰亚胺进行器件构筑 24
4.2.4力场调控下析氢性能的测试 25
第5章 总结与展望 26
参考文献 27
附录 30
附录1 30
附录2 32
致谢 33
第1章 绪论
1.1引言
二维过渡金属硫属化合物(TMDs)因其特殊的结构和优异的性能,在光电器件、能量转换、电催化等领域都具有十分重要的研究价值[1]。 近年来,人们通过外加电场、力场等方法[2],对TMDs材料进行一定的调节控制,从而改变它的性能。一方面,应力可以大范围连续调节二维TMDs材料的能带结构;另一方面,二维TMDs材料对外力的作用也比较敏感 [3],使得它的调节效率比较高;另外,二维TMDs材料还具有较大的断裂强度,故可以进行大范围的性质调控的需求[4] [5]。因此,力场调控是一种有效的调节二维TMDs材料性能的方法。
目前,力场调控可以通过改变二维TMDs材料的晶格结构和晶格对称性,来实现对二维TMDs材料带隙等性质的调节,从而进一步影响其光学、电学性质[6],如TMDs材料的电催化析氢性能。因此二维TMDs材料的力场调控对于材料的电催化析氢性能的影响,成为了一个非常值得研究分析的问题。本文首先阐述二维MoS2、MoSe2材料的制备以及物性表征,然后针对MoS2进行下一步试验,将制备的MoS2转移至柔性可拉伸基底上并组装力场调控设备,再进一步探究力场调控对于MoS2光学性质的影响以及对其电催化析氢反应性能的影响,最后展望了应力调控二维TMDs的发展趋势,并指出了未来在TMDs材料电催化析氢反应等研究中存在的挑战。
1.2 二维TMDs材料的结构、性质及其制备方法
请支付后下载全文,论文总字数:24353字
相关图片展示:

您可能感兴趣的文章
- 甲基丙烯酸修饰氢氧化镁微粒及其表征开题报告
- 碳点修饰SiO2纳米球的制备与表征文献综述
- 二维VOPO4纳米片在水系锌离子电池中的研究文献综述
- 塑料注射成型的实验研究: 型腔压力和模具温度对产品质量的影响外文翻译资料
- 一种用于同时电化学检测铅(II)、镉(II)和锌(II)的具有分层MXene-铋纳米复合材料的微铣式微电网传感器外文翻译资料
- 日光驱动的可充电抗菌和抗病毒纳米纤维膜在生物保护中应用外文翻译资料
- 一种无金属的聚合物光催化剂,用于在可 见光下从水中制氢外文翻译资料
- 二维共价自组装:将共价有机骨架纳米球连接到晶体和多孔薄膜中外文翻译资料
- 模拟二维材料的粉末X射线衍射图外文翻译资料
- 基于碳化硅反应活性的烧结添加剂外文翻译资料




